
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
US Medicaid
NA
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Big Plasma Glucagon
2. Glucagon-like-immunoreactivity
3. Gut Glucagon-like Immunoreactants
1. Glucagonum
2. Glucagone
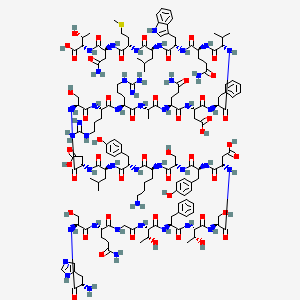
3. His-ser-glu(nh2)-gly-thr-phe-thr-ser-asp-tyr-ser-lys-tyr-leu-asp-ser-arg-arg-ala-glu(nh2)-asp-phe-val-glu(nh2)-trp-leu-met-asp(nh2)-thr
4. Glucagon-like-immunoreactivity
5. Glucaton
6. Bovine Glucagon
7. Glukagon Novo
8. Glucagon, Pig
9. Glucagon (dog)
10. Glucagon (pig)
11. Glucagon (ox)
12. Big Plasma Glucagon
13. Glucagone [dcit]
14. Glucagonum [inn-latin]
15. Glucagon (xenopus Laevis)
16. Glucagon (saimiri Sciureus)
17. Unii-76la80ig2g
18. 76la80ig2g
19. Glucagon (mesocricetus Auratus)
20. Glucagon, Porcine, For Bioassay
21. Glucagon [usp:inn:ban:jan]
22. Schembl15268863
23. Gut Glucagon-like Immunoreactants
24. Hsdb 3337
25. Dtxsid101016809
26. Glucagon, Porcine, For Immunoassay
27. Hsqgtftsdyskyldsrraqdfvqwlmnt
28. Einecs 232-708-2
29. Ncgc00167140-01
30. Glucagon, Acetate Salt, >=97.0% (hplc)
31. Human Glucagon, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
32. His-ser-gln-gly-thr-phe-thr-ser-asp-tyr-ser-lys-tyr-leu-asp-ser-arg-arg-ala-gln-asp-phe-val-gln-trp-leu-met-asn-thr
33. L-histidyl-l-seryl-l-glutaminylglycyl-l-threonyl-l-phenylalanyl-l-threonyl-l-seryl-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-tyrosyl-l-seryl-l-lysyl-l-tyrosyl-l-leucyl-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-seryl-l-arginyl-l-arginyl-l-alanyl-l-glutaminyl-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanyl-l-valyl-l-glutaminyl-l-tryptophyl-l-leucyl-l-methionyl-l-asparaginyl-l-threonine
34. L-threonine, L-histidyl-l-seryl-l-glutaminylglycyl-l-threonyl-l-phenylalanyl-l-threonyl-l-seryl-l-.alpha.-aspartyl-l-tyrosyl-l-seryl-l-lysyl-l-tyrosyl-l-leucyl-l-.alpha.-aspartyl-l-seryl-l-arginyl-l-argin Yl-l-alanyl-l-glutaminyl-l-.alpha.-aspartyl-l-phenylalanyl-l-valyl-l-glutaminyl-l-tryptophyl-l-leucyl-l-methionyl-l-asparaginyl-
35. L-threonine, L-histidyl-l-seryl-l-glutaminylglycyl-l-threonyl-l-phenylalanyl-l-threonyl-l-seryl-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-tyrosyl-l-seryl-l-lysyl-l-tyrosyl-l-leucyl-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-seryl-l-arginyl-l-arginyl-l-alanyl-l-glytaminyl-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanyl-l-valyl-l-glutaminyl-l-tryptophyl-l-leucyl-l-methionyl-l-asparaginyl-
| Molecular Weight | 3482.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C153H225N43O49S |
| XLogP3 | -16.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 55 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 55 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 115 |
| Exact Mass | 3481.6190567 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 3480.6157019 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 1560 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 246 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 8160 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 31 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Gastrointestinal Agents; Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Glucagon is used in the treatment of lower esophageal obstruction due to foreign bodies, including food boluses. /NOT included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 1440
Glucagon may be of use in treating myocardial depression due to calcium channel blocking agents in those patients in whom conventional therapies have been ineffective. /NOT included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 1440
Glucagon administered in large intravenous doses is used to treat the cardiotoxic effects, specifically bradycardia and hypotension, in overdoses of beta-adrenergic blocking agents. Glucagon may be used with the proterenol or dobutamine. Supplemental potassium may be necessary for treated patients since glucagon tends to reduce serum potassium. /NOT included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 1440
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for GLUCAGON (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
...EFFECTIVE ONLY WHEN ADMIN PARENTERALLY. ITS HYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT IS...OF RELATIVELY BRIEF DURATION. .../SUPPLEMENTARY CARBOHYDRATES SHOULD BE GIVEN AS SOON AS POSSIBLE AFTER PATIENT RESPONDS/. AN ADDITIONAL SUGAR SOURCE IS ESPECIALLY IMPORTANT IN JUVENILES...
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 1045
Since glucagon is a protein, the possibility of hypersensitivity reactions should be considered.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service--Drug Information 94. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc. 1994 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2076
Side/Adverse Effects: Those indicating need for medical attention only if they continue or are bothersome: Nausea or vomiting - incidence is generally dependent upon dose and (with intravenous use) the rate of injection; these effects may be diminished by slower intravenous administration.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 1441
Glucagon should not be used to treat birth asphyxia or hypoglycemia in premature infants or in infants who have had intrauterine growth retardation.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 1440
Glucagon has been used as an aid in the diagnosis of insulinoma and pheochromocytoma; however, USP advisory panels do not generally recommend this use because of questions about safety.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 1440
Glucagon is indicated as a diagnostic aid in radiologic exams to temporarily inhibit the movement of the gastrointestinal tract and to treat severe hypoglycemia.
FDA Label
Baqsimi is indicated for the treatment of severe hypoglycaemia in adults, adolescents, and children aged 4 years and over with diabetes mellitus.
Ogluo is indicated for the treatment of severe hypoglycaemia in adults, adolescents, and children aged 2 years and over with diabetes mellitus.
Treatment of hypoglycaemia
Glucagon is indicated as a diagnostic aid in radiologic exams to temporarily inhibit the movement of the gastrointestinal tract and severe hypoglycemia. Glucagon raises blood sugar through activation of hepatic glucagon receptors, stimulating glycogenolysis and the release of glucose. Glucagon has a short duration of action. Glucagon may cause hyperglycemia in diabetic patients.
H04AA01
H04AA01
H - Systemic hormonal preparations, excl. sex hormones and insulins
H04 - Pancreatic hormones
H04A - Glycogenolytic hormones
H04AA - Glycogenolytic hormones
H04AA01 - Glucagon
Absorption
A 1mg intravenous dose of glucagon reaches a Cmax of 7.9ng/mL with a Tmax of 20 minutes. An intramuscular dose reaches a Cmax of 6.9ng/mL with a Tmax of 13 minutes. A 3mg dose of glucagon nasal powder reaches a Cmax of 6130pg/mL with a Tmax of 15 minutes.
Route of Elimination
Elimination of glucagon is not fully characterized in literature, however the kidney and liver appear to contribute significantly in animal models. The liver and kidney are responsible for approximately 30% of glucagon elimination each.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of glucagon is 0.25L/kg. The apparent volume of distribution is 885L.
Clearance
A 1mg intravenous dose of glucagon has a clearance of 13.5mL/min/kg.
Because of its polypeptide nature, glucagon is destroyed in the GI tract, and therefore must be administered parenterally.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service--Drug Information 94. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc. 1994 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2075
Glucagon is a protein and so it is metabolized into smaller polypeptides and amino acids in the liver, kidney, and plasma.
The half life of glucagon is 26 minutes for an intramuscular dose. The half life of glucagon nasal powder is approximately 35 minutes. The half life of glucagon by a subcutaneous auto-injector or pre-filled syringe is 32 minutes.
Glucagon has a plasma half-life of about 3-10 minutes.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service--Drug Information 94. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc. 1994 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2075
Glucagon binds to the glucagon receptor activating Gs and Gq. This activation activates adenylate cyclase, which increases intracellular cyclic AMP and activates protein kinase A. Activating Gq activates phospholipase C, increases production of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate, and releases intracellular calcium. Protein kinase A phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase kinase, which phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase, which phosphorylates glycogen, causing its breakdown. Glucagon also relaxes smooth muscle of the stomach, duodenum, small bowel, and colon.
Glucagon increases the blood glucose concentration by mobilizing hepatic glycogen and thus is effective only when hepatic glycogen is available. Patients with reduced glycogen stores (eg, starvation, adrenal insufficiency, alcoholic hypoglycemia) cannot respond to glucagon.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 1045
Glucagon produces extra hepatic effects that are independent of its hyperglycemic action. Although the exact mechanism(s) of action has not been conclusively determined, glucagon produces relaxation of smooth muscle of the stomach, duodenum, small intestine, and colon. The drug has also been shown to inhibit gastric and pancreatic secretions.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service--Drug Information 94. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc. 1994 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2075
Promotes hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Stimulates adenylate cyclase to produce increased cyclic-AMP, which is involved in a series of enzymatic activities. The resultant effects are increased concentrations of plasma glucose, a relaxant effect on smooth musculature, and an inotropic myocardial effect. Hepatic stores of glycogen are necessary for glucagon to elicit an antihypoglycemic effect.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 1441

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
61
PharmaCompass offers a list of Glucagon API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Glucagon manufacturer or Glucagon supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Glucagon manufacturer or Glucagon supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Glucagon API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Glucagon API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Glucagon Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Glucagon Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Glucagon Recombinant manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Glucagon Recombinant, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Glucagon Recombinant manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Glucagon Recombinant API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Glucagon Recombinant manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Glucagon Recombinant supplier is an individual or a company that provides Glucagon Recombinant active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Glucagon Recombinant finished formulations upon request. The Glucagon Recombinant suppliers may include Glucagon Recombinant API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Glucagon Recombinant suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Glucagon Recombinant DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Glucagon Recombinant active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Glucagon Recombinant DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Glucagon Recombinant USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Glucagon Recombinant DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Glucagon Recombinant USDMF includes data on Glucagon Recombinant's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Glucagon Recombinant USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Glucagon Recombinant suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Glucagon Recombinant Drug Master File in Japan (Glucagon Recombinant JDMF) empowers Glucagon Recombinant API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Glucagon Recombinant JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Glucagon Recombinant JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Glucagon Recombinant suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Glucagon Recombinant CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Glucagon Recombinant Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Glucagon Recombinant CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Glucagon Recombinant EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Glucagon Recombinant to their clients by showing that a Glucagon Recombinant CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Glucagon Recombinant CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Glucagon Recombinant CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Glucagon Recombinant CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Glucagon Recombinant DMF.
A Glucagon Recombinant CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Glucagon Recombinant CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Glucagon Recombinant suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Glucagon Recombinant as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Glucagon Recombinant API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Glucagon Recombinant as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Glucagon Recombinant and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Glucagon Recombinant NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Glucagon Recombinant suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Glucagon Recombinant Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Glucagon Recombinant GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Glucagon Recombinant GMP manufacturer or Glucagon Recombinant GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Glucagon Recombinant CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Glucagon Recombinant's compliance with Glucagon Recombinant specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Glucagon Recombinant CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Glucagon Recombinant CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Glucagon Recombinant may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Glucagon Recombinant EP), Glucagon Recombinant JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Glucagon Recombinant USP).
