
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
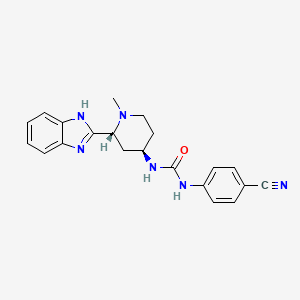

1. 1-(2-(1h-benzo(d)imidazol-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-(4-cyanophenyl)urea
2. Daurismo
3. Pf-04449913
1. 1095173-27-5
2. Pf-04449913
3. Pf 04449913
4. Daurismo
5. 1-((2r,4r)-2-(1h-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-(4-cyanophenyl)urea
6. 1-[(2r,4r)-2-(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl]-3-(4-cyanophenyl)urea
7. K673dmo5h9
8. Chembl2043437
9. Pf-4449913
10. C21h22n6o
11. Glasdegib (pf-04449913)
12. Pf-913
13. Glasdegib [usan:inn]
14. Glasdegibum
15. Unii-k673dmo5h9
16. N-[(2r,4r)-2-(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl]-n'-(4-cyanophenyl)urea
17. N-((2r,4r)-2-(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-n'-(4-cyanophenyl)urea
18. Glasdegib [inn]
19. Glasdegib [mi]
20. Glasdegib (usan/inn)
21. Glasdegib [usan]
22. Glasdegib [who-dd]
23. Pf-04449913;glasdegib
24. Gtpl8201
25. Schembl2068480
26. Glasdegib(pf-04449913)
27. Ex-a858
28. Chebi:145428
29. Dtxsid201025881
30. Amy38164
31. Vtb17327
32. Bdbm50385635
33. Mfcd25976839
34. Nsc775772
35. Zinc68251434
36. Ccg-268350
37. Db11978
38. Nsc-775772
39. Ncgc00378600-02
40. Ac-35176
41. Bs-14357
42. Hy-16391
43. S7160
44. D10636
45. J-690029
46. Q27077810
47. N-[(2r,4r)-2-(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1-methyl-4-piperidinyl]-n'-(4-cyanophenyl)urea
48. 4-[(2r)-2-[(1r)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-hydroxyethyl]-1-pyrrolidinyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)-benzonitrile
| Molecular Weight | 374.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H22N6O |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 374.18550935 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 374.18550935 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 96.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 595 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Glasdegib, in combination with cytarabine, is indicated for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia in adult patients who are over 75 years old or that have co-morbidities that preclude intensive induction chemotherapy. Acute myeloid leukemia is characterized by abnormal production of myeloblasts, red cells, or platelets. It is considered a cancer of blood and bone marrow and it is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults.
FDA Label
Daurismo is indicated, in combination with low-dose cytarabine, for the treatment of newly diagnosed de novo or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) in adult patients who are not candidates for standard induction chemotherapy.
In preclinical studies, glasdegib achieved a significant reduction in leukemic stem cell burden in xenograft models and a reduction in cell population expressing leukemic stem cell markers. In clinical trials, glasdegib demonstrated a marked downregulation of more than 80% of the expression of glioma-associated transcriptional regulator GL11 in skin. In this same study 8% of the studied individuals with acute myeloid leukemia achieved morphological complete remission while 31% achieved stable disease state. The latest clinical trial proved glasdegib to generate an overall survival of 8.3 months which was almost double to what has been observed in patients under low-dose cytarabine treatment. As well, there have been reports of dose-dependent QTc prolongation in patients administered with glasdegib.
L01XX63
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XJ - Hedgehog pathway inhibitors
L01XJ03 - Glasdegib
Absorption
Glasdegib presents a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile which is observed by the presence of a broad dose-proportional maximum plasma concentration. In this study and on a dose of 50 mg, the median time to reach a maximum concentration of 321 ng/ml was of 4 hours with an AUC of 9587 ng.h/ml. The oral bioavailability of glasdegib is reported to be of 55%. In a multiple dose study of 50 mg, the Cmax, tmax and AUC was reported to be 542 ng/ml, 4 h and 9310 ng.h/ml respectively. In this same study, the average concentration at a steady state was of 388 ng/ml. The absorption rates of glasdegib can be modified by the concomitant consumption of a high-fat, high-calorie meal.
Route of Elimination
From the administered dose of glasdegib, 49% is eliminated in the urine from which 17% is excreted as the unchanged form while 42% is eliminated in feces where 20% represents the unchanged form.
Volume of Distribution
Glasdegib reported volume of distribution in a dose of 50 mg is of 225 L.
Clearance
The clearance rate of 50 mg of glasdegib is reported to be of 5.22 L/h.
After oral administration, glasdegib was primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 with minor contributions of CYP2C8 and UGT1A9. The amount of unchanged glasdegib in plasma accounts only for 69% of the administered dose.
The reported half-life of glasdegib is of 17.4 hours.
Glasdegib is a potent and selective inhibitor of the hedgehog signaling pathway that acts by binding to the smoothened (SMO) receptor. The hedgehog signaling pathway is involved in maintenance of neural and skin stem cells. In this pathway, the binding of specific ligands to the transmembrane receptor patched (PTCH1) allows the activation of the transcriptional regulators GL11, GL12 and modulation of the gene expression through SMO-mediated signaling. The aberrant activation of the hedgehog pathway is thought to be implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia, medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma due to the hyperproliferative state that a modification on this pathway will produce.
Market Place

ABOUT THIS PAGE
94
PharmaCompass offers a list of Glasdegib API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Glasdegib manufacturer or Glasdegib supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Glasdegib manufacturer or Glasdegib supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Glasdegib API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Glasdegib API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Glasdegib Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Glasdegib Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Glasdegib manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Glasdegib, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Glasdegib manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Glasdegib API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Glasdegib manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Glasdegib supplier is an individual or a company that provides Glasdegib active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Glasdegib finished formulations upon request. The Glasdegib suppliers may include Glasdegib API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Glasdegib suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Glasdegib Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Glasdegib GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Glasdegib GMP manufacturer or Glasdegib GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Glasdegib CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Glasdegib's compliance with Glasdegib specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Glasdegib CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Glasdegib CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Glasdegib may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Glasdegib EP), Glasdegib JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Glasdegib USP).
