Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
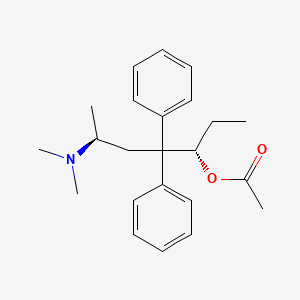

1. (3r,6r)-3-acetoxy-6-dimethylamino-4,4-diphenylheptane
2. 6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenyl-3-heptanol Acetate
3. Acemethadone
4. Acetylmethadol
5. Alphacetylmethadol
6. Amidolacetate
7. Dimepheptanol
8. Laam
9. Levo Alpha Acetylmethadol
10. Levo-alpha-acetylmethadol
11. Levoacetylmethadol
12. Levomethadyl
13. Levomethadyl Acetate Hydrochloride
14. Methadol
15. Methadyl Acetate
16. Orlaam
1. Levacetylmethadol
2. Laam
3. Levo-alphacetylmethadol
4. Levomethadyl
5. Orlaam
6. 1-alpha-acetylmethadol
7. Levo-methadyl Acetate
8. 1477-40-3
9. (-)-alpha-acetylmethadol
10. Levo-alpha-acetylmethadol
11. Levacetilmetadol
12. Alpha-l-acetylmethadol
13. Levacetylmethadolum
14. Levacetylmethadol [inn]
15. Alpha-(-)-acetylmethadol
16. Levacetilmetadol [inn-spanish]
17. Levacetylmethadolum [inn-latin]
18. L-alpha-acetylmethadol
19. Levoacetyl Methadol
20. Levomethadyl Acetate [usan]
21. Dea No. 9648
22. (-)-6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenyl-3-heptanol Acetate (ester)
23. Laa-m
24. Levacetylmethadol (inn)
25. 34433-66-4
26. Levomethadyl Acetate (usan)
27. Chebi:6441
28. (1s,4s)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-ethyl-2,2-diphenylpentyl Acetate
29. [(3s,6s)-6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenylheptan-3-yl] Acetate
30. R3b637y991
31. N-alpha-acetylmethadol
32. (3s,6s)-6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenylheptan-3-yl Acetate
33. Benzeneethanol, Beta-((2s)-2-(dimethylamino)propyl)-alpha-ethyl-beta-phenyl-, Acetate (ester), (alphas)-
34. Benzeneethanol, Beta-(2-(dimethylamino)propyl)-alpha-ethyl-beta-phenyl-, Acetate (ester), (s-(r*,r*))-
35. Unii-r3b637y991
36. 3-heptanol, 6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenyl-, Acetate (ester), (3s,6s)-(-)-
37. Benzeneethanol, Beta-[(2s)-2-(dimethylamino)propyl]-alpha-ethyl-beta-phenyl-, Acetate (ester), (alphas)-
38. Benzeneethanol, Beta-[2-(dimethylamino)propyl]-alpha-ethyl-beta-phenyl-, Acetate (ester), [s-(r*,r*)]-
39. Chembl1514
40. Bidd:pxr0155
41. Schembl93805
42. Bidd:gt0373
43. Gtpl7212
44. Dtxsid3023211
45. Levacetylmethadol [mart.]
46. Levomethadyl Acetate [mi]
47. (3s,6s)-6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenylheptan-2-yl Acetate
48. Levacetylmethadol [who-dd]
49. Zinc1530967
50. Levacetylmethadol [ema Epar]
51. Db01227
52. Benzeneethanol, Beta-(2-(dimethylamino)propyl)-alpha-ethyl-beta-phenyl-, Acetate(ester), (-)
53. Ncgc00247347-01
54. [s-(r*,r*)]-beta-[2-dimethylamino)propyl]-alpha-ethyl-beta-phenylbenzeneethanol Acetate (ester)
55. Ft-0700555
56. C08012
57. D04716
58. Q411799
59. (1s,4s)-(6-dimethylamino-4,4-diphenyl-heptan-3-yl) Acetate
60. 3-heptanol, 6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenyl-, Acetate (ester), (3s,6s)-(-)- (8ci)
61. Benzeneethanol, .beta.-(2-(dimethylamino)propyl)-.alpha.-ethyl-.beta.-phenyl-, Acetate (ester), (-)-
62. Benzeneethanol, Beta-[(2s)-2-(dimethylamino)propyl]-alpha-ethyl-beta-phenyl-, Acetate (ester), (alphas)- (9ci)
| Molecular Weight | 353.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H31NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 353.235479232 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 353.235479232 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 404 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment and management of opiate dependence. It is sometimes used to treat severe pain in terminal patients.
ORLAAM is indicated for the substitution maintenance treatment of opiate addiction in adults previously treated with methadone, as part of a comprehensive treatment plan including medical, social and psychological care.
ORLAAM should be administered under the supervision of physicians with experience in addiction treatment and whenever practicable, in centres specialising in the treatment of drug addiction.
ORLAAM is not intended for take home use.
Levomethadyl acetate (also known as LAAM) is a synthetic synthetic opioid analgesic with multiple actions quantitatively similar to those as morphine, the most prominent of which involve the central nervous system and organs composed of smooth muscle. However, levomethadyl acetate is more active and more toxic than morphine. The principal actions of therapeutic value are analgesia and sedation and detoxification or temporary maintenance in narcotic addiction. In this respect, the drug is similar to Methadone and also has structural similarities to it. The levomethadyl acetate abstinence syndrome, although qualitatively similar to that of morphine, differs in that the onset is slower, the course is more prolonged, and the symptoms are less severe.
Analgesics, Opioid
Compounds with activity like OPIATE ALKALOIDS, acting at OPIOID RECEPTORS. Properties include induction of ANALGESIA or NARCOSIS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics, Opioid.)
N02AC
N - Nervous system
N07 - Other nervous system drugs
N07B - Drugs used in addictive disorders
N07BC - Drugs used in opioid dependence
N07BC03 - Levacetylmethadol
Absorption
Levomethadyl acetate is rapidly absorbed from an oral solution.
Levomethadyl acetate is demethylated to nor-levomethadyl acetate which is again demethylated to dinor-levomethadyl acetate. This extensive first pass metabolism produces 2 metabolites that are more active than the parent drug.
2.6 days
Opiate receptors (Mu, Kappa, Delta) are coupled with G-protein receptors and function as both positive and negative regulators of synaptic transmission via G-proteins that activate effector proteins. Binding of the opiate stimulates the exchange of GTP for GDP on the G-protein complex. As the effector system is adenylate cyclase and cAMP located at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, opioids decrease intracellular cAMP by inhibiting adenylate cyclase. Subsequently, the release of nociceptive neurotransmitters such as substance P, GABA, dopamine, acetylcholine and noradrenaline is inhibited. Opioids also inhibit the release of vasopressin, somatostatin, insulin and glucagon. Levomethadyl acetate effectively opens calcium-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channels (OP1 receptor agonist), resulting in hyperpolarization and reduced neuronal excitability.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
79
PharmaCompass offers a list of Levomethadyl Acetate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Levomethadyl Acetate manufacturer or Levomethadyl Acetate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Levomethadyl Acetate manufacturer or Levomethadyl Acetate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Levomethadyl Acetate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Levomethadyl Acetate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Levomethadyl Acetate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Levomethadyl Acetate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Levomethadyl Acetate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Levomethadyl Acetate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Levomethadyl Acetate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Levomethadyl Acetate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Levomethadyl Acetate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Levomethadyl Acetate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Levomethadyl Acetate finished formulations upon request. The Levomethadyl Acetate suppliers may include Levomethadyl Acetate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Levomethadyl Acetate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Levomethadyl Acetate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Levomethadyl Acetate GMP manufacturer or Levomethadyl Acetate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Levomethadyl Acetate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Levomethadyl Acetate's compliance with Levomethadyl Acetate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Levomethadyl Acetate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Levomethadyl Acetate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Levomethadyl Acetate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Levomethadyl Acetate EP), Levomethadyl Acetate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Levomethadyl Acetate USP).
