
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
VMF
0
FDF
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
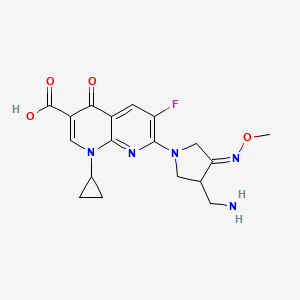

1. 7-(3-aminomethyl-4-methoxyimino-pyrrolidine-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-(1,8)-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
2. Factive
3. Gemifloxacin Mesylate
4. Lb 20304
5. Lb-20304
6. Lb20304
7. Sb 265805
8. Sb-265805
9. Sb265805
1. Gemifioxacin
2. 175463-14-6
3. Gemifloxacin [inn]
4. Gemifloxacin Mesilate
5. Factiv
6. Gemifloxacin (inn)
7. Lb-20304
8. 7-(3-aminomethyl-4-methoxyimino-pyrrolidine-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-(1,8)-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
9. Chembl430
10. Okr68y0e4t
11. Chebi:101853
12. Sb-265805
13. (z)-7-(3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
14. 7-[(4z)-3-(aminomethyl)-4-methoxyimino-pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
15. 7-[3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
16. Factiv (tn)
17. Lb 20304
18. Unii-okr68y0e4t
19. Sr-05000001958
20. Hsdb 8027
21. 7-(3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
22. Gemifloxacin [mi]
23. Gemifloxacin [vandf]
24. Bspbio_002308
25. 204519-64-2
26. Gemifloxacin [who-dd]
27. Schembl136633
28. Dtxsid3048495
29. Schembl13414391
30. Bdbm50178917
31. Akos015907681
32. Am84619
33. Db01155
34. Ncgc00178711-01
35. Ncgc00178711-06
36. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 7-(3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)-1-pyrrolidinyl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
37. 7-(3-aminomethyl)-4-methoxyimino-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
38. Sbi-0206906.p001
39. Hy-116229
40. Cs-0064428
41. D08012
42. Ab01563334_01
43. 463g146
44. A812090
45. Sr-05000001958-2
46. Brd-a40787240-066-02-0
47. Brd-a40787240-066-03-8
48. (+/-)-7-(3-(aminomethyl)-4-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 7(sup 4)-(z)-(o)-methyloxime)
49. (s,z)-7-(3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
50. 1,4-dihydro-1-cyclopropyl-4-oxo-6-fluoro-7-[3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)pyrrolidine-1-yl]-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
51. 1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-1-cyclopropyl-4-oxo-7-[(3e)-4-(aminomethyl)-3-(methoxyimino)pyrrolidine-1-yl]-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
52. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 7-(3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)-1-pyrrolidinyl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4- Oxo-
53. 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid, 7-[(4z)-3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)-1-pyrrolidinyl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
54. 7-[(4z)-3-(aminomethyl)-4-(methoxyimino)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
55. 7-[(4z)-3-(aminomethyl)-4-methoxyimino-pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid;gemifloxacin
56. 7-{3-aminomethyl-4-[(z)-methoxyimino]-pyrrolidin-1-yl}-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
57. Gemifloxacin; 7-(3-aminomethyl)-4-methoxyimino-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1, 4-dihydro-[1, 8]naphthyridine-3-carboxylic Acid; 210353-56-3
| Molecular Weight | 389.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H20FN5O4 |
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 389.14993230 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 389.14993230 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 121 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 725 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Factive |
| PubMed Health | Gemifloxacin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent for oral administration. Gemifloxacin, a compound related to the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics, is available as the mesylate salt in the sesquihydrate form. Chem... |
| Active Ingredient | Gemifloxacin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 320mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lg Life Sciences |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Factive |
| PubMed Health | Gemifloxacin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent for oral administration. Gemifloxacin, a compound related to the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics, is available as the mesylate salt in the sesquihydrate form. Chem... |
| Active Ingredient | Gemifloxacin mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 320mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lg Life Sciences |
Anti-Bacterial Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Gemifloxacin is used for the treatment of acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis caused by susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, or Moraxella catarrhalis. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 381
Gemifloxacin is used for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) of mild to moderate severity caused by susceptible S. pneumoniae (including multidrug-resistant strains), H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae (formerly Chlamydia pneumoniae), or Klebsiella pneumoniae. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 381
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Factive, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart and lung transplants.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) tablet, (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=63f60426-e27f-4258-9bfc-b4a15ebdca83
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Factive, may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid Factive in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) tablet, (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=63f60426-e27f-4258-9bfc-b4a15ebdca83
Fluoroquinolones, including gemifloxacin, cause arthropathy and osteochondrosis in immature animals of various species. The relevance of these adverse effects in immature animals to use in humans is unknown.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 382
Fluoroquinolones, including gemifloxacin, are associated with increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all age groups. This risk is further increased in older adults (usually those older than 60 years of age), individuals receiving concomitant corticosteroids, and kidney, heart, or lung transplant recipients. Other factors that may independently increase risk of tendon rupture include strenuous physical activity, renal failure, and previous tendon disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Tendinitis and tendon rupture have been reported in patients receiving fluoroquinolones who did not have any of these risk factors. Fluoroquinolone-associated tendinitis and tendon rupture most frequently involve the Achilles tendon and may require surgical repair. Tendinitis and tendon rupture in the rotator cuff (shoulder), hand, biceps, thumb, and other tendon sites also reported. Tendon rupture can occur during or following fluoroquinolone therapy and has been reported up to several months after completion of therapy. Advise patients to rest and refrain from exercise and contact a clinician at the first sign of tendinitis or tendon rupture (e.g., pain, swelling, or inflammation of a tendon or weakness or inability to use a joint). Discontinue gemifloxacin if pain, swelling, inflammation, or rupture of a tendon occurs.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 382
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Gemifloxacin (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of bacterial infection caused by susceptible strains such as S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, or M. catarrhalis, S. pneumoniae (including multi-drug resistant strains [MDRSP]), M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, or K. pneumoniae.
FDA Label
Gemifloxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Gemifloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. Gemifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA15 - Gemifloxacin
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The absolute bioavailability averages approximately 71%.
Route of Elimination
Gemifloxacin and its metabolites are excreted via dual routes of excretion.Following oral administration of gemifloxacin to healthy subjects, a mean ( SD) of 61 9.5% of the dose was excreted in the feces and 36 9.3% in the urine as unchanged drug and metabolites. The mean ( SD) renal clearance following repeat doses of 320 mg was approximately 11.6 3.9 L/hr (range 4.6-6 L/hr), which indicates active secretion is involved in the renal excretion of gemifloxacin.
Volume of Distribution
1.66 to 12.12 L/kg
Clearance
renal cl=11.6+/- 3.9 L/hr [Healthy subjects receiving repeat doses of 320 mg orally]
Gemifloxacin, given as an oral tablet, is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak plasma concentrations of gemifloxacin were observed between 0.5 and 2 hours following oral tablet administration and the absolute bioavailability of the 320 mg tablet averaged approximately 71% (95% CI 60%-84%). Following repeat oral doses of 320 mg to healthy subjects, the mean + or - SD maximal gemifloxacin plasma concentrations (Cmax) and systemic drug exposure (AUC (0-24)) were 1.61 + or - 0.51 ug/mL (range 0.70-2.62 ug/mL) and 9.93 + or - 3.07 ug.hr/mL (range 4.71-20.1 ug.hr/mL), respectively. In patients with respiratory and urinary tract infections (n=1423), similar estimates of systemic drug exposure were determined using a population pharmacokinetics analysis (geometric mean AUC (0-24), 8.36 ug.hr/mL; range 3.2 -47.7 ug.hr/mL).
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) tablet, (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=54c4b48b-cad7-4889-808f-f741352a2c97
In vitro binding of gemifloxacin to plasma proteins in healthy subjects is approximately 60 to 70% and is concentration independent. After repeated doses, the in vivo plasma protein binding in healthy elderly and young subjects ranged from 55% to 73% and was unaffected by age. Renal impairment does not significantly affect the protein binding of gemifloxacin. The blood-to-plasma concentration ratio of gemifloxacin was 1.2:1. The geometric mean for Vdss/F is 4.18 L/kg (range, 1.66 - 12.12 L/kg). Gemifloxacin is widely distributed throughout the body after oral administration. Concentrations of gemifloxacin in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid exceed those in the plasma. Gemifloxacin penetrates well into lung tissue and fluids.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) tablet, (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=54c4b48b-cad7-4889-808f-f741352a2c97
Gemifloxacin and its metabolites are excreted via dual routes of excretion. Following oral administration of gemifloxacin to healthy subjects, a mean (+ or - SD) of 61 + or - 9.5% of the dose was excreted in the feces and 36 + or - 9.3% in the urine as unchanged drug and metabolites. The mean (+ or - SD) renal clearance following repeat doses of 320 mg was approximately 11.6 + or - 3.9 L/hr (range 4.6-17.6 L/hr), which indicates active secretion is involved in the renal excretion of gemifloxacin. The mean (+ or - SD) plasma elimination half-life at steady state following 320 mg to healthy subjects was approximately 7 + or - 2 hours (range 4-12 hours).
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) tablet, (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=54c4b48b-cad7-4889-808f-f741352a2c97
Gemifloxacin is metabolized to a limited extent by the liver. All metabolites formed are minor (<10% of the administered oral dose); the principal ones are N-acetyl gemifloxacin, the E-isomer of gemifloxacin and the carbamyl glucuronide of gemifloxacin.
Gemifloxacin is metabolized to a limited extent by the liver. The unchanged compound is the predominant drug-related component detected in plasma (approximately 65%) up to 4 hours after dosing. All metabolites formed are minor (<10% of the administered oral dose); the principal ones are N-acetyl gemifloxacin, the E-isomer of gemifloxacin and the carbamyl glucuronide of gemifloxacin. Cytochrome P450 enzymes do not play an important role in gemifloxacin metabolism, and the metabolic activity of these enzymes is not significantly inhibited by gemifloxacin.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for FACTIVE (gemifloxacin mesylate) tablet, (November 2011). Available from, as of February 28, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=54c4b48b-cad7-4889-808f-f741352a2c97
7 (± 2) hours
Gemifloxacin has an elimination half life of about 7 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 384
The bactericidal action of gemifloxacin results from inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, which are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination.
Like other fluoroquinolone anti-infective agents, gemifloxacin inhibits DNA synthesis in susceptible organisms via inhibition of type II DNA topoisomerases (DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV). However, unlike many other fluoroquinolones, gemifloxacin targets both DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV in susceptible S. pneumoniae. Although cross-resistance can occur between gemifloxacin and other fluoroquinolones, gemifloxacin may be active against some strains of S. pneumoniae resistant to ciprofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 384
The fluroquinolone gemifloxacin was examined for its capacity to modulate secretion of cytokines by human monocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Monocytes from six male and two female healthy volunteers were stimulated with LPS, exposed to gemifloxacin and the amounts of secreted IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-alpha measured at 3, 6 and 24 h. The results revealed that LPS alone increased secretion of each cytokine significantly. Treatment of the LPS-stimulated monocytes with gemifloxacin resulted in a significant inhibition (p < 0.01) of secretion of each of the cytokines from monocytes of the eight volunteers. Nuclear extracts of the human monocyte cell line, THP-1, were used in the electrophoretic mobility shift assay to determine whether gemifloxacin affects nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) activation. In addition, RNA from THP-1 cells was used in Northern blots to determine whether inhibition of secretion of IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha by gemifloxacin occurred at the transcription or translation level. Whereas LPS induced a rapid increase in NF-kappa B activation, gemifloxacin alone did not. Gemifloxacin did not affect the kinetics or decrease the extent of activation. Northern blots indicated that the inhibitory activity of gemifloxacin occurred post-transcription. Thus, gemifloxacin may modulate the immune response by altering secretion of cytokines by human monocytes. Although the concentrations of gemifloxacin used were higher than those observed in the serum of human volunteers treated with the dose under clinical development, it should be taken into consideration that concentrations at tissue and intracellular levels may be considerably higher than serum concentrations.
PMID:15008941 Araujo F et al; Clin Microbiol Infect 10 (3): 213-9 (2004)
Fluoroquinolones prolong the QT interval by blocking voltage-gated potassium channels, especially the rapid component of the delayed rectifier potassium current I(Kr), expressed by HERG (the human ether-a-go-go-related gene). According to the available case reports and clinical studies, moxifloxacin carries the greatest risk of QT prolongation from all available quinolones in clinical practice and it should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors for Torsades de pointes (TdP).
PMID:22156660 Briasoulis A et al; Cardiology 120 (2): 103-10 (2011)

API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
29
PharmaCompass offers a list of Gemifloxacin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Gemifloxacin manufacturer or Gemifloxacin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Gemifloxacin manufacturer or Gemifloxacin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Gemifloxacin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Gemifloxacin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Gemifloxacin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Gemifloxacin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE supplier is an individual or a company that provides GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE finished formulations upon request. The GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE suppliers may include GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE USDMF includes data on GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE Drug Master File in Korea (GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE. The MFDS reviews the GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE written confirmation (GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE APIs or GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE GMP manufacturer or GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE GMP API supplier for your needs.
A GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE's compliance with GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE EP), GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (GEMIFLOXACIN MESYLATE USP).
