
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
VMF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
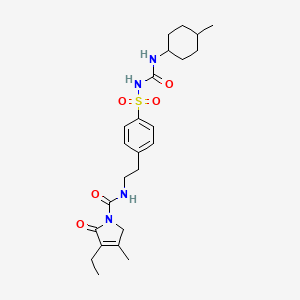

1. 1-(4-(2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrrolinecarboxamido)ethyl)phenylsulfonyl)-3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)urea
2. Amarel
3. Amaryl
4. Glymepiride
5. Hoe 490
6. Hoe-490
7. Roname
1. 93479-97-1
2. Amaryl
3. Glimepirid
4. Amarel
5. Glimepirida
6. Glimepiridum
7. Hoe-490
8. Glimepride
9. Hoe 490
10. Cis-glimepiride
11. 684286-46-2
12. Glimepiride, Cis-
13. Glimperide
14. Glimepiride Impurity A
15. 4-ethyl-3-methyl-n-[2-[4-[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoylsulfamoyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-oxo-2h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
16. Chebi:5383
17. 1-((p-(2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1-carboxamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea
18. Endial
19. Nsc-759809
20. 24t6xir2mz
21. 6ky687524k
22. 261361-60-8
23. Ncgc00016960-03
24. Glimepiridum [latin]
25. Roname
26. Glimepirida [spanish]
27. Cas-93479-97-1
28. Glista Od
29. Dsstox_cid_20675
30. Dsstox_rid_79534
31. Dsstox_gsid_40675
32. 1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide, 3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-(2-(4-(((((4-methylcyclohexyl)amino)carbonyl)amino)sulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-2-oxo-, Trans-
33. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-[2-(4-{[(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}phenyl)ethyl]-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
34. Glymepirid
35. Glorion
36. Glemax
37. Glimer
38. Solosa
39. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-[2-(4-{[(cis-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}phenyl)ethyl]-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
40. Smr000466368
41. Amaryl (tn)
42. Ccris 7083
43. Sr-05000001508
44. Unii-24t6xir2mz
45. Brn 5365754
46. Gimepiride
47. Vitamine
48. Niddaryl
49. Sugral
50. Hoe490
51. Unii-6ky687524k
52. Glimepiride,(s)
53. 1-[[4-[2-[[(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrol-1-yl)carbonyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]sulphonyl]-3-(cis-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea (cis-glimepiride)
54. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoylsulfamoyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-5h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
55. Glimepiride [usan:usp:inn:ban]
56. Amaryl, Glista Od
57. Glimepiride- Bio-x
58. Mfcd00878417
59. Cpd000466368
60. Glimepiride [mi]
61. Prestwick0_000651
62. Prestwick1_000651
63. Prestwick2_000651
64. Prestwick3_000651
65. Glimepiride [inn]
66. Glimepiride [jan]
67. Glimepiride [usan]
68. Glimepiride [vandf]
69. Chembl1481
70. Glimepiride [mart.]
71. Oprea1_382896
72. Schembl16084
73. Schembl16086
74. Bspbio_000681
75. Glimepiride [usp-rs]
76. Glimepiride [who-dd]
77. Glimepiride Cis-isomer
78. Mls000759495
79. Mls001076674
80. Mls001401419
81. Mls003915622
82. Mls006011260
83. Spbio_002602
84. Glimepiride [ema Epar]
85. Bpbio1_000751
86. Chembl149223
87. Gtpl6820
88. Schembl8738802
89. Glimepiride (jp17/usp/inn)
90. Dtxsid5040675
91. Schembl14371714
92. Schembl14965363
93. Chebi:92609
94. Dtxsid20861130
95. Glimepiride [orange Book]
96. Glimepiride For System Suitability
97. Glimepiride [ep Monograph]
98. Glimepiride [usp Impurity]
99. Hms1570c03
100. Hms2052l03
101. Hms2090k18
102. Hms2097c03
103. Hms2235l07
104. Hms3269a09
105. Hms3372o07
106. Hms3394l03
107. Hms3413k06
108. Hms3654f17
109. Hms3677k06
110. Hms3714c03
111. Pharmakon1600-01504915
112. Zinc537791
113. Glimepiride [usp Monograph]
114. Bcp05331
115. Duetact Component Glimepiride
116. Hy-b0104
117. Tox21_110713
118. Ac-476
119. Bdbm50237590
120. Nsc759809
121. Nsc813217
122. S1344
123. Stl451059
124. Stl453194
125. Glimepiride Related Compound A
126. Akos015894919
127. Akos015969663
128. Glimepiride, >=98% (hplc), Solid
129. Tox21_110713_1
130. Zinc100001976
131. Zinc100070954
132. Ab07644
133. Bcp9000728
134. Ccg-101156
135. Cs-1844
136. Db00222
137. Glimepiride Component Of Duetact
138. Ks-5238
139. Nc00406
140. Nsc 759809
141. Nsc-813217
142. Ncgc00016960-01
143. Ncgc00016960-02
144. Ncgc00016960-04
145. Ncgc00016960-05
146. Ncgc00016960-07
147. Ncgc00161404-01
148. Ncgc00161404-02
149. Ncgc00181757-01
150. Ncgc00371061-02
151. Ncgc00371061-06
152. 1-{[4-(2-{[(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrol-1-yl)carbonyl]amino}ethyl)phenyl]sulfonyl}-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea
153. 1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide, 2,5-dihydro-3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(2-(4-(((((4-methylcyclohexyl)amino)carbonyl)amino)sulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-2-oxo-, Trans-
154. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-((1r,4r)-4-methylcyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro
155. Bg164507
156. Smr001550123
157. Glimepiride 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
158. Ab00513874
159. Cs-0165191
160. Ft-0626713
161. Ft-0668978
162. G0395
163. Glimepiride Impurity A [ep Impurity]
164. Sw196369-4
165. C07669
166. D00593
167. Glimepiride Related Compound A [usp-rs]
168. Ab00513874-06
169. Ab00513874-08
170. Ab00513874-09
171. Ab00513874_10
172. Ab00513874_11
173. 479g971
174. A844609
175. A899888
176. Q425027
177. Q-201158
178. Sr-05000001508-1
179. Sr-05000001508-2
180. Sr-05000001508-3
181. Brd-k34776109-001-03-4
182. Brd-k42693031-001-01-8
183. Glimepiride Related Compound A [usp Impurity]
184. Q27253874
185. Glimepiride, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
186. Glimepiride, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
187. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-((1r,4r)-4-methylcyclohexylcarbamoyl)
188. Glimepiride, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
189. Sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
190. Glimepiride For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
191. 1-((4-(2-(((3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrol-1-yl)carbonyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(cis-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea
192. 1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide, 3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-(2-(4-(((((cis-4-methylcyclohexyl)amino)carbonyl)amino)sulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-2-oxo-
193. 1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide, 3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[[[[(trans- 4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-
194. 3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
195. 3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[[[[(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
196. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-n-(2-{4-[({[(1r,4r)-4-methylcyclohexyl]carbamoyl}amino)sulfonyl]phenyl}ethyl)-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
197. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-(((1r,4r)-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
198. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-(((1s,4s)-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide? (glimepiride Impurity Pound(c)
199. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-((1r,4r)-4-methylcyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
200. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-((rel-(1r,4r)-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
201. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-((trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
202. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-[2-(4-{[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}phenyl)ethyl]-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
203. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-[2-(4-{[(cis-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}phenyl)ethyl]-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-car
204. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[[3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)ureido]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
205. 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-{2-[4-({[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl]amino}sulfonyl)phenyl]ethyl}-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
206. N'-{[4-(2-{[(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrol-1-yl)carbonyl]amino}ethyl)phenyl]sulfonyl}-n-(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamimidic Acid
207. N-(4-ethyl-3-methyl-5-oxo-2h-pyrrol-1-yl)-3-[4-[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoylsulfamoyl]phenyl]propanamide;glimepiride
208. N-[4-[2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1-carboxamido)-ethyl]-benzenesulfonyl]-n'-4-methylcyclohexylurea
209. Trans-1-(4-(2-(3-ethyl-4-me-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamido)ethyl)phenylsulfonyl)-3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)urea
210. Trans-3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methyl Cyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
211. Trans-3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxamide
212. Trans-3-ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-n-[2-[4-[[[[trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1h-pyrrole-1-carboxyamide
| Molecular Weight | 490.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H34N4O5S |
| XLogP3 | 3.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 490.22499137 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 490.22499137 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 133 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 895 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amaryl |
| PubMed Health | Glimepiride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | AMARYL is an oral sulfonylurea that contains the active ingredient glimepiride. Chemically, glimepiride is identified as 1-[[p-[2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1-carboxamido) ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea (C24H34N4O5S)... |
| Active Ingredient | Glimepiride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 4mg; 2mg; 1mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glimepiride |
| PubMed Health | Glimepiride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glimepiride Tablets, USP are an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Glimepiride, USP is a white to yellowish-white, crystalline, odorless to practically odorless powder formulated into tablets of 1-mg, 2-mg, and 4-mg strengths... |
| Active Ingredient | Glimepiride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg; 8mg; 4mg; 6mg; 2mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Labs Fl; Teva; Accord Hlthcare; Aurobindo Pharma; Invagen Pharms; Hikma Pharms; Indoco Remedies; Micro Labs Ltd India; Vintage; Dr Reddys Labs; Carlsbad; Mylan |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amaryl |
| PubMed Health | Glimepiride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | AMARYL is an oral sulfonylurea that contains the active ingredient glimepiride. Chemically, glimepiride is identified as 1-[[p-[2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1-carboxamido) ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea (C24H34N4O5S)... |
| Active Ingredient | Glimepiride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 4mg; 2mg; 1mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glimepiride |
| PubMed Health | Glimepiride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glimepiride Tablets, USP are an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Glimepiride, USP is a white to yellowish-white, crystalline, odorless to practically odorless powder formulated into tablets of 1-mg, 2-mg, and 4-mg strengths... |
| Active Ingredient | Glimepiride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg; 8mg; 4mg; 6mg; 2mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Labs Fl; Teva; Accord Hlthcare; Aurobindo Pharma; Invagen Pharms; Hikma Pharms; Indoco Remedies; Micro Labs Ltd India; Vintage; Dr Reddys Labs; Carlsbad; Mylan |
Glimepiride is indicated for the management of type 2 diabetes in adults as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control as monotherapy. It may also be indicated for use in combination with metformin or insulin to lower blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes whose high blood sugar levels cannot be controlled by diet and exercise in conjunction with an oral hypoglycemic (a drug used to lower blood sugar levels) agent alone.
Glimepiride stimulates the secretion of insulin granules from the pancreatic beta cells and improves the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin to increase peripheral glucose uptake, thus reducing plasma blood glucose levels and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) levels. A multi-center, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the efficacy of glimepiride (18 mg) as monotherapy titrated over 10 weeks compared with placebo in T2DM subjects who were not controlled by diet alone. In this study, there was a reduction in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) by 46 mg/dL, post-prandial glucose (PPG) by 72 mg/dL, and HbA1c by 1.4% more than the placebo. In another randomized study comprising of patients with T2DM receiving either placebo or one of the three doses (1, 4, or 8 mg) of glimepiride during a 14-week study period, all glimepiride regimens significantly reduced FPG, PPG, and HbA1c values (P < 0.001) compared to placebo by the end of the study period. The 4- and 8-mg doses of glimepiride were more effective than the 1-mg dose; however, the 4-mg dose provided a nearly maximal antihyperglycemic effect.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
A10BB12
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BB - Sulfonylureas
A10BB12 - Glimepiride
Absorption
Glimepiride is completely absorbed after oral administration within 1 hour of administration with a linear pharmacokinetics profile. Following administration of a single oral dose of glimepiride in healthy subjects and with multiple oral doses with type 2 diabetes, the peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) were reached after 2 to 3 hours post-dose. Accumulation does not occur after multiple doses. When glimepiride was given with meals, the time to reach Cmax was increased by 12% while the mean and AUC (area under the curve) were decreased by 8 to 9%, respectively. In a pharmacokinetic study of Japanese patients with T2DM, Cmax value in once-daily dose was higher than those in twice-daily doses. The absolute bioavailability of glimepiride is reported to be complete following oral administration.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration of glimepiride in healthy male subjects, approximately 60% of the total radioactivity was recovered in the urine in 7 days, with M1 and M2 accounting for 80-90% of the total radioactivity recovered in the urine. The ratio of M1 to M2 was approximately 3:2 in two subjects and 4:1 in one subject. Approximately 40% of the total radioactivity was recovered in feces where M1 and M2 accounted for about 70% of the radioactivity and a ratio of M1 to M2 being 1:3. No parent drug was recovered from urine or feces.
Volume of Distribution
Following intravenous dosing in healthy subjects, the volume of distribution was 8.8 L (113 mL/kg).
Clearance
A single-dose, crossover, dose-proportionality (1, 2, 4, and 8 mg) study in normal subjects and from a single- and multiple-dose, parallel, dose proportionality (4 and 8 mg) study in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) were performed. In these studies, the total body clearance was 52.1 +/- 16.0 mL/min, 48.5 +/- 29.3 mL/min in patients with T2D given a single oral dose, and 52.7 +/- 40.3 mL/min in patients with T2D given multiple oral doses. Following intravenous dosing in healthy subjects, the total body clearance was 47.8 mL/min.
Glimepiride is reported to undergo hepatic metabolism. Following either an intravenous or oral dose, glimepiride undergoes oxidative biotransformation mediated by CYP2C9 enzyme to form a major metabolite, cyclohexyl hydroxymethyl derivative (M1), that is pharmacologically active. M1 can be further metabolized to the inactive metabolite carboxyl derivative (M2) by one or several cytosolic enzymes. M1 retained approximately one third of the pharmacologic activity of its parent in an animal model, with a half-life of 3-6 hours. However, whether the glucose-lowering effect of M1 is clinically significant is not clear.
Glimepiride has known human metabolites that include Cyclohexylhydroymethylglimepiride.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The elimination half-life of glimepiride is approximately 5 to 8 hours, which can increase up to 9 hours following multiple doses.
ATP-sensitive potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells that are gated by intracellular ATP and ADP. The hetero-octomeric complex of the channel is composed of four pore-forming Kir6.2 subunits and four regulatory sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) subunits. Alternative splicing allows the formation of channels composed of varying subunit isoforms expressed at different concentrations in different tissues. In pancreatic beta cells, ATP-sensitive potassium channels play a role as essential metabolic sensors and regulators that couple membrane excitability with glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). When there is a decrease in the ATP:ADP ratio, the channels are activated and open, leading to K+ efflux from the cell, membrane hyperpolarization, and suppression of insulin secretion. In contrast, increased uptake of glucose into the cell leads to elevated intracellular ATP:ADP ratio, leading to the closure of channels and membrane depolarization. Depolarization leads to activation and opening of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and consequently an influx of calcium ions into the cell. Elevated intracellular calcium levels causes the contraction of the filaments of actomyosin responsible for the exocytosis of insulin granules stored in vesicles. Glimepiride blocks the ATP-sensitive potassium channel by binding non-specifically to the B sites of both sulfonylurea receptor-1 (SUR1) and sulfonylurea receptor-2A (SUR2A) subunits as well as the A site of SUR1 subunit of the channel to promote insulin secretion from the beta cell.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
32
PharmaCompass offers a list of Glimepiride API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Glimepiride manufacturer or Glimepiride supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Glimepiride manufacturer or Glimepiride supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Glimepiride API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Glimepiride API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Glimepiride Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Glimepiride Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Glimepiride manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Glimepiride, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Glimepiride manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Glimepiride API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Glimepiride manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Glimepiride supplier is an individual or a company that provides Glimepiride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Glimepiride finished formulations upon request. The Glimepiride suppliers may include Glimepiride API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Glimepiride suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Glimepiride DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Glimepiride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Glimepiride DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Glimepiride USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Glimepiride DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Glimepiride USDMF includes data on Glimepiride's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Glimepiride USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Glimepiride suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Glimepiride Drug Master File in Japan (Glimepiride JDMF) empowers Glimepiride API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Glimepiride JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Glimepiride JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Glimepiride suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Glimepiride Drug Master File in Korea (Glimepiride KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Glimepiride. The MFDS reviews the Glimepiride KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Glimepiride KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Glimepiride KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Glimepiride API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Glimepiride suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Glimepiride CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Glimepiride Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Glimepiride CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Glimepiride EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Glimepiride to their clients by showing that a Glimepiride CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Glimepiride CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Glimepiride CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Glimepiride CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Glimepiride DMF.
A Glimepiride CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Glimepiride CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Glimepiride suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Glimepiride written confirmation (Glimepiride WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Glimepiride manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Glimepiride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Glimepiride APIs or Glimepiride finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Glimepiride WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Glimepiride suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Glimepiride as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Glimepiride API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Glimepiride as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Glimepiride and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Glimepiride NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Glimepiride suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Glimepiride Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Glimepiride GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Glimepiride GMP manufacturer or Glimepiride GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Glimepiride CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Glimepiride's compliance with Glimepiride specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Glimepiride CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Glimepiride CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Glimepiride may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Glimepiride EP), Glimepiride JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Glimepiride USP).

