
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
South Africa
0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
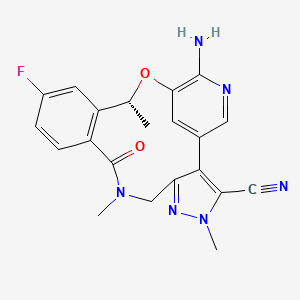

1. (10r)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2h-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo(4,3-h)(2,5,11)benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
2. 7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2h-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo(4,3-h)(2,5,11)benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
3. Loratinib
4. Lorbrena
5. Pf-06463922
6. Pf06463922
1. 1454846-35-5
2. Pf-06463922
3. Loratinib
4. Lorbrena
5. Pf06463922
6. Pf 06463922
7. Osp71s83eu
8. Chembl3286830
9. C21h19fn6o2
10. (10r)-7-amino-12-fluoro-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-2h-4,8-methenopyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
11. (16r)-19-amino-13-fluoro-4,8,16-trimethyl-9-oxo-17-oxa-4,5,8,20-tetrazatetracyclo[16.3.1.02,6.010,15]docosa-1(22),2,5,10(15),11,13,18,20-octaene-3-carbonitrile
12. 2h-4,8-methenopyrazolo(4,3-h)(2,5,11)benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile, 7-amino-12-fluoro-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-, (10r)-
13. Lorviqua
14. Mfcd28144520
15. (10r)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2h-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
16. Unii-osp71s83eu
17. Lorlatinibum
18. Lorlatinib,pf-06463922
19. Pf-6463922
20. 4cli
21. 4clj
22. Lorbrena (tn)
23. 2h-4,8-methenopyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile, 7-amino-12-fluoro-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-, (10r)-
24. Lorlatinib [mi]
25. Lorlatinib [inn]
26. Lorlatinib [jan]
27. Lorlatinib [usan:inn]
28. Lorlatinib [usan]
29. Pfe-pkis 10
30. Lorlatinib [who-dd]
31. 7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2h-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo(4,3-h)(2,5,11)benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
32. Lorlatinib (jan/usan/inn)
33. Pf06463922(lorlatinib)
34. Gtpl7476
35. Lorlatinib [orange Book]
36. Pf-06463922 Lorlatinib
37. Schembl15261807
38. Amy3295
39. Ex-a828
40. Chebi:143117
41. Dtxsid201027944
42. Bcp10287
43. Bdbm50018830
44. Nsc780108
45. Nsc800990
46. S7536
47. Zinc98208524
48. Akos027250753
49. Ccg-268718
50. Cs-3983
51. Db12130
52. Nsc-780108
53. Nsc-800990
54. Ncgc00386417-02
55. Ncgc00386417-13
56. Ac-30881
57. Hy-12215
58. A14207
59. D11012
60. A857523
61. J-690185
62. Q27285820
63. (10r)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2h-4,8- Methenopyrazolo(4,3-h)(2,5,11)benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
64. (10r)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2h-4,8-methenopyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile
65. (r)-26-amino-55-fluoro-11,4,7-trimethyl-6-oxo-11h-3-oxa-7-aza-2(3,5)-pyridina-1(4,3)-pyrazola-5(1,2)-benzenacyclooctaphane-15-carbonitrile
| Molecular Weight | 406.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H19FN6O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 406.15535203 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 406.15535203 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 700 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Lorlatinib is a third-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) indicated for the treatment of patients with ALK-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has progressed on a) the prior use of crizotinib and at least one other ALK inhibitor for metastatic disease, or b) the prior use of alectinib as the first ALK inhibitor therapy for metastatic disease, or c) the prior use of certinib as the first ALK inhibitor therapy for metastatic disease.
FDA Label
Lorviqua as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)positive advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) previously not treated with an ALK inhibitor.
Lorviqua as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with ALKpositive advanced NSCLC whose disease has progressed after:
- alectinib or ceritinib as the first ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy; or
- crizotinib and at least one other ALK TKI.
Based on data from Study B7461001, exposure-response relationships for Grade 3 or 4 hypercholesterolemia and for any Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction were observed at steady-state exposures achieved at the recommended dosage, with higher probability of the occurrence of adverse reactions with increasing lorlatinib exposure. In 295 patients who received lorlatinib at the recommended dosage of 100 mg once daily and had an ECG measurement in the same Study B7461001, the maximum mean change from baseline for their PR interval was 16.4 ms (2-sided 90% upper confidence interval [CI] 19.4 ms). Among the 284 patients with PR interval <200 ms at baseline, 14% had PR interval prolongation 200 ms after starting use with lorlatinib. The prolongation of PR interval occurred in a concentration-dependent manner and atrioventricular block occurred in 1% of patients. Finally, in 275 patients who received lorlatinib at the recommended dosage in the activity-estimating portion of Study B7461001, no large mean increases from baseline in the QTcF interval (i.e., >20 ms) were detected.
L01ED05
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01ED - Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (alk) inhibitors
L01ED05 - Lorlatinib
Absorption
The median lorlatinib Tmax was 1.2 hours (0.5 to 4 hours) following a single oral 100 mg dose and 2 hours (0.5 to 23 hours) following 100 mg orally once daily at steady state. The mean absolute bioavailability is 81% (90% CI 75.7%, 86.2%) after oral administration compared to intravenous administration. Administration of lorlatinib with a high fat, high-calorie meal (approximately 1000 calories with 150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrate, and 500 to 600 calories from fat) had no clinically meaningful effect on lorlatinib pharmacokinetics.
Route of Elimination
Following a single oral 100 mg dose of radiolabeled lorlatinib, 48% of the radioactivity was recovered in urine (<1% as unchanged) and 41% in feces (about 9% as unchanged).
Volume of Distribution
The mean (CV%) steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) was 305 L (28%) following a single intravenous dose.
Clearance
The mean oral clearance (CL/F) was 11 L/h (35%) following a single oral 100 mg dose and increased to 18 L/h (39%) at steady state, suggesting autoinduction.
In vitro, lorlatinib is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and UGT1A4, with minor contribution from CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP3A5, and UGT1A3. In plasma, a benzoic acid metabolite (M8) of lorlatinib resulting from the oxidative cleavage of the amide and aromatic ether bonds of lorlatinib accounted for 21% of the circulating radioactivity in a human [14C] mass balance study. The oxidative cleavage metabolite, M8, is pharmacologically inactive.
The mean plasma half-life (t) of lorlatinib was 24 hours (40%) after a single oral 100 mg dose of lorlatinib.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for up to 85% of lung cancer cases worldwide and remains a particularly difficult to treat condition. The gene rearrangement of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a genetic alteration that drives the development of NSCLC in a number of patients. Ordinarily, ALK is a natural endogenous tyrosine kinase receptor that plays an important role in the development of the brain and elicits activity on various specific neurons in the nervous system. Subsequnetly, lorlatinib is a kinase inhibitor with in vitro activity against ALK and number of other tyrosine kinase receptor related targets including ROS1, TYK1, FER, FPS, TRKA, TRKB, TRKC, FAK, FAK2, and ACK. Lorlatinib demonstrated in vitro activity against multiple mutant forms of the ALK enzyme, including some mutations detected in tumors at the time of disease progression on crizotinib and other ALK inhibitors. Moreover, lorlatinib possesses the capability to cross the blood-brain barrier, allowing it to reach and treat progressive or worsening brain metastases as well. The overall antitumor activity of lorlatinib in in-vivo models appears to be dose-dependent and correlated with the inhibition of ALK phosphorylation. Although many ALK-positive metastatic NSCLC patients respond to initial tyrosine kinase therapies, such patients also often experience tumor progression. Various clinical trials performed with lorlatinib, however, have demonstrated its utility to effect tumor regression in ALK-positive metastatic NSCLC patients who experience tumor progression despite current use or having already used various first and second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors like crizotinib, alectinib, or ceritinib.
 Biophore is a research-driven global pharmaceutical company focused on niche APIs for the generic industry.
Biophore is a research-driven global pharmaceutical company focused on niche APIs for the generic industry.
 TAPI, a leading global supplier of APIs, provides over 350 products and customized CDMO solutions for every stage of development.
TAPI, a leading global supplier of APIs, provides over 350 products and customized CDMO solutions for every stage of development.


Registrant Name : Korea Pfizer Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Registration Date : 2021-11-30
Registration Number : Su87-30-ND
Manufacturer Name : Pfizer Ireland Pharmaceuticals Unlimited Company
Manufacturer Address : Ringaskiddy API Plant, Ringaskiddy, Co. Cork, P43 X336, Ireland


 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
Registrant Name : Korea Pfizer Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Registration Date : 2021-11-30
Registration Number : Su87-30-ND
Manufacturer Name : Pfizer Ireland Pharmaceutica...
Manufacturer Address : Ringaskiddy API Plant, Ringaskiddy, Co. Cork, P43 X336, Ireland

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results] Biophore is a research-driven global pharmaceutical company focused on niche APIs for the generic industry.
Biophore is a research-driven global pharmaceutical company focused on niche APIs for the generic industry.
About the Company : Biophore, founded in 2007, develops and manufactures niche and complex pharmaceutical products. With USFDA- and EU-approved API facilities, a dedicated intermediates site and an R&...
 TAPI, a leading global supplier of APIs, provides over 350 products and customized CDMO solutions for every stage of development.
TAPI, a leading global supplier of APIs, provides over 350 products and customized CDMO solutions for every stage of development.
About the Company : Founded in 1935, TAPI Technology & API Services has a long legacy of advancing health through innovation. Today, we offer one of the industry’s most comprehensive API portfolios ...
About the Company : Beijing Sjar Technology Development Co., Ltd. founded in 2014, it is a high-tech enterprise which specialized in the research and development of active pharmaceutical ingredients a...

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
20
PharmaCompass offers a list of Lorlatinib API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Lorlatinib manufacturer or Lorlatinib supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Lorlatinib manufacturer or Lorlatinib supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Lorlatinib API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Lorlatinib API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Lorlatinib Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Lorlatinib Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Lorlatinib manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Lorlatinib, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Lorlatinib manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Lorlatinib API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Lorlatinib manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Lorlatinib supplier is an individual or a company that provides Lorlatinib active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Lorlatinib finished formulations upon request. The Lorlatinib suppliers may include Lorlatinib API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Lorlatinib suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Lorlatinib Drug Master File in Korea (Lorlatinib KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Lorlatinib. The MFDS reviews the Lorlatinib KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Lorlatinib KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Lorlatinib KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Lorlatinib API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Lorlatinib suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
Lorlatinib Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Lorlatinib GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Lorlatinib GMP manufacturer or Lorlatinib GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Lorlatinib CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Lorlatinib's compliance with Lorlatinib specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Lorlatinib CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Lorlatinib CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Lorlatinib may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Lorlatinib EP), Lorlatinib JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Lorlatinib USP).

