
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
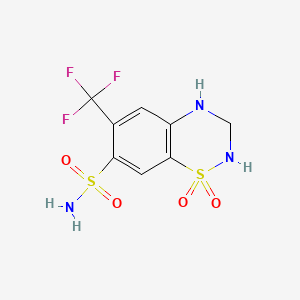

1. Diucardin
2. Trifluoromethylhydrothiazide
1. 135-09-1
2. Diuredemina
3. Glomerulin
4. Hidroflumetiazid
5. Diucardin
6. Diurometon
7. Flutizide
8. Saluron
9. Hydroflumethizide
10. Hidroalogen
11. Spandiuril
12. Bristab
13. Robezon
14. Enjit
15. Trifluoromethylhydrothiazide
16. Bristurin
17. Elodrine
18. Hydrenox
19. Leodrine
20. Olmagran
21. Rodiuran
22. Vergonil
23. Finuret
24. Rontyl
25. Sisuril
26. Hydol
27. Naclex
28. Trifluoromethylhydrazide
29. Di-ademil
30. Dihydroflumethazide
31. Dihydroflumethiazide
32. Hydroflumethazide
33. Elodrin
34. Metforylthiadiazin
35. Metflorylthiazidine
36. Methforylthiazidine
37. Idroflumetiazide
38. Hidroflumetiazida
39. Hydroflumethiazidum
40. 6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
41. Component Of Salutensin
42. Nsc 44627
43. 6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
44. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-, 1,1-dioxide
45. 6-trifluoromethyl-3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamoyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
46. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
47. 3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
48. Nsc-44627
49. 3,4-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-7-sulfamoylbenzo-1,2,4-thiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
50. 3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
51. 6-trifluoromethyl-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
52. 7-sulfamyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
53. Mls000028516
54. Chebi:5784
55. Rivosil
56. Di-adenil
57. Metforylthiazidin
58. 501cfl162r
59. Nsc44627
60. Naciex (glaxo)
61. 6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo-[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
62. Ncgc00016401-01
63. Cas-135-09-1
64. Smr000058284
65. Dsstox_cid_3132
66. Idroflumetiazide [dcit]
67. 3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulphonamide-1,1-dioxide
68. Dsstox_rid_76886
69. Dsstox_gsid_23132
70. Hydroflumethiazide-13c-d2
71. Hidroflumetiazida [inn-spanish]
72. Hydroflumethiazidum [inn-latin]
73. Saluron (tn)
74. Hsdb 3340
75. Sr-01000003094
76. Einecs 205-173-8
77. Brn 0342692
78. River
79. Unii-501cfl162r
80. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1?^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
81. Hydroflumethiazide (jan/usp/inn)
82. Prestwick_268
83. 7-sulfamyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1, 1-dioxide
84. Hydroflumethiazide [usp:inn:ban:jan]
85. Spectrum_000905
86. Opera_id_326
87. Prestwick0_000013
88. Prestwick1_000013
89. Prestwick2_000013
90. Prestwick3_000013
91. Spectrum2_001010
92. Spectrum3_000460
93. Spectrum4_000010
94. Spectrum5_000832
95. Cid_3647
96. Chembl1763
97. Schembl27028
98. Bspbio_000045
99. Bspbio_002140
100. Kbiogr_000359
101. Kbioss_001385
102. 4-27-00-08035 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
103. Mls001148090
104. Divk1c_000512
105. Spectrum1500341
106. Bmcl182567 Compound 6b
107. Spbio_001139
108. Spbio_001966
109. Hydroflumethiazide [mi]
110. Bpbio1_000051
111. Gtpl7197
112. Hydroflumethiazide [inn]
113. Hydroflumethiazide [jan]
114. Dtxsid3023132
115. Bdbm25897
116. Hms501j14
117. Hydroflumethiazide [hsdb]
118. Kbio1_000512
119. Kbio2_001385
120. Kbio2_003953
121. Kbio2_006521
122. Kbio3_001360
123. Hydroflumethiazide [vandf]
124. Ninds_000512
125. 3,2,4-thiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
126. Hms1568c07
127. Hms1920f05
128. Hms2091l13
129. Hms2095c07
130. Hms2235e09
131. Hms3259c15
132. Hms3371h03
133. Hms3712c07
134. Hydroflumethiazide [mart.]
135. Pharmakon1600-01500341
136. Zinc897225
137. Hydroflumethiazide [usp-rs]
138. Hydroflumethiazide [who-dd]
139. Tox21_110422
140. Ccg-40228
141. Mfcd00057316
142. Nsc757071
143. S9504
144. 3,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
145. 6-trifluoromethyl-7-sulfamoyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
146. 7-sulfamoyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
147. Akos015913797
148. Tox21_110422_1
149. Cs-w011956
150. Db00774
151. Hy-w011240
152. Nc00496
153. Nsc-757071
154. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
155. 2h-1,2, 4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3, 4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-, 1,1-dioxide
156. 3, 4-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-7-sulfamoylbenzo-1,2,4-thiadiazine 1, 1-dioxide
157. 3,4-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
158. 3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamoyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
159. 6-trifluoromethyl-3, 4-dihydro-7-sulfamoyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
160. 6-trifluoromethyl-7-sulfamoyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2, 4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
161. Hydroflumethiazide [orange Book]
162. Idi1_000512
163. Ncgc00016401-02
164. Ncgc00016401-03
165. Ncgc00016401-04
166. Ncgc00016401-05
167. Ncgc00016401-06
168. Ncgc00016401-09
169. Ncgc00023353-03
170. Ncgc00023353-04
171. Hydroflumethiazide [usp Monograph]
172. Wln: T66 Bswm Em Dhj Hxfff Iszw
173. Sbi-0051411.p003
174. Db-042267
175. Ab00052016
176. Ft-0614319
177. Hydroflumethiazide, Analytical Standard, ~97%
178. Salutensin Component Hydroflumethiazide
179. C07763
180. D00654
181. Ab00052016_15
182. Hydroflumethiazide Component Of Salutensin
183. A806882
184. 3,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
185. J-006640
186. Q3791957
187. Sr-01000003094-2
188. Sr-01000003094-3
189. Sr-01000003094-5
190. 6-trifluoromethyl-3,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
191. Brd-k36862742-001-05-8
192. Brd-k36862742-001-15-7
193. Brd-k36862742-001-24-9
194. 6-trifluoromethyl-7-sulfamoyl-3,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
195. 7-sulfamoyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
196. Hydroflumethiazide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
197. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
198. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1$l^{6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
199. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-16,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
200. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
201. 2h-1,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-, 1,1-dioxide
202. 3, 4-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-2h-1,2, 4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
203. 3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide-1,1-dioxide
204. 3,4-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulphonamide-1,1-dioxide
205. 3,4-dihydro-6-trifluoromethyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7sulphonamide-1,1-dioxide
206. 3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamoyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2h-1,2, 4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
207. 6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide #
208. 6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide1,1-dioxide
209. 7-sulfamoyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3, 4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
210. 1,1-bis(oxidanylidene)-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
211. 1,1-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1l-6-2-4-benzathiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
| Molecular Weight | 331.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H8F3N3O4S2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 330.99083258 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 330.99083258 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 135 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 578 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Saluron |
| Drug Label | Saluron (hydroflumethiazide) is a potent oral diuretic-antihypertensive agent of low toxicity. Each tablet contains 50 mg of hydroflumethiazide.Saluron is 2H-1,2,4-Benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-, 1,1-dioxide. Hyd... |
| Active Ingredient | Hydroflumethiazide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shire |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Saluron |
| Drug Label | Saluron (hydroflumethiazide) is a potent oral diuretic-antihypertensive agent of low toxicity. Each tablet contains 50 mg of hydroflumethiazide.Saluron is 2H-1,2,4-Benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3,4-dihydro-6-(trifluoromethyl)-, 1,1-dioxide. Hyd... |
| Active Ingredient | Hydroflumethiazide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shire |
Antihypertensive Agents; Diuretics, Thiazide
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
POTENT ORALLY ADMIN DIURETIC USEFUL IN MGMNT OF EDEMA ASSOC WITH CARDIAC FAILURE, HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS, PREMENSTRUAL TENSION, & STEROID ADMIN. ...ALSO RECOMMENDED FOR TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATE HYPERTENSION EITHER ALONE OR IN COMBINATION WITH OTHER ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 870
EXCEPT FOR FACT THAT SMALLER DOSAGE IS REQUIRED FOR HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE...NO CONVINCING EVIDENCE OF SIGNIFICANT DIFFERENCES IN THERAPEUTIC, METABOLIC, OR TOXIC OR SENSITIZATION IN EDEMATOUS OR HYPERTENSIVE PT OVER THAT OF PARENT COMPD, FLUMETHIAZIDE, OR PROTOTYPE CHLOROTHIAZIDE.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 870
REFRACTORY CASES MAY REQUIRE AS MUCH AS 200 MG/DAY IN DIVIDED DOSES. DOSAGE SHOULD BE ADJUSTED TO PROVIDE MIN EFFECTIVE DOSE FOR INDIVIDUAL PT.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 870
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
PERIODIC SERUM ELECTROLYTE DETERMINATION SHOULD BE DONE ON ALL PATIENTS IN ORDER TO DETECT ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE SUCH AS HYPONATREMIA, HYPOCHLOREMIC ALKALOSIS, & HYPOKALEMIA. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN ANURIA, PATIENTS HYPERSENSITIVE TO THESE & OTHER SULFONAMIDE DRUGS, & IN OTHERWISE HEALTHY PREGNANT WOMEN WITH OR WITHOUT MILD EDEMA. ...SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION IN PATIENTS WITH RENAL DISEASE, SINCE THEY MAY PPT AZOTEMIA. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
One of the most common adverse effects of the thiazides is potassium depletion which occurs in most patients. Potassium depletion may cause cardiac arrhythmias and is particularly important in patients receiving cardiac glycosides because hypokalemia potentiates the cardiac toxicity (e.g., increased ventricular irritability) of these agents. Potassium concentrations may be especially low in patients with primary or secondary aldosteronism, in patients with a low potassium intake, in those receiving other potassium-depleting drugs, and in patients with other losses of potassium, as in vomiting and diarrhea. Intermittent rather than continuous administration of the thiazides and/or ingestion of potassium-rich foods may reduce or prevent potassium depletion; however, prophylactic administration of a potassium supplement such as potassium chloride solution or a potassium-sparing diuretic may be necessary in patients whose serum potassium concentration is less than about 3 mEq/L. Enteric-coated potassium-containing tablets should not be used because of the possibility of GI ulceration. /Thiazides/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2163
Hypercalcemia may also occur infrequently in patients receiving thiazides, especially in patients receiving vitamin D or having mild hyperparathyroidism. Hypomagnesemia may also occur. /Thiazides/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2164
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
Used as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. Also used in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effect of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension.
Hydroflumethiazide is an oral thiazide used to treat hypertension and edema. High blood pressure adds to the workload of the heart and arteries. If it continues for a long time, the heart and arteries may not function properly. This can damage the blood vessels of the brain, heart, and kidneys, resulting in a stroke, heart failure, or kidney failure. High blood pressure may also increase the risk of heart attacks. Like other thiazides, Hydroflumethiazide promotes water loss from the body (diuretics). Thiazides inhibit Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue.
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit SODIUM CHLORIDE SYMPORTERS. They act as DIURETICS. Excess use is associated with HYPOKALEMIA. (See all compounds classified as Sodium Chloride Symporter Inhibitors.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03A - Low-ceiling diuretics, thiazides
C03AA - Thiazides, plain
C03AA02 - Hydroflumethiazide
Absorption
Hydroflumethiazide is incompletely but fairly rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
THIAZIDES ARE ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT & OWE THEIR USEFULNESS LARGELY TO THEIR EFFECTIVENESS BY ORAL ROUTE. ABSORPTION IS RELATIVELY RAPID. MOST AGENTS SHOW DEMONSTRABLE DIURETIC EFFECT WITHIN HR AFTER ORAL ADMIN. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
IN GENERAL, THIAZIDES WITH RELATIVELY LONG DURATIONS OF ACTION SHOW PROPORTIONATELY HIGH DEGREE OF BINDING TO PLASMA PROTEINS & ARE REABSORBED BY RENAL TUBULES. ... DRUG PASSES READILY THROUGH PLACENTAL BARRIER TO FETUS. ALL THIAZIDES PROBABLY UNDERGO ACTIVE SECRETION IN PROXIMAL TUBULE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
AFTER IV INFUSION OF HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE, 2 DISTRIBUTION PHASES, T/2 OF 0.26 & 0.85 HR. AFTER SINGLE ORAL DOSE OF 2 UMOL/KG, T/2 BETA SHORTER THAN AFTER DOSE OF 6 UMOL/KG, WITH MEAN T/2 BETA OF 8.7 & 17.9 HR.
PMID:499309 BROERS O, JACOBSEN S; EUR J CLIN PHARMACOL 16 (2): 125 (1979)
AFTER ORAL ADMIN OF HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE EVERY 24 HR FOR 7 DAYS, MEAN BIOL T/2 OF 6.85 HR; MEAN T/2 OF METABOLITE WAS 17.7 HR. 0.652 OF DOSE EXCRETED UNCHANGED IN URINE, 0.049 AS METABOLITE. MEAN RENAL PLASMA CLEARANCE OF DRUG WAS 0.356 L/HR/KG.
PMID:477713 BROERS O, JACOBSEN S; EUR J CLIN PHARMACOL 15 (4): 281 (1979)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Essentially unchanged
AFTER REPEATED ORAL ADMIN OF 100 MG EVERY 24 HR FOR 7 DAYS TO HEALTHY MALES, METABOLITE 2,4-DISULFAMYL-5-TRIFLUOROMETHYLANILINE DETERMINED.
PMID:477713 BROERS O, JACOBSEN S; EUR J CLIN PHARMACOL 15 (4): 281 (1979)
It appears to have a biphasic biological half-life with an estimated alpha-phase of about 2 hours and an estimated beta-phase of about 17 hours
Half-life is 12-27 hr. /From table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 703
/Hydroflumethiazide has a/ estimated distribution half-life of approximately 2 hours and an estimated terminal elimination half-life of approximately 17 hours ... .
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2171
Hydroflumethiazide is a thiazide diuretic that inhibits water reabsorption in the nephron by inhibiting the sodium-chloride symporter (SLC12A3) in the distal convoluted tubule, which is responsible for 5% of total sodium reabsorption. Normally, the sodium-chloride symporter transports sodium and chloride from the lumen into the epithelial cell lining the distal convoluted tubule. The energy for this is provided by a sodium gradient established by sodium-potassium ATPases on the basolateral membrane. Once sodium has entered the cell, it is transported out into the basolateral interstitium via the sodium-potassium ATPase, causing an increase in the osmolarity of the interstitium, thereby establishing an osmotic gradient for water reabsorption. By blocking the sodium-chloride symporter, Hydroflumethiazide effectively reduces the osmotic gradient and water reabsorption throughout the nephron.
...BENZOTHIADIAZIDES HAVE DIRECT EFFECT ON RENAL TUBULAR TRANSPORT OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE...INDEPENDENT OF ANY EFFECT ON CARBONIC ANHYDRASE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 899
NATURE OF CHEM INTERACTION BETWEEN THIAZIDES & SPECIFIC RENAL RECEPTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR CHLORURETIC EFFECT IS NOT KNOWN; NO CRITICAL ENZYMATIC REACTIONS HAVE BEEN IDENTIFIED. /THIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
THIAZIDES INHIBIT REABSORPTION OF SODIUM &...CHLORIDE IN DISTAL SEGMENT. ... AS CLASS...HAVE IMPORTANT ACTION ON EXCRETION OF POTASSIUM THAT RESULTS FROM INCR SECRETION OF CATION BY DISTAL TUBULE. ... GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE MAY BE REDUCED BY THIAZIDES, PARTICULARLY WITH IV ADMIN FOR EXPTL PURPOSES. /THIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
THIAZIDES MAY DECR EXCRETION OF URIC ACID IN MAN, THUS INCR ITS CONCN IN PLASMA. HYPERURICEMIC EFFECT RESULTS PRIMARILY FROM INHIBITION OF TUBULAR SECRETION OF URATE. ... UNLIKE MOST OTHER NATRIURETIC AGENTS...DECR RENAL EXCRETION OF CALCIUM RELATIVE TO THAT OF SODIUM... /ENHANCE/ EXCRETION OF MAGNESIUM... /THIAZIDES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
26
PharmaCompass offers a list of Hydroflumethiazide API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Hydroflumethiazide manufacturer or Hydroflumethiazide supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Hydroflumethiazide manufacturer or Hydroflumethiazide supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Hydroflumethiazide API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Hydroflumethiazide API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Hydroflumethiazide Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Hydroflumethiazide Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Hydroflumethiazide manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Hydroflumethiazide, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Hydroflumethiazide manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Hydroflumethiazide API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Hydroflumethiazide supplier is an individual or a company that provides Hydroflumethiazide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Hydroflumethiazide finished formulations upon request. The Hydroflumethiazide suppliers may include Hydroflumethiazide API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Hydroflumethiazide Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Hydroflumethiazide GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Hydroflumethiazide GMP manufacturer or Hydroflumethiazide GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Hydroflumethiazide CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Hydroflumethiazide's compliance with Hydroflumethiazide specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Hydroflumethiazide CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Hydroflumethiazide CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Hydroflumethiazide may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Hydroflumethiazide EP), Hydroflumethiazide JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Hydroflumethiazide USP).
