
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
VMF
0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
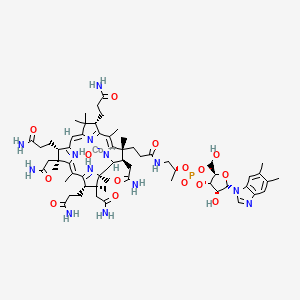

1. Hydroxo-cobalamin
2. Hydroxocobalamin
3. Hydroxycobalamin
1. Hydroxycobalamin
2. Hydroxocobalamin
3. Hydroxycob(lll)alamin
4. 13422-51-0
5. C08230
| Molecular Weight | 1347.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C62H90CoN13O15P |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 20 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 26 |
| Exact Mass | 1346.574890 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1346.574890 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 453 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 92 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 3150 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 13 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cyanokit |
| PubMed Health | Hydroxocobalamin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Cyanide Antidote |
| Drug Label | Hydroxocobalamin, the active ingredient in Cyanokit, is cobinamide dihydroxide dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono (inner salt), 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1--D-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole. The drug substance is the hydroxylated active form of vi.. |
| Active Ingredient | Hydroxocobalamin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5gm/vial (5gm/kit) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Merck Sante Sas |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Hydroxocobalamin |
| PubMed Health | Hydroxocobalamin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Cyanide Antidote |
| Drug Label | Hydroxocobalamin, the active ingredient in Cyanokit, is cobinamide dihydroxide dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono (inner salt), 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1--D-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole. The drug substance is the hydroxylated active form of vi.. |
| Active Ingredient | Hydroxocobalamin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cyanokit |
| PubMed Health | Hydroxocobalamin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Cyanide Antidote |
| Drug Label | Hydroxocobalamin, the active ingredient in Cyanokit, is cobinamide dihydroxide dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono (inner salt), 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1--D-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole. The drug substance is the hydroxylated active form of vi.. |
| Active Ingredient | Hydroxocobalamin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5gm/vial (5gm/kit) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Merck Sante Sas |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Hydroxocobalamin |
| PubMed Health | Hydroxocobalamin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Cyanide Antidote |
| Drug Label | Hydroxocobalamin, the active ingredient in Cyanokit, is cobinamide dihydroxide dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono (inner salt), 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1--D-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole. The drug substance is the hydroxylated active form of vi.. |
| Active Ingredient | Hydroxocobalamin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs |
Hematinics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Cyanokit is indicated for the treatment of known or suspected cyanide poisoning.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 62 ed., Montvale, NJ 2008, p. 1032
Pernicious anemia, both uncomplicated and accompanied by nervous system involvement.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Hydroxocobalamin (February 2006). Available from, as of October 3, 2008: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=6636
The US government considers cyanide to be among the most likely agents of chemical terrorism. Cyanide differs from many other biological or chemical agents for which little or no defense is available because its individual and public health effects are largely remediable through appropriate preparedness and response. Because the toxicity of the cyanide antidote currently available in the United States renders it ill-suited for use in terrorist incidents and other situations requiring rapid out-of-hospital treatment, hydroxocobalamin--an effective and safe cyanide antidote being used in other countries--has been introduced in the United States. Unlike the other available cyanide antidote, hydroxocobalamin can be administered at the scene of a cyanide disaster, and it need not be reserved for cases of confirmed cyanide poisoning but can be administered in cases of suspected poisoning. Both of these attributes facilitate the rapid intervention necessary for saving lives. To realize the potential benefits of hydroxocobalamin, progress also needs to be realized in other aspects of readiness, including but not limited to developing plans for ensuring local and regional availability of antidote, educating emergency responders and health care professionals in the recognition and management of cyanide poisoning, and raising public awareness of the potential for a chemical weapons attack and of how to respond.
PMID:17976798 Eckstein M; J Emerg Med. 2008 Jul;35(1):59-65 (2008)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for HYDROXOCOBALAMIN (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Caution should be exercised when administering other cyanide antidotes simultaneously with Cyanokit, as the safety of coadministration has not been established. If a decision is made to administer another cyanide antidote with Cyanokit, these drugs should not be administered concurrently in the same IV line.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 62 ed., Montvale, NJ 2008, p. 1033
Use caution in the management of patients with known anaphylactic reactions to hydroxocobalamin or cyanocobalamin. Consideration should be given to use of alternative therapies, if available. Allergic reactions may include: anaphylaxis, chest tightness, edema, urticaria, pruritus, dyspnea, and rash. Allergic reactions including angioneurotic edema have also been reported in postmarketing experience.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 62 ed., Montvale, NJ 2008, p. 1033
Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: B12: Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: None. /from Table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 140 (1994)
While determination of blood cyanide concentration is not required for management of cyanide poisoning and should not delay treatment with Cyanokit, collecting a pretreatment blood sample may be useful for documenting cyanide poisoning as sampling post- Cyanokit use may be inaccurate.
Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 62 ed., Montvale, NJ 2008, p. 1033
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for HYDROXOCOBALAMIN (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Treatment of known or suspected cyanide poisoning.
Cyanokit is to be administered together with appropriate decontamination and supportive measures.
Hematinics
Agents which improve the quality of the blood, increasing the hemoglobin level and the number of erythrocytes. They are used in the treatment of anemias. (See all compounds classified as Hematinics.)
Vitamin B Complex
A group of water-soluble vitamins, some of which are COENZYMES. (See all compounds classified as Vitamin B Complex.)
V03AB33
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B03 - Antianemic preparations
B03B - Vitamin b12 and folic acid
B03BA - Vitamin b12 (cyanocobalamin and analogues)
B03BA03 - Hydroxocobalamin
V - Various
V03 - All other therapeutic products
V03A - All other therapeutic products
V03AB - Antidotes
V03AB33 - Hydroxocobalamin
The possibility of direct transport of hydroxocobalamin from the nasal cavity into the cerebrospinal fluid after nasal administration in rats was investigated and the results were compared with a human study. Hydroxocobalamin was given to rats (n=8) both intranasally (214 ug/rat) and intravenously (49.5 ug/rat) into the jugular vein using a Vascular Access Port (VAP). Prior to and after drug administration, blood and cerebrospinal fluid samples were taken and analysed by radioimmunoassay. The AUCcerebrospinal fluid/AUCplasma ratio after nasal delivery does not differ from the ratio after intravenous infusion, indicating that hydroxocobalamin enters the cerebrospinal fluid via the blood circulation across the blood-brain barrier (BBB). This same transport route is confirmed by the cumulative AUC-time profiles in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma, demonstrating a 30 min delay between plasma absorption and cerebrospinal fluid uptake of hydroxocobalamin in rats and in a comparative human study. The present results in rats show that there is no additional uptake of hydroxocobalamin in the cerebrospinal fluid after nasal delivery compared to intravenous administration, which is in accordance with the results found in humans.
PMID:14668053 Van den Berg MP et al; J Drug Target 11 (6): 325-31 (2003)
Fifty percent of the administered dose of hydroxocobalamin disappears from the injection site in 2.5 hours. Hydroxocobalamin is bound to plasma proteins and stored in the liver. It is excreted in the bile and undergoes some enterohepatic recycling. Within 72 hours after injection of 500 to 1000 mcg of hydroxocobalamin, 16 to 66 percent of the injected dose may appear in the urine. The major portion is excreted within the first 24 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Hydroxocobalamin (February 2006). Available from, as of October 3, 2008: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=6636
Hydroxocobalamin is absorbed more slowly from the site of injection than is cyanocobalamin and there is some evidence that liver uptake of hydroxocobalamin may be greater than that of cyanocobalamin. It is believed that the increased retention of hydroxocobalamin compared with that of cyanocobalamin results from the greater affinity of hydroxocobalamin for both specific and nonspecific binding proteins in blood and tissues, as well as to its slower absorption from the injection site.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists. AHFS Drug Information 2008. Bethesda, Maryland 2008
In the presence of gastric acid and pancreatic proteases, dietary vitamin B12 is released from food and salivary binding protein and bound to gastric intrinsic factor. When the vitamin B12-intrinsic factor complex reaches the ileum, it interacts with a receptor on the mucosal cell surface and is actively transported into circulation. Adequate intrinsic factor, bile, and sodium bicarbonate (to provide a suitable pH) all are required for ileal transport of vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 deficiency in adults is rarely the result of a deficient diet per se; rather, it usually reflects a defect in one or another aspect of this complex sequence of absorption. Achlorhydria and decreased secretion of intrinsic factor by parietal cells secondary to gastric atrophy or gastric surgery is a common cause of vitamin B12 deficiency in adults. Antibodies to parietal cells or intrinsic factor complex also can play a prominent role in producing a deficiency. A number of intestinal diseases can interfere with absorption, including pancreatic disorders (loss of pancreatic protease secretion), bacterial overgrowth, intestinal parasites, sprue, and localized damage to ileal mucosal cells by disease or as a result of surgery. /Vitamin B-12/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 11th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2006., p. 1454-5
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for HYDROXOCOBALAMIN (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Toxicokinetics of hydroxocobalamin were studied in rats and in dogs after single administration. In dogs, the AUCs of free cobalamins-(III) and total cobalamins-(III) increased proportionally to the dose. Mean Cmax measured for free- and total cobalamins-(III) were 1 to 5 fold higher than those measured in humans treated with 5.0 and 10.0 g hydroxocobalamin. Terminal half-lives reached approximately 6 and 8 hours for free and total cobalamins-(III), respectively in dogs. Corresponding figures in rats amounted to 3 and 5 hours. In dogs, the clearance of total cobalamins-(III) (0.064 to 0.083 L/h/kg) was 6-7 fold lower than clearance of free cobalamins-(III).
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) for Authorized Medicinal Products for Human Use; Cyanokit, Scientific Discussion (2007). Available from, as of November 24, 2008: https://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/cyanokit/cyanokit.htm
The binding of hydroxocobalamin to proteins may be regarded as reversible metabolism. Hydroxocobalamin also reacts with cyanide thereby forming cyanocobalamin. This complex is highly stable and is therefore regarded as a physiological end product of hydroxocobalamin especially during cyanide intoxication.
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) for Authorized Medicinal Products for Human Use; Cyanokit, Scientific Discussion (2007). Available from, as of November 24, 2008: https://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/cyanokit/cyanokit.htm
In normal individuals, hydroxocobalamin has a plasma half life of 3-20 hours. In patients with cyanide poisoning, the half life is 14-24 hours.
Olson, K.R. (Ed.); Poisoning & Drug Overdose. 5th ed. Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. New York, N.Y. 2007., p. 459
Hydroxocobalamin is a complexation agent that acts by direct binding of the cyanide ions, resulting in cyanocobalamin which is a highly stable, nontoxic compound that is excreted in the urine. In addition, increased blood pressure observed in some healthy subjects of the phase I clinical study and results of a non-clinical study performed in anesthetized rabbits suggest an interference of hydroxocobalamin with the NO system.
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) for Authorized Medicinal Products for Human Use; Cyanokit, Scientific Discussion (2007). Available from, as of November 24, 2008: https://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/cyanokit/cyanokit.htm
VITAMIN B12 IS IMPLICATED IN PROTEIN SYNTH THROUGH ITS ROLE IN SYNTH OF AMINE ACID METHIONINE... /COBALAMINS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1329
COENZYME B12 IS REQUIRED FOR HYDROGEN TRANSFER & ISOMERIZATION WHEREBY METHYLMALONATE IS CONVERTED TO SUCCINATE, THUS INVOLVING COBALAMIN IN BOTH FAT & CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM. ... METHYLCOBALAMIN IS REQUIRED FOR CONVERSION OF HOMOCYSTEINE TO METHIONINE IN MAMMALS. /COBALAMINS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1329

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
71
PharmaCompass offers a list of Hydroxocobalamin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Hydroxocobalamin manufacturer or Hydroxocobalamin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Hydroxocobalamin manufacturer or Hydroxocobalamin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Hydroxocobalamin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Hydroxocobalamin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Hydroxocobalamin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Hydroxocobalamin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Hydroxocobalamin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Hydroxocobalamin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Hydroxocobalamin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Hydroxocobalamin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Hydroxocobalamin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Hydroxocobalamin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Hydroxocobalamin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Hydroxocobalamin finished formulations upon request. The Hydroxocobalamin suppliers may include Hydroxocobalamin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Hydroxocobalamin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Hydroxocobalamin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Hydroxocobalamin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Hydroxocobalamin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Hydroxocobalamin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Hydroxocobalamin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Hydroxocobalamin USDMF includes data on Hydroxocobalamin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Hydroxocobalamin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Hydroxocobalamin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Hydroxocobalamin Drug Master File in Japan (Hydroxocobalamin JDMF) empowers Hydroxocobalamin API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Hydroxocobalamin JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Hydroxocobalamin JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Hydroxocobalamin suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Hydroxocobalamin Drug Master File in Korea (Hydroxocobalamin KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Hydroxocobalamin. The MFDS reviews the Hydroxocobalamin KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Hydroxocobalamin KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Hydroxocobalamin KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Hydroxocobalamin API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Hydroxocobalamin suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Hydroxocobalamin written confirmation (Hydroxocobalamin WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Hydroxocobalamin manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Hydroxocobalamin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Hydroxocobalamin APIs or Hydroxocobalamin finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Hydroxocobalamin WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Hydroxocobalamin suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Hydroxocobalamin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Hydroxocobalamin API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Hydroxocobalamin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Hydroxocobalamin and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Hydroxocobalamin NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Hydroxocobalamin suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Hydroxocobalamin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Hydroxocobalamin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Hydroxocobalamin GMP manufacturer or Hydroxocobalamin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Hydroxocobalamin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Hydroxocobalamin's compliance with Hydroxocobalamin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Hydroxocobalamin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Hydroxocobalamin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Hydroxocobalamin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Hydroxocobalamin EP), Hydroxocobalamin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Hydroxocobalamin USP).
