
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
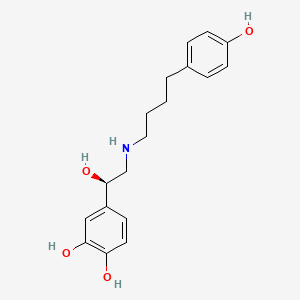

1. Arbutamine Hydrochloride
2. Arbutamine Hydrochloride, (r)-isomer
3. Genesa
1. 128470-16-6
2. Arbutaminum
3. Arbutamina
4. B07l15yaev
5. Chebi:50580
6. 4-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butylamino]ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol
7. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-[[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl]amino]ethyl]-
8. 4-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-{[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl]amino}ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol
9. Arbutamine [inn:ban]
10. Arbutaminum [inn-latin]
11. Arbutamina [inn-spanish]
12. Unii-b07l15yaev
13. Arbutamine [mi]
14. Arbutamine [inn]
15. Arbutamine [vandf]
16. Arbutamine [who-dd]
17. Schembl521645
18. Chembl1201251
19. Dtxsid00155908
20. Db01102
21. Hy-16056
22. Cs-0006131
23. Q4784959
24. (r)-3,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-(((4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)methyl)benzyl Alcohol
25. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)ethyl)-, (1r)
| Molecular Weight | 317.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H23NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 317.16270821 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 317.16270821 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 93 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 320 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used to elicit acute cardiovascular responses (cardiac stumulant), similar to those produced by exercise, in order to aid in diagnosing the presence or absence of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients who cannot exercise adequately.
Adrenergic beta-Agonists
Drugs that selectively bind to and activate beta-adrenergic receptors. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Agonists.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01C - Cardiac stimulants excl. cardiac glycosides
C01CA - Adrenergic and dopaminergic agents
C01CA22 - Arbutamine
Primarily metabolized to methoxyarbutamine. Another possible metabolite is ketoarbutamine. The metabolites of arbutamine appear to have less pharmacological activity and a longer half-life and than the parental drug.
Elimination half-life is approximately 8 minutes.
Arbutamine is a synthetic catecholamine with positive chronotropic and inotropic properties. The chronotropic (increase in heart rate) and inotropic (increase in force of contraction) effects of arbutamine serve to mimic exercise by increasing cardiac work (producing stress) and provoke myocardial ischemia in patients with compromised coronary arteries. The increase in heart rate caused by arbutamine is thought to limit regional subendocardial perfusion, thereby limiting tissue oxygenation. In functional assays, arbutamine is more selective for beta-adrenergic receptors than for alpha-adrenergic receptors. The beta-agonist activity of arbutamine provides cardiac stress by increasing heart rate, cardiac contractility, and systolic blood pressure. The degree of hypotension that occurs for a given chronotropic activity is less with arbutamine than, for example, with isoproterenol because alpha receptor activity is retained.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
45
PharmaCompass offers a list of Genesa API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Genesa manufacturer or Genesa supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Genesa manufacturer or Genesa supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Genesa API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Genesa API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Genesa Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Genesa Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Genesa manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Genesa, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Genesa manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Genesa API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Genesa supplier is an individual or a company that provides Genesa active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Genesa finished formulations upon request. The Genesa suppliers may include Genesa API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Genesa suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Genesa DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Genesa active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Genesa DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Genesa USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Genesa DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Genesa USDMF includes data on Genesa's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Genesa USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Genesa suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
Genesa Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Genesa GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Genesa GMP manufacturer or Genesa GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Genesa CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Genesa's compliance with Genesa specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Genesa CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Genesa CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Genesa may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Genesa EP), Genesa JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Genesa USP).
