
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
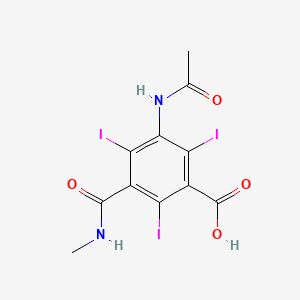

1. Acid, Iotalamic
2. Acid, Iothalamic
3. Acid, Methalamic
4. Angio Conray
5. Angio-conray
6. Angioconray
7. Conray 420
8. Iodothalamate
9. Iothalamate
10. Iothalamate, Sodium
11. Iothalamic Acid
12. Iothalamic Acid, Calcium (2:1) Salt
13. Iothalamic Acid, Monosilver (1+) Salt
14. Iothalamic Acid, Monosodium Salt
15. Iothalamic Acid, Monosodium Salt, Dimer
16. Lopamidol
17. Methalamic Acid
18. Sodium Iothalamate
1. Iothalamic Acid
2. 2276-90-6
3. 3-acetamido-2,4,6-triiodo-5-(methylcarbamoyl)benzoic Acid
4. 5-acetamido-2,4,6-triiodo-n-methylisophthalamic Acid
5. Iotalamic Acid [inn]
6. Mi-216
7. Nsc-759891
8. 16chd79mix
9. 3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-[(methylamino)carbonyl]benzoic Acid
10. Acidum Jotalamicum
11. Acido Iotalamico
12. Iothalamic Acid [usan]
13. Acide Iotalamique
14. Acidum Iotalamicum
15. Acide Iotalamique [inn-french]
16. Acido Iotalamico [inn-spanish]
17. Acidum Iotalamicum [inn-latin]
18. Einecs 218-897-4
19. Mi 216
20. Unii-16chd79mix
21. Iothalamic Acid [usan:usp]
22. Iothalamic-acid-d3
23. Benzoic Acid, 3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-((methylamino)carbonyl)-
24. Iothalamic Acid (usp)
25. Ec 218-897-4
26. Iothalamate [vandf]
27. Schembl38419
28. Iotalamic Acid [jan]
29. Iothalamic Acid [mi]
30. Iotalamic Acid (jp17/inn)
31. Iothalamicacid(200mg)
32. Iotalamic Acid [mart.]
33. Chembl1201300
34. Dtxsid5023164
35. Iotalamic Acid [who-dd]
36. Schembl23630220
37. Chebi:31713
38. Iothalamic Acid [usp-rs]
39. Hms3264d13
40. Pharmakon1600-01503836
41. Bcp13316
42. Hy-b1053
43. Zinc3830961
44. Iotalamic Acid [ep Impurity]
45. Nsc759891
46. Akos025402283
47. Benzoic Acid,3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-[(methylamino)carbonyl]-
48. Ac-7611
49. Ccg-213208
50. Cs-4575
51. Db09133
52. Iothalamic Acid [usp Monograph]
53. Nsc 759891
54. Ncgc00183042-01
55. Ft-0740526
56. D01258
57. Ab01563288_01
58. 276i906
59. Sr-01000944232
60. Q-201246
61. Q6064129
62. Sr-01000944232-1
63. 5-acetylamino-2,4,6-triiodo-n-methyl-isophthalamic Acid
64. 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-d-glucitol 5-acetamido-2,4,6 Triiodo-n-methylisophthalamate
65. Benzoic Acid, 3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-((methylamino)carbonyl
| Molecular Weight | 613.91 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H9I3N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 613.7696 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 613.7696 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 421 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Conray is indicated for use in excretory urography, cerebral angiography, peripheral arteriography, venography, arthrography, direct cholangiography, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, contrast enhancement of computed tomographic brain images, cranial computerized angiotomography, intravenous digital subtraction angiography and arterial digital subtraction angiography. Conray may also be used for enhancement of computed tomographic scans performed for detection and evaluation of lesions in the liver, pancreas, kidneys, abdominal aorta, mediastinum, abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Contrast Media
Substances used to allow enhanced visualization of tissues. (See all compounds classified as Contrast Media.)
V - Various
V08 - Contrast media
V08A - X-ray contrast media, iodinated
V08AA - Watersoluble, nephrotropic, high osmolar x-ray contrast media
V08AA04 - Iotalamic acid
Absorption
Renal accumulation is sufficiently rapid that maximum radiographic density in the calyces and pelves occurs, in most instances, about 3 to 8 minutes after injection. In patients with impaired renal function, diagnostic opacification frequently is achieved only after prolonged periods.
Route of Elimination
Following intravascular injection, Conray is rapidly transported through the circulatory system to the kidneys and is excreted unchanged in the urine by glomerular filtration. The liver and small intestine provide the major alternate route of excretion. In patients with severe renal impairment, the excretion of this contrast medium through the gallbladder and into the small intestine sharply increases.
In patients with normal renal function, the alpha and beta half-lives of Conray were approximately 10 and 90 minutes, respectively.
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
93
PharmaCompass offers a list of Iotalamic Acid API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Iotalamic Acid manufacturer or Iotalamic Acid supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Iotalamic Acid manufacturer or Iotalamic Acid supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Iotalamic Acid API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Iotalamic Acid API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Iotalamic Acid Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Iotalamic Acid Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Iothalamic Acid manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Iothalamic Acid, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Iothalamic Acid manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Iothalamic Acid API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Iothalamic Acid manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Iothalamic Acid supplier is an individual or a company that provides Iothalamic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Iothalamic Acid finished formulations upon request. The Iothalamic Acid suppliers may include Iothalamic Acid API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Iothalamic Acid suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Iothalamic Acid DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Iothalamic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Iothalamic Acid DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Iothalamic Acid USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Iothalamic Acid DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Iothalamic Acid USDMF includes data on Iothalamic Acid's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Iothalamic Acid USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Iothalamic Acid suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Iothalamic Acid as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Iothalamic Acid API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Iothalamic Acid as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Iothalamic Acid and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Iothalamic Acid NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Iothalamic Acid suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Iothalamic Acid Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Iothalamic Acid GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Iothalamic Acid GMP manufacturer or Iothalamic Acid GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Iothalamic Acid CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Iothalamic Acid's compliance with Iothalamic Acid specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Iothalamic Acid CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Iothalamic Acid CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Iothalamic Acid may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Iothalamic Acid EP), Iothalamic Acid JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Iothalamic Acid USP).
