
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
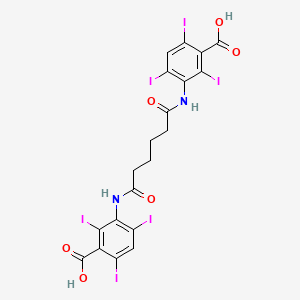

1. Adipiodon
2. Bilignost
3. Biligrafine
4. Bilipolinum
5. Cholografin
6. Endocistobil
7. Endographin
1. Adipiodone
2. 606-17-7
3. Iodipamic Acid
4. Cholografin
5. Bilignost
6. Bilignostum
7. Cholospect
8. Biligrafin
9. Transbilix
10. Adipiodona
11. Adipiodonum
12. Adipiodonum [inn-latin]
13. Adipiodona [inn-spanish]
14. 3,3'-[(1,6-dioxohexane-1,6-diyl)diimino]bis(2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid)
15. 3,3'-(adipoyldiimino)bis(2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid)
16. Adipiodone [inn]
17. 3-[[6-(3-carboxy-2,4,6-triiodoanilino)-6-oxohexanoyl]amino]-2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid
18. Adipiodon
19. Tkq858a3vw
20. Iodipamide Meglumine
21. Benzoic Acid, 3,3'-((1,6-dioxo-1,6-hexanediyl)diimino)bis(2,4,6-triiodo-
22. Nsc-757423
23. 3-[5-[(3-carboxy-2,4,6-triiodo-phenyl)carbamoyl]pentanoylamino]-2,4,6-triiodo-benzoic Acid
24. Ncgc00016523-03
25. Cas-606-17-7
26. Dsstox_cid_3153
27. Benzoic Acid, 3,3'-[(1,6-dioxo-1,6-hexanediyl)diimino]bis[2,4,6-triiodo-
28. Dsstox_rid_76893
29. Adipic Acid Di(3-carboxy-2,4,6-triiodoanilide)
30. Dsstox_gsid_23153
31. 3,3-adipoyldiiminobis(2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid)
32. Iodipamide (usp)
33. Adipiodone (jan/inn)
34. Iodipamide [usp:inn]
35. Einecs 210-105-5
36. Unii-tkq858a3vw
37. Biligrafine
38. Brn 2230896
39. N,n''-adipoyl-bis(3-amino-2,4,6-triiodbenzoesaeure)
40. Hsdb 8066
41. Starbld0009605
42. Iodipamide (adipiodone)
43. Iodipamide [mi]
44. Adipiodone [jan]
45. Prestwick0_000939
46. Prestwick1_000939
47. Prestwick2_000939
48. Prestwick3_000939
49. Adipiodone [mart.]
50. Adipiodone [who-dd]
51. Iodipamide [usp-rs]
52. Schembl37678
53. Bspbio_000878
54. 4-14-00-01122 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
55. Mls001066414
56. 3,3'-adipoyldiiminobis(2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid)
57. Spbio_003047
58. 3,3'(adipoyldiimino)bis(2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid)
59. Bpbio1_000966
60. Gtpl7400
61. Benzoic Acid, 3,3'-(adipoyldiimino)bis(2,4,6-triiodo-
62. Chembl1165268
63. Dtxsid6023153
64. Chebi:31176
65. Hms1570l20
66. Hms2097l20
67. Hms2232c09
68. Hms3370i13
69. Hms3714l20
70. Iodipamide [usp Monograph]
71. Hy-b1292
72. Tox21_113504
73. Mfcd00058983
74. Akos015964892
75. Tox21_113504_1
76. Ccg-220939
77. Db04711
78. Nsc 757423
79. Ncgc00016523-01
80. Ncgc00016523-02
81. Ncgc00016523-04
82. Ncgc00016523-05
83. Smr000471884
84. Db-053672
85. Ab00513970
86. Cs-0013062
87. Ft-0627253
88. I0299
89. D01774
90. Iodipamide, Analytical Standard, For Drug Analysis
91. Sr-01000760542
92. Q4682934
93. Sr-01000760542-2
94. Brd-k67261995-001-03-4
95. Iodipamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
96. 3-{5-[(3-carboxy-2,4,6-triiodophenyl)carbamoyl]pentanamido}-2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid
97. 3-[[6-[(3-carboxy-2,4,6-triiodophenyl)amino]-6-oxohexanoyl]amino]-2,4,6-triiodobenzoic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 1139.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H14I6N2O6 |
| XLogP3 | 5.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 1139.5120 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1139.5120 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 133 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 714 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Contrast Media
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Cholografin Meglumine is indicated for intravenous cholangiography and cholecystography as follows: (a) visualization of the gallbladder and biliary ducts in the differential diagnosis of acute abdominal conditions, (b) visualization of the biliary ducts, especially in patients with symptoms after cholecystectomy, and (c) visualization of the gallbladder in patients unable to take oral contrast media or to absorb contrast media from the gastrointestinal tract. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for cholografin meglumine (Iodipamide Meglumine) injection, solution (June 2008). Available from, as of July 9, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=430c343b-bad6-4584-8c63-05bca0b203a2
THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Diagnostic aid (radiopaque medium-cholecystographic)
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 873
THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY (VETERINARY): Diagnostic aid (radiopaque medium)
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 873
Iodipamide meglumine is contraindicated for use in intrathecal procedures.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for cholografin meglumine (Iodipamide Meglumine) injection, solution (June 2008). Available from, as of July 9, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=430c343b-bad6-4584-8c63-05bca0b203a2
Iodipamide meglumine is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to salts of iodipamide or who exhibit sensitivity reactions to the test dose. It is also contraindicated in patients with concomitant severe impairment of renal and liver function.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for cholografin meglumine (Iodipamide Meglumine) injection, solution (June 2008). Available from, as of July 9, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=430c343b-bad6-4584-8c63-05bca0b203a2
Serious adverse reactions have been reported due to the inadvertent intrathecal administration of iodinated contrast media that are not indicated for intrathecal use. These serious adverse reactions include: death, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema. Special attention must be given to insure that this drug product is not inadvertently administered intrathecally.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for cholografin meglumine (Iodipamide Meglumine) injection, solution (June 2008). Available from, as of July 9, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=430c343b-bad6-4584-8c63-05bca0b203a2
The possibility exists for inadvertent administration into the intrathecal space during epidural administrations. Therefore, epidural administration procedures, such as pain management catheter placement, should not be performed with use of this product.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for cholografin meglumine (Iodipamide Meglumine) injection, solution (June 2008). Available from, as of July 9, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=430c343b-bad6-4584-8c63-05bca0b203a2
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Iodipamide (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Iodipamide is used as a contrast agent for cholecystography and intravenous cholangiography.
Following intravenous administration of Cholografin Meglumine, iodipamide is carried to the liver where it is rapidly secreted. The contrast medium appears in the bile within 10 to 15 minutes after injection, thus permitting visualization of the hepatic and common bile ducts, even in cholecystectomized patients. The biliary ducts are readily visualized within about 25 minutes after administration, except in patients with impaired liver function. The gallbladder begins to fill within an hour after injection; maximum filling is reached after two to two and one-half hours. The contrast medium is finally eliminated in the feces without passing through the enterohepatic circulation, except for approximately 10 percent of the intravenously administered dose which is excreted through the kidneys.
Contrast Media
Substances used to allow enhanced visualization of tissues. (See all compounds classified as Contrast Media.)
V - Various
V08 - Contrast media
V08A - X-ray contrast media, iodinated
V08AC - Watersoluble, hepatotropic x-ray contrast media
V08AC04 - Adipiodone
To characterize the saturation kinetics of iodipamide, timed samples of blood, urine, and bile were taken from two unanesthetized dogs infused with iodipamide at increasing rates to achieve various steady state blood concentrations. Biliary excretion rate of iodipamide reached an asymptote with increasing blood concentration, indicating a biliary transport maximum (Tm) of 15.2 to 16.2 mgI/min. Urinary excretion was not a pure, first order process and urinary excretion rate was higher than the glomerular filtration rate corrected for plasma protein binding, suggesting that active tubular secretion may play a part. Extrarenal elimination followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Estimates of maximum rate (Vm) and Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) were obtained graphically. The estimated values of Vm were 4 to 6 times that of biliary Tm. In acute infusion experiments the iodipamide excreted in the bile and urine and that remaining in the organs analyzed accounted for only a fraction of the dose administered; no significant accumulation of iodipamide was found in the liver.
PMID:856758 Lin SK et al; Invest Radiol 12 (2): 175-9 (1977)
The contrast agent for biliary tract visualization, iodipamide, is strongly bound to serum albumin. The relationship between the affinity of the contrast agent for albumin and its preferential uptake and excretion by the liver has been unclear. The role of serum albumin on hepatic uptake and excretion of iodipamide therefore was investigated on the isolated perfused rabbit liver. With the perfusate containing fully reconstituted rabbit plasma protein or 3.5 g/100 mL rabbit albumin alone, the iodipamide excretion is initially extremely slow. It then increases gradually to about 6 mug/gm liver per min by 60 minutes and thereafter remains constant. The half-time of transfer to the bile is about 130 min. Without albumin in the perfusate the initial clearance rate of iodipamide is rapid, with half-time transfer to the bile of about 40 min. Rabbit serum globulins have no effect on iodipamide excretion. Thus, binding of iodipamide to albumin retards the transfer of iodipamide from plasma to the bile, probably due to competition between albumin and the anion binding protein of the liver.
PMID:1254421 Song CS et al; Invest Radiol 11 (1): 39-44 (1976)
The contrast medium is eliminated in the feces without passing through the enterohepatic circulation, except for approximately 10 percent of the intravenously administered dose which is excreted through the kidneys.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for cholografin meglumine (Iodipamide Meglumine) injection, solution (June 2008). Available from, as of July 9, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=430c343b-bad6-4584-8c63-05bca0b203a2
Hepatic.
Organic iodine compounds block x-rays as they pass through the body, thereby allowing body structures containing iodine to be delineated in contrast to those structures that do not contain iodine. The degree of opacity produced by these iodinated organic compounds is directly proportional to the total amount (concentration and volume) of the iodinated contrast agent in the path of the x-rays. Iodipamide's primary excretion through the hepato-biliary system and concentration in bile allows visualization of the gallbladder and biliary ducts.
... The iodine in the contrast medium is responsible for the absorption of x-rays and the resulting opacification of the organ system or other area under investigation. ...
PMID:3902331 Swanson DP et al; Clin Pharm 4 (5): 527-38 (1985)
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
14
PharmaCompass offers a list of Iodipamide API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Iodipamide manufacturer or Iodipamide supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Iodipamide manufacturer or Iodipamide supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Iodipamide API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Iodipamide API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Iodipamide Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Iodipamide Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Iodipamide manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Iodipamide, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Iodipamide manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Iodipamide API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Iodipamide supplier is an individual or a company that provides Iodipamide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Iodipamide finished formulations upon request. The Iodipamide suppliers may include Iodipamide API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Iodipamide suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Iodipamide DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Iodipamide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Iodipamide DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Iodipamide USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Iodipamide DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Iodipamide USDMF includes data on Iodipamide's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Iodipamide USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Iodipamide suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
Iodipamide Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Iodipamide GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Iodipamide GMP manufacturer or Iodipamide GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Iodipamide CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Iodipamide's compliance with Iodipamide specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Iodipamide CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Iodipamide CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Iodipamide may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Iodipamide EP), Iodipamide JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Iodipamide USP).

