
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
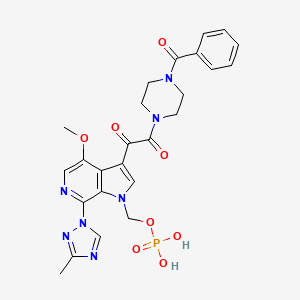

1. (3-((4-benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)(oxo)acetyl)-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-c)pyridin-1-yl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
2. 1,2-ethanedione, 1-(4-benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-(4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1-((phosphonooxy)methyl)-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-c)pyridin-3-yl)-
3. Bms-663068
1. 864953-29-7
2. Bms-663068
3. Bms-663068 Free Acid
4. Bms 663068
5. Fostemsavir [usan]
6. Rukobia
7. Fostemsavir(bms-663068)
8. 97iq273h4l
9. 864953-29-7(free Base)
10. Fostemsavir (usan)
11. [3-[2-(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoacetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl]methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
12. Bms663068
13. Piperazine, 1-benzoyl-4-((4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1-((phosphonooxy)methyl)-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-c)pyridin-3-yl)oxoacetyl)-
14. (3-(2-(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoacetyl)-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
15. Unii-97iq273h4l
16. Fostemsavir & N6
17. [3-[2-(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxo-acetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl]methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
18. 1,2-ethanedione, 1-(4-benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-(4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1-((phosphonooxy)methyl)-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-c)pyridin-3-yl)-
19. 1,2-ethanedione, 1-(4-benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-[4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-3-yl]-
20. Gsk3684934
21. Fostemsavir & Pg16
22. Fostemsavir & 4dm2m
23. Fostemsavir & Vrc03
24. Fostemsavir & Ch106
25. Fostemsavir & 35o22
26. Fostemsavir & Pgt128
27. Fostemsavir [mi]
28. Fostemsavir [inn]
29. Fostemsavir & 3bnc117
30. Fostemsavir & Pg16-imab
31. Fostemsavir [who-dd]
32. Fostemsavir & Pgt128-imab
33. Fostemsavir & Vrc07-523
34. Schembl754395
35. Fostemsavir; Bms-663068
36. Chembl3301594
37. Gtpl11100
38. Dtxsid40235596
39. Fostemsavir & Nih45-46g54w
40. Bcp13226
41. Ex-a1973
42. Bms-626529 & 4dm2m
43. Hy-15440a
44. S7220
45. Zinc14210883
46. Bms-626529 & Pg16-imab
47. Bms-663038
48. Cs-1059
49. Db11796
50. Sb11250
51. Bms-626529 & Pgt128-imab
52. Bms626-529 & Vrc03
53. Gsk-3684934
54. Bms-626529 & N6
55. Bms-626529 & Pg16
56. Compound 35 [pmid: 29271653]
57. Ncgc00510187-01
58. Ac-30663
59. Bms-626529 & Pgt128
60. Bms-626529 & Ch106
61. Bms-626529 & 3bnc117
62. Bms-626529 & 35o22
63. Bms-626529 & Vrc07-523
64. Bms626-529 & Nih45-46g54w
65. D10707
66. A863152
67. Q17001240
68. ({3-[2-(4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoacetyl]-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl}methoxy)phosphonic Acid
69. (3-((4-benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)(oxo)acetyl)-4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-c)pyridin-1-yl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
70. (3-((4-benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-oxoacetyl)-4-methoxy- 7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-c)pyridin- 1-yl)methyl Dihydrogen Phosphate
71. 1-(4-benzoyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-[4-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-1-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-3-yl]-1,2-ethanedione
| Molecular Weight | 583.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H26N7O8P |
| XLogP3 | -0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 583.15804781 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 583.15804781 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 182 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1020 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Fostemsavir is indicated, in combination with other antiretrovirals, for the treatment of multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection in heavily treatment-experienced adults failing their current antiretroviral therapy due to resistance, intolerance, or safety concerns.
Rukobia, in combination with other antiretrovirals, is indicated for the treatment of adults with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection for whom it is otherwise not possible to construct a suppressive anti-viral regimen.
Temsavir inhibits the first stage in the HIV-1 viral lifecycle: attachment. It has a moderate duration of action necessitating twice-daily dosing. Fostemsavir, administered at roughly 4x the recommended human dose, has been observed to significantly prolong the QTc-interval. Patients with a history of QTc-prolongation, those receiving other QTc-prolonging medications, and/or those with pre-existing cardiac disease should use fostemsavir with caution, and should be monitored at baseline and throughout therapy for signs or symptoms suggestive of QTc-prolongation. Fostemsavir should also be used with caution in patients with hepatitis B or C co-infection as elevations in hepatic transaminases were observed in greater proportions in these populations in clinical trials.
Anti-HIV Agents
Agents used to treat AIDS and/or stop the spread of the HIV infection. These do not include drugs used to treat symptoms or opportunistic infections associated with AIDS. (See all compounds classified as Anti-HIV Agents.)
HIV Fusion Inhibitors
Inhibitors of the fusion of HIV to host cells, preventing viral entry. This includes compounds that block attachment of HIV ENVELOPE PROTEIN GP120 to CD4 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as HIV Fusion Inhibitors.)
J05AX
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AX - Other antivirals
J05AX29 - Fostemsavir
Absorption
The absorption of temsavir is significantly limited by suboptimal dissolution and solubility following oral administration. Fostemsavir, a phosphonooxymethyl prodrug of temsavir, has improved aqueous solubility and stability under acidic conditions as compared to its parent drug - following oral administration of fostemsavir, the absolute bioavailability is approximately 26.9%. The Cmax and AUCtau following oral administration of fostemsavir 600mg twice daily was 1770 ng/mL and 12,900 ng.h/L, respectively, with a Tmax of approximately 2 hours. Co-administration of fostemsavir with a standard meal increases its AUC by approximately 10%, while co-administration with a high-fat meal increases its AUC by approximately 81%.
Route of Elimination
Temsavir is highly metabolized, after which it is excreted in the urine and feces as inactive metabolites. Approximately 51% of a given dose is excreted in the urine, with <2% comprising unchanged parent drug, and 33% is excreted in the feces, of which 1.1% is unchanged parent drug.
Volume of Distribution
The steady-state volume of distribution of temsavir following intravenous administration is approximately 29.5 L.
Clearance
The mean clearance and apparent clearance of temsavir, the active metabolite of fostemsavir, are 17.9 L/h and 66.4 L/h, respectively.
Fostemsavir is rapidly hydrolyzed to temsavir, its active metabolite, by alkaline phosphatase(s) present at the brush border membrane of the intestinal lumen. Temsavir undergoes further biotransformation to two predominant inactive metabolites: BMS-646915, a product of hydrolysis by esterases, and BMS-930644, an N-dealkylated metabolite generated via oxidation by CYP3A4. Approximately 36.1% of an administered oral dose is metabolized by esterases, 21.2% is metabolized by CYP3A4, and <1% is conjugated by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT) prior to elimination. Both temsavir and its two predominant metabolites are known to inhibit BCRP.
The half-life of temsavir is approximately 11 hours. Fostemsavir is generally undetectable in plasma following oral administration.
The gp120 subunit within the gp160 envelope glycoprotein of HIV-1 is a new and novel target in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. These subunits are responsible for facilitating the first step in the viral life cycle, attachment, by mediating the interaction between the virus and host cell CD4 receptors. Following attachment, HIV-1 undergoes assembly, budding, and maturation within the host cell, after which mature viral particles are released to continue the viral life cycle. Fostemsavir's active metabolite, temsavir, is an HIV-1 attachment inhibitor. It binds directly to the gp120 subunit to inhibit viral interaction with host CD4 receptors, thereby preventing the initial attachment required for viral replication. It has also been shown to inhibit other gp120-dependent post-attachment steps required for viral entry.
Global Sales Information

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
75
PharmaCompass offers a list of Fostemsavir API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Fostemsavir manufacturer or Fostemsavir supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Fostemsavir manufacturer or Fostemsavir supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Fostemsavir API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Fostemsavir API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Fostemsavir Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Fostemsavir Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Fostemsavir manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Fostemsavir, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Fostemsavir manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Fostemsavir API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Fostemsavir manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Fostemsavir supplier is an individual or a company that provides Fostemsavir active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Fostemsavir finished formulations upon request. The Fostemsavir suppliers may include Fostemsavir API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Fostemsavir suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Fostemsavir as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Fostemsavir API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Fostemsavir as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Fostemsavir and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Fostemsavir NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Fostemsavir suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Fostemsavir Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Fostemsavir GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Fostemsavir GMP manufacturer or Fostemsavir GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Fostemsavir CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Fostemsavir's compliance with Fostemsavir specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Fostemsavir CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Fostemsavir CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Fostemsavir may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Fostemsavir EP), Fostemsavir JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Fostemsavir USP).
