
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
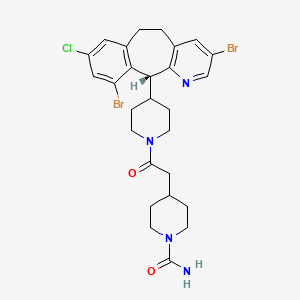

1. (+)4-(2-(4-(8-chloro-3,10-dibromo-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo(5,6)cyclohepta(1,2-b)pyridin-11-yl)-1-piperidinyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1-piperidinecarboxamide
2. 1-piperidinecarboxamide, 4(2-(4-(11r-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo(5,6)cyclohepta(1,2-b)pyridine-11-yl)-1-piperidinyl)-2-oxoethyl)-
3. 4-(2-(4-(8-chloro-3,10-dibromo-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo-(5,6)-cyclohepta(1,2-b)-pyridin-11(r)-yl)-1-piperidinyl)-2-oxo-ethyl)-1-piperidinecarboxamide
4. Sarasar
5. Sch 66336
6. Sch-66336
7. Sch66336
8. Zokinvy
1. 193275-84-2
2. Sarasar
3. Sch66336
4. Sch 66336
5. Sch-66336
6. Zokinvy
7. Chembl298734
8. Lonafarnib [usan]
9. Iow153004f
10. (+)-4-(2-(4-(11r)-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo(5,6)cyclohepta(1,2-b)pyridin-11-yl)-piperidin-1-yl))-2-oxoethyl)-piperidine-1-carboxamide
11. (r)-4-(2-(4-(3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl)piperidin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)piperidine-1-carboxamide
12. 1-piperidinecarboxamide, 4-(2-(4-((11r-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo(5,6)cyclohepta(1,2-b)pyridin-11-yl)-1-piperidinyl)-2-oxoethyl)-
13. 1-piperidinecarboxamide, 4-[2-[4-[(11r)-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl]-1-piperidinyl]-2-oxoethyl]-
14. 4-[2-[4-(6,15-dibromo-13-chloro-4-azatricyclo[9.4.0.03,8]pentadeca-1(11),3(8),4,6,12,14-hexaen-2-yl)piperidin-1-yl]-2-oxoethyl]piperidine-1-carboxamide
15. 4-[2-[4-[(2r)-6,15-dibromo-13-chloro-4-azatricyclo[9.4.0.03,8]pentadeca-1(11),3(8),4,6,12,14-hexaen-2-yl]piperidin-1-yl]-2-oxoethyl]piperidine-1-carboxamide
16. 1-piperidinecarboxamide, 4-(2-(4-((11r)-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo(5,6)cyclohepta(1,2-b)pyridin-11-yl)-1-piperidinyl)-2-oxoethyl)-
17. 4-(2-{4-[(11r)-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl]piperidin-1-yl}-2-oxoethyl)piperidine-1-carboxamide
18. Smr004701448
19. Lonafarnib (usan/inn)
20. Lonafarnib [usan:inn]
21. Lonafarnib (sch66336)
22. Lonafarnibum
23. Unii-iow153004f
24. 4-(2-(4-(8-chloro-3,10-dibromo-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo-(5,6)-cyclohepta(1,2-b)-pyridin-11(r)-yl)-1-piperidinyl)-2-oxo-ethyl)-1-piperidinecarboxamide
25. Sch-066336
26. 4-[2-[4-[(11r)-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl]-1-piperidinyl]-2-oxoethyl]-1-piperidinecarboxamide
27. 1o5m
28. Lonafarnib [mi]
29. Lonafarnib [inn]
30. (non-labelled)lonafarnib-d9
31. Lonafarnib [who-dd]
32. Schembl19032
33. Mls006010423
34. Mls006011106
35. Gtpl8024
36. Lonafarnib [orange Book]
37. Lonafarnib, >=98% (hplc)
38. Bdbm14459
39. Chebi:47097
40. Dtxsid90172927
41. Bcp07027
42. Ex-a1630
43. Zinc3950115
44. Nsc719467
45. S2797
46. Akos005145760
47. Ccg-270312
48. Cs-0792
49. Db06448
50. Nsc-719467
51. Ncgc00346707-01
52. Ac-32661
53. As-56182
54. Hy-15136
55. Sw220034-1
56. C73675
57. D04768
58. J-514232
59. Q3258910
60. (+)-4-[2-[4-(8-chloro-3,10-dibromo-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11(r)-yl)-1-piperidin-yl]-2-oxo-ethyl]-1-piperidinecarboxamide
61. (+)-4[2-[4-(8-chloro-3,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[5,6] Cyclohepta[1,2-b]-pyridin-11(r)-yl-1-piperidinyl]-2-oxo-ethyl]-1-piperidinecarboxamide
62. 4-(2-{4-[(2r)-6,15-dibromo-13-chloro-4-azatricyclo[9.4.0.0^{3,8}]pentadeca-1(11),3,5,7,12,14-hexaen-2-yl]piperidin-1-yl}-2-oxoethyl)piperidine-1-carboxamide
63. 4-[2-[4-[(11r)-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[1,2]cyclohepta[2,4-b]pyridin-11-yl]piperidin-1-yl]-2-oxoethyl]piperidine-1-carboxamide
64. 4-[2-[4-[(11r)-3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl]-1-piperidinyl]-2-oxoethyl]-1-piperidi Necarboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 638.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H31Br2ClN4O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 638.04818 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 636.05023 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 79.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 790 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Lonafarnib is a farnesyltransferase inhibitor indicated in patients aged 12 months and older with a body surface area of at least 0.39 m2 to reduce the risk of mortality associated with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS). It is also indicated in this same population for the treatment of processing-deficient progeroid laminopathies that either involve a heterozygous _LMNA_ mutation resulting in the accumulation of a progerin-like protein or homozygous/compound heterozygous mutations in _ZMPSTE24_.
Zokinvy is indicated for the treatment of patients 12 months of age and older with a genetically confirmed diagnosis of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome or a processing-deficient progeroid laminopathy associated with either a heterozygous LMNA mutation with progerin-like protein accumulation or a homozygous or compound heterozygous ZMPSTE24 mutation.
Lonafarnib is a direct farnesyl transferase inhibitor that reduces the farnesylation of numerous cellular proteins, including progerin, the aberrantly truncated form of lamin A that accumulates in progeroid laminopathies such as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Treatment with lonafarnib has been associated with electrolyte abnormalities, myelosuppression, and increased liver enzyme levels (AST/ALT), although causation remains unclear. Also, lonafarnib is known to cause nephrotoxicity in rats and rod-dependent low-light vision decline in monkeys at plasma levels similar to those achieved under recommended dosing guidelines in humans; patients taking lonafarnib should undergo regular monitoring for both renal and ophthalmological function. In addition, based on observations from animal studies with rats, monkeys, and rabbits with plasma drug concentrations approximately equal to those attained in humans, lonafarnib may cause both male and female fertility impairment and embryo-fetal toxicity.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A16 - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16A - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX - Various alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AX20 - Lonafarnib
Absorption
The absolute oral bioavailability of lonafarnib is unknown; in healthy subjects administration of either 75 or 100 mg of lonafarnib twice daily resulted in mean peak plasma concentrations (%CV) of 834 (32%) and 964 (32%) ng/mL, respectively. Twice daily administration of 115 mg/m2 lonafarnib in HGPS patients resulted in a median tmax of 2 hours (range 0-6), mean Cmax of 1777 1083 ng/mL, mean AUC0-8hr of 9869 6327 ng\*hr/mL, and a mean AUCtau of 12365 9135 ng\*hr/mL. The corresponding values for a dose of 150 mg/m2 are: 4 hours (range 0-12), 2695 1090 ng/mL, 16020 4978 ng\*hr/mL, and 19539 6434 ng\*hr/mL, respectively. Following a single oral dose of 75 mg in healthy subjects, the Cmax of lonafarnib decreased by 55% and 25%, and the AUC decreased by 29% and 21% for a high/low-fat meal compared to fasted conditions.
Route of Elimination
Up to 240 hours following oral administration of 104 mg [14C]-lonafarnib in fasted healthy subjects, approximately 62% and <1% of the initial radiolabeled dose was recovered in feces and urine, respectively. The two most prevalent metabolites were the active HM21 and HM17, which account for 14% and 15% of plasma radioactivity.
Volume of Distribution
In healthy patients administered either 75 or 100 mg lonafarnib twice daily, the steady-state apparent volumes of distribution were 97.4 L and 87.8 L, respectively.
Lonafarnib is metabolized _in vitro_ primarily by CYP3A4/5 and partially by CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2E1. Formation of the primary metabolites involves oxidation and subsequent dehydration in the pendant piperidine ring.
Lonafarnib has a mean half-life of approximately 4-6 hours following oral administration of 100 mg twice daily in healthy subjects.
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder estimated to affect approximately one in 20 million individuals resulting in premature ageing, associated cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and musculoskeletal effects and early death around 14 years of age. The _LMNA_ gene encodes lamin A and lamin C, two proteins involved in nuclear integrity and function at the inner nuclear membrane. Under normal conditions, the 12-exon _LMNA_ gene produces full-length prelamin A, which undergoes farnesylation of the C-terminal _CaaX_ motif, followed by proteolytic cleavage of the terminal three amino acids (_aaX_) by the metalloproteinase ZMPSTE24, subsequent carboxymethylation, and finally removal of the last 15 amino acids to yield mature, unfarnesylated, lamin A protein. In HGPS, a single heterozygous C-to-T mutation at position 1824 results in a cryptic splice site that removes the last 150 nucleotides of exon 11 and a concomitant 50-amino acid deletion in the C-terminus of the prelamin A protein. This aberrant prelamin A protein, often called progerin, is permanently farnesylated but unable to complete maturation due to the removal of the second endoproteolytic cleavage site. Although the exact mechanism is unclear, progerin accumulation results in a host of adverse symptoms associated with ageing such as skeletal dysplasia, joint contractures, atherosclerosis, myocardial fibrosis/dysfunction, scleroderma-like cutaneous effects, lipoatrophy, alopecia, and a severe failure to thrive. An additional notable effect of HGPS is increased vascular and peripheral calcification. Children affected by HGPS typically die due to myocardial infarction or stroke. Mechanistic understanding of HGPS remains unclear, although a recent study correlated progerin accumulation, telomere dysfunction, DNA damage-mediated inflammatory cytokine release, and HGPS symptoms, suggesting that the nuclear effects of progerin accumulation may result in pleiotropic downstream effects. Lonafarnib is a farnesyl transferase (FTase) inhibitor (FTI), with a reported IC50 value of 1.9 nM; lonafarnib is specific for FTase, as it does not appreciably inhibit the related GGPT-1 enzyme at concentrations up to 50 M. Inhibition of progerin farnesylation reduces progerin accumulation in the inner nuclear membrane, which subsequently slows the progression of HGPS and other progeroid laminopathies.
NDC Package Code : 12869-230
Start Marketing Date : 2020-11-20
End Marketing Date : 2025-12-31
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1kg/kg)
Marketing Category : BULK INGREDIENT

NDC Package Code : 70277-002
Start Marketing Date : 2020-11-30
End Marketing Date : 2025-12-31
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1mg/500mg)
Marketing Category : DRUG FOR FURTHER PROCESSING

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
15
PharmaCompass offers a list of Lonafarnib API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Lonafarnib manufacturer or Lonafarnib supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Lonafarnib manufacturer or Lonafarnib supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Lonafarnib API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Lonafarnib API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Lonafarnib Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Lonafarnib Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Lonafarnib manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Lonafarnib, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Lonafarnib manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Lonafarnib API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Lonafarnib supplier is an individual or a company that provides Lonafarnib active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Lonafarnib finished formulations upon request. The Lonafarnib suppliers may include Lonafarnib API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Lonafarnib suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Lonafarnib as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Lonafarnib API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Lonafarnib as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Lonafarnib and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Lonafarnib NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Lonafarnib suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Lonafarnib Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Lonafarnib GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Lonafarnib GMP manufacturer or Lonafarnib GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Lonafarnib CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Lonafarnib's compliance with Lonafarnib specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Lonafarnib CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Lonafarnib CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Lonafarnib may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Lonafarnib EP), Lonafarnib JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Lonafarnib USP).
