

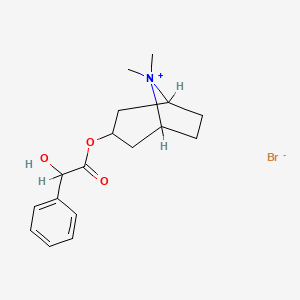

1. Hmbromide
2. Homatropine Methylbromide
3. Homatropine Methylbromide Iodide, (3(r)-endo)-isomer
4. Homatropine Methylbromide Iodide, (3(s)-endo)-isomer
5. Homatropine Methylbromide, (3(r)-endo)-isomer
6. Homatropine Methylbromide, (3(s)-endo)-isomer
7. Homatropine Methylbromide, Endo-(+-)-isomer
1. Homatropine Methylbromide
2. Homatropine Methobromide
3. Omatropina Metilbromuro
4. Methylhomatropine Bromide
5. 80-49-9
6. 8-methylhomatropinium Bromide
7. Tropinium Methobromide Mandelate
8. Homatropine Methyl Bromide
9. Methylhomatropinum Bromatum
10. Methylbromure D'homatropine
11. 3-alpha-hydroxy-8-methyl-1-alpha-h,5-alpha-h-tropanium Bromide Mandelate
12. Nsc34399
13. Schembl77827
14. Chebi:50373
15. Akos015896228
16. Db00725
17. 3-[2-hydroxy(phenyl)acetoxy]-8,8-dimethyl-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane Bromide
18. Ncgc00094694-01
19. Ncgc00094694-02
20. Db-056442
21. D90875
22. H-2560
| Molecular Weight | 370.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H24BrNO3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 369.09396 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 369.09396 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 374 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Used in conjunction with antacids or histamine H2-receptor antagonists in the treatment of peptic ulcers, gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers, to reduce further gastric acid secretion and delay gastric emptying.
Homatropine methylbromide belongs to the group of medicines called anti-muscarinics. Homatropine is used to treat duodenal or stomach ulcers or intestine problems. It can be used together with antacids or other medicine in the treatment of peptic ulcer. It may also be used to prevent nausea, vomiting, and motion sickness.
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A03 - Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders
A03B - Belladonna and derivatives, plain
A03BB - Belladonna alkaloids, semisynthetic, quaternary ammonium compounds
A03BB06 - Homatropine methylbromide
Homatropine is a quaternary ammonium muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Homatropine methylbromide inhibits the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine on structures innervated by postganglionic cholinergic nerves as well as on smooth muscles that respond to acetylcholine but lack cholinergic innervation. These postganglionic receptor sites are present in the autonomic effector cells of the smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes, and exocrine glands. Depending on the dose, anticholinergics may reduce the motility and secretory activity of the gastrointestinal system, and the tone of the ureter and urinary bladder and may have a slight relaxant action on the bile ducts and gallbladder.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?
