
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz

1. Hmovannad
2. Hexanicit
3. Hexopal
4. Inositol Hexanicotinate
5. Inositol Nicotinate
6. Inositolniacinate
7. Meso-inositol Hexanicotinate
8. Nicolip
9. Palohex
10. Phorilingual
11. Tolanate
1. Inositol Nicotinate
2. 6556-11-2
3. Inositol Hexanicotinate
4. Mesotal
5. Dilexpal
6. Hexanicotol
7. Myo-inositol Hexanicotinate
8. Hexanicit
9. Esantene
10. Dilcit
11. Mesonex
12. Hexanicotinoyl Inositol
13. Hexopal
14. Linodil
15. Palohex
16. Inositoli Nicotinas
17. Win 9154
18. Hamovannad
19. Hamovannid
20. Inositol Niacinate [usan]
21. Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexayl Hexanicotinate
22. Myo-inositol, Hexa-3-pyridinecarboxylate
23. Nsc-49506
24. Inositol Nicotinate [inn]
25. [2,3,4,5,6-pentakis(pyridine-3-carbonyloxy)cyclohexyl] Pyridine-3-carboxylate
26. A99mk953kz
27. Chebi:31699
28. 1,2,3,5/4,6 Cyclohexanehexol Hexanicotinate
29. Nsc49506
30. Win-9154
31. Inositol Nicotinate (inn)
32. Inositol Niacinate (usan)
33. Rel-(1r,2r,3s,4r,5s,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexayl Hexanicotinate
34. Inositol Hexanicotinate (jan)
35. Inositol Hexanicotinate [jan]
36. (1r,2r,3s,4s,5r,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexayl Hexanicotinate
37. Nicotinato De Inositol
38. Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexayl Hexapyridine-3-carboxylate
39. Inositolo Nicotinato [dcit]
40. Inositoli Nicotinas [inn-latin]
41. Nicotinic Acid, With 1,2-trans, 3-cis, 4-trans, 5-cis, 6-cis-cyclohexanehexol
42. Inositolo Nicotinato
43. Einecs 229-485-9
44. Nicotinate D'inositol [inn-french]
45. Palohex (tn)
46. Inositol, Hexanicotinate, Myo-
47. Nsc 49506
48. Nicotinate D'inositol
49. Nicotinato De Inositol [inn-spanish]
50. Inositol-hexanicotinate
51. Myo-inosithexanicotinat
52. Brn 0077649
53. Mesoinositol Hexanicotinate
54. 1,2,3,54,6 Cyclohexanehexol Hexanicotinate
55. Unii-a99mk953kz
56. Schembl122590
57. Schembl122591
58. Inositol Niacinate [mi]
59. Chembl1094982
60. Dtxsid2023147
61. Schembl13557040
62. Chebi:33064
63. Dtxsid10859980
64. Inositol Nicotinate [mart.]
65. Nsc81283
66. Zinc3830930
67. Inositol Nicotinate [who-dd]
68. Mfcd00006387
69. Nsc-81283
70. S4987
71. Akos015951374
72. Akos015960653
73. Zinc150338506
74. Ac-8131
75. Db08949
76. Ncgc00532507-01
77. 497820-05-0
78. As-13351
79. Hy-122365
80. Cs-0084450
81. Ft-0627238
82. Ft-0627239
83. D01813
84. D70660
85. 5-22-02-00067 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
86. A914042
87. Sr-01000883744
88. Q6036641
89. Sr-01000883744-1
90. Brd-k00566342-001-01-0
91. 2,3,4,5,6-pentakis((3-pyridinylcarbonyl)oxy)cyclohexyl Nicotinate
92. 3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid, 1,2,3,4,5,6-cyclohexanehexayl Ester
93. (1r,2r,3s,4r,5s,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexayl Hexanicotinate
94. Rel-(1r,2r,3s,4r,5s,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaylhexanicotinate
95. Nicotinic Acid, Ester, With 1,2-trans, 3-cis, 4-trans, 5-cis, 6-cis-cyclohexanehexol
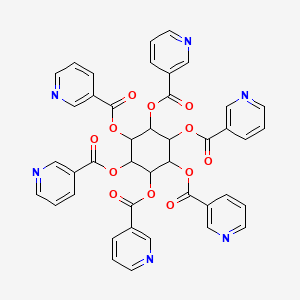
| Molecular Weight | 810.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C42H30N6O12 |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 18 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 18 |
| Exact Mass | 810.19217041 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 810.19217041 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 235 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 60 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1210 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated as a dietary supplement for the source of niacin. Has been investigated for potential beneficial effects on serum lipids. In Europe, inositol hexanicotinate is indicated as a patented drug known as Hexopal, which is therapeutically indicated for the symptomatic relief of severe intermittent claudication and Raynauds phenomenon.
Inositol nicotinate mediates a vasodilatory, lipid-lowering and fibrinolytic effect on the cardiovascular system. Like other niacins, inositol nicotinate is a lipid-regulating agent that reduces the levels of plasma triglycerides, atherogenic apolipoprotein B (apoB)-containing lipoproteins (VLDL, LDL and lipoprotein a) while increasing antiatherogenic apoA-I-containing HDL levels.
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C04 - Peripheral vasodilators
C04A - Peripheral vasodilators
C04AC - Nicotinic acid and derivatives
C04AC03 - Inositol nicotinate
Absorption
Gastrointestinal absorption of inositol hexanicotinate varies widely, with an average of 70% of an orally ingested dose absorbed from stomach and upper small intestines into the bloodstream as intact form. The maximum serum levels of nicotinic acid is reached approximately 6-10 hours after oral ingestion. At low concentrations, the absorption of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide is mediated by sodium ion-dependent facilitated diffusion. At higher concentrations, passive diffusion predominates with doses of 3 to 4 g of niacin being almost completely absorbed.
Route of Elimination
Unabsorbed inositol nicotinate is detected in feces.
Volume of Distribution
Mean Vd following intravenous administration of 50mg/kg of inositol nicotinate in rats is 1051250 mL/kg.
Clearance
Mean clearance rate following intravenous administration of 50mg/kg of inositol nicotinate in rats is 65.419 mL/min/kg.
Inositol nicotinate undergoes hydrolysis by plasma esterases, releasing free nicotinic acid and inositol in a sustained manner. The process takes more than 48hours, where the bloodstream enzymatic hydrolysis of inositol hexanicotinate was found to be slower in the first ester linkage of inositol hexanicotinate than in subsequent linkages. Sequential hydrolytic steps of inositol nicotinate forms one nicotinic acid molecule in each step, producing eventually six molecules of nicotinic acid and one inositol moiety.
Mean elimination half life in healthy human adults is approximately one hour.
Inositol nicotinate and other niacins directly and noncompetitively inhibit microsomal enzyme diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) responsible for esterification of fatty acids to form triglycerides, resulting in decreased triglyceride synthesis and hepatic atherogenic lipoprotein secretion. Inhibitied triglyceride synthesis results in accelerated intracellular hepatic apo B degradation and the decreased secretion of VLDL and LDL particles. Niacin also inhibits hepatic expression of beta-chain adenosine triphosphate synthase which inhibits the removal or uptake of HDLapo A-I. It is also suggested that niacin increases vascular endothelial cell redox state, resulting in the inhibition of oxidative stress and vascular inflammatory genes or key cytokines involved in atherosclerosis. It acts as a ligand on G-protein coupled receptor 109A (HCAR2/HM74A) and 109B (HCAR3/HM74) which mediates the anti-lipolytic and lipid-lowering effects of nicotinic acid. Niacin-mediated signalling of GPR109A expressed on adipocytes and G(i)-mediated decrease in cAMP levels result in decreased lipolysis, fatty acid mobilization, and triglyceride synthesis. The action of inositol nicotinate on GPR109A expressed on skin and macrophages to cause increased prostaglandin D2/E2 activity is thought to be less significant compared to other niacin molecules as it involves sustained release that leads to less flushing.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
63
PharmaCompass offers a list of Inositol niacinate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Inositol niacinate manufacturer or Inositol niacinate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Inositol niacinate manufacturer or Inositol niacinate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Inositol niacinate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Inositol niacinate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Inositol niacinate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Inositol niacinate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Inositol niacinate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Inositol niacinate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Inositol niacinate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Inositol niacinate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Inositol niacinate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Inositol niacinate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Inositol niacinate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Inositol niacinate finished formulations upon request. The Inositol niacinate suppliers may include Inositol niacinate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Inositol niacinate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Inositol niacinate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Inositol niacinate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Inositol niacinate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Inositol niacinate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Inositol niacinate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Inositol niacinate USDMF includes data on Inositol niacinate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Inositol niacinate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Inositol niacinate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Inositol niacinate written confirmation (Inositol niacinate WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Inositol niacinate manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Inositol niacinate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Inositol niacinate APIs or Inositol niacinate finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Inositol niacinate WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Inositol niacinate suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
Inositol niacinate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Inositol niacinate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Inositol niacinate GMP manufacturer or Inositol niacinate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Inositol niacinate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Inositol niacinate's compliance with Inositol niacinate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Inositol niacinate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Inositol niacinate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Inositol niacinate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Inositol niacinate EP), Inositol niacinate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Inositol niacinate USP).
