


1. Anaspaz
2. Atropine Sulfate, 3(s)-endo-isomer
3. Atropine, 3(s)-endo-isomer
4. Cytospaz
5. Hyoscyamine
6. Hyoscyamine Hydrobromide
7. Hyoscyamine Hydrochloride
8. Hyoscyamine Sulfate
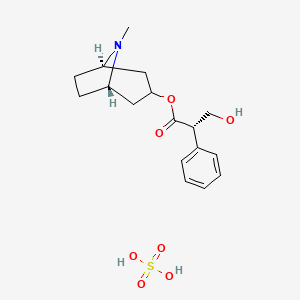
9. Hyoscyamine Sulfate Anhydrous
1. Hyoscyamine Sulfate
2. Schembl34273
3. Chembl1697729
| Molecular Weight | 387.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H25NO7S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 387.13517331 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 387.13517331 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 133 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 434 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Adjuvants, Anesthesia
Agents that are administered in association with anesthetics to increase effectiveness, improve delivery, or decrease required dosage. (See all compounds classified as Adjuvants, Anesthesia.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Bronchodilator Agents
Agents that cause an increase in the expansion of a bronchus or bronchial tubes. (See all compounds classified as Bronchodilator Agents.)
Muscarinic Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous ACETYLCHOLINE or exogenous agonists. Muscarinic antagonists have widespread effects including actions on the iris and ciliary muscle of the eye, the heart and blood vessels, secretions of the respiratory tract, GI system, and salivary glands, GI motility, urinary bladder tone, and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Muscarinic Antagonists.)
Mydriatics
Agents that dilate the pupil. They may be either sympathomimetics or parasympatholytics. (See all compounds classified as Mydriatics.)
Parasympatholytics
Agents that inhibit the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system. The major group of drugs used therapeutically for this purpose is the MUSCARINIC ANTAGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Parasympatholytics.)

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?
