
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
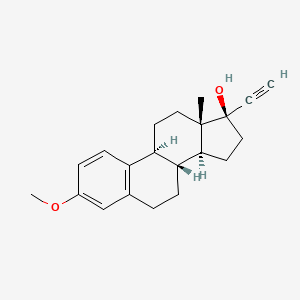

1. 19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-methoxy-, (17alpha)-
2. Ethinyl Estradiol 3 Methyl Ether
3. Ethinyl Estradiol 3-methyl Ether
1. 72-33-3
2. Menophase
3. Norquen
4. Devocin
5. Ovastol
6. Ee3me
7. Ethynylestradiol 3-methyl Ether
8. Mestranolum
9. 3-methoxyethynylestradiol
10. Ee(sub3)me
11. Ethynylestradiol Methyl Ether
12. 3-methylethynylestradiol
13. 3-o-methylethynylestradiol
14. Compound 33355
15. Inostral
16. 3-methylethynyloestradiol
17. 3-methoxyethynyloestradiol
18. 3-methoxy-17alpha-ethynylestradiol
19. Sc 4725
20. Ee3-me
21. 17-ethynyloestradiol 3-methyl Ether
22. Component Of Norinyl
23. Eei3me
24. Component Of Ortho-novum
25. (8r,9s,13s,14s,17r)-17-ethynyl-3-methoxy-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-ol
26. Ee-3me
27. Ethinylestradiol 3-methyl Ether
28. Ethinyloestradiol 3-methyl Ether
29. Ethynyloestradiol 3-methyl Ether
30. Mls000028595
31. B2v233xge7
32. Chebi:6784
33. 17-ethynylestradiol 3-methyl Ether
34. Component Of Ovulen
35. Component Of Norquen
36. Delta-mve
37. 17alpha-ethynylestradiol 3-methyl Ether
38. Nsc-84032
39. (8r,9s,13s,14s,17r)-17-ethynyl-3-methoxy-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-ol
40. Inostral (steroid)
41. Mestranolo [dcit]
42. Ncgc00093347-02
43. Mestranolo
44. Smr000059128
45. (17beta)-17-ethynyl-3-(methyloxy)estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-ol
46. Dsstox_cid_814
47. Dsstox_rid_75804
48. Dsstox_gsid_20814
49. Mestranolum [inn-latin]
50. Caswell No. 547a
51. .delta.-mve
52. 17alpha-ethinyl Estradiol 3-methyl Ether
53. 17-ethynyl-3-methoxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-ol
54. 3-methoxy-17alpha-ethinylestradiol
55. 3-methoxy-17alpha-ethinyloestradiol
56. 3-methoxy-17alpha-ethynyloestradiol
57. 3-methoxy-17-alpha-ethinylestradiol
58. 3-methoxy-17-alpha-ethynylestradiol
59. 17alpha-ethynylestradiol Methyl Ether
60. 3-methoxy-17-alpha-ethinyloestradiol
61. 3-methoxy-17-alpha-ethynyloestradiol
62. Ccris 377
63. 17-alpha-ethynyloestradiol Methyl Ether
64. 17alpha-ethinylestradiol 3-methyl Ether
65. 8027 C. B.
66. 17alpha-ethynyloestradiol 3-methyl Ether
67. 3-methoxy-17-ethynyloestradiol-17-beta
68. Mestranol [steroidal Oestrogens]
69. 17alpha-ethinyl Oestradiol 3-methyl Ether
70. Hsdb 3588
71. 17-alpha-ethinyl Estradiol 3-methyl Ether
72. 17-alpha-ethinyl Oestradiol 3-methyl Ether
73. Einecs 200-777-8
74. Nsc 84032
75. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 115401
76. 17beta-estradiol, 17-ethynyl-, 3-(methyl Ether)
77. Brn 2625905
78. Unii-b2v233xge7
79. Nsc84032
80. 17-ethynyl-3-methoxy-1,3,5(10)-oestratien-17-beta-ol
81. Ai3-51798
82. 3-methoxy-17alpha-ethynyl-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-17beta-ol
83. 19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-methoxy-, (17.alpha.)-
84. 3-methoxy-17alpha-ethynyl-1,3,5(10)-oestratrien-17beta-ol
85. 17-alpha-ethynyl-3-methoxy-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-17-beta-ol
86. 3-methoxy-17-alpha-ethynyl-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-17-beta-ol
87. 3-methoxy-17-alpha-ethynyl-1,3,5(10)-oestratrien-17-beta-ol
88. Cas-72-33-3
89. 3-methoxy-17-alpha-19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol
90. 3-methoxy-19-nor-17-alpha-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol
91. 3-methoxy-19-nor-17alpha-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol
92. 19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-methoxy-, (17alpha)-
93. Prestwick_966
94. Mestranol, 99%
95. Mestranol [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
96. Estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17beta-ol, 17-ethynyl-3-methoxy-
97. Mestranol [inn]
98. Mestranol [jan]
99. Opera_id_872
100. Mestranol [mi]
101. Mestranol [hsdb]
102. Mestranol [usan]
103. 17alpha-19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-methoxy-
104. Estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-beta-ol, 17-alpha-ethynyl-3-methoxy-
105. Prestwick0_000846
106. Prestwick1_000846
107. Prestwick2_000846
108. Prestwick3_000846
109. Mestranol [vandf]
110. (+)-17-alpha-ethynyl-17-beta-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1,3,5(10)-estratriene
111. (17-alpha)-3-methoxy-19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol
112. 17-ethynyl-3-methoxyestra-1(10),2,4-trien-17-ol
113. Ee3 Me
114. Mestranol [mart.]
115. (+)-17-alpha-ethynyl-17-beta-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1,3,5(10)-oestratriene
116. 17-alpha-ethynyl-3-methoxy-17-beta-hydroxy-delta-1,3,5(10)-estratriene
117. 17-alpha-ethynyl-3-methoxy-17-beta-hydroxy-delta-1,3,5(10)-oestratriene
118. 3,17-beta-dihydroxy-17-alpha-ethynyl-1,3,5(10)-estratriene-3-methyl Ether
119. Mestranol [usp-rs]
120. Mestranol [who-dd]
121. Schembl41391
122. Bspbio_000831
123. Mls001077321
124. Mls001424224
125. Bidd:er0199
126. Spbio_002752
127. Mestranol (jp17/usp/inn)
128. Bpbio1_000915
129. Ethynylestradiol-3-methyl Ether
130. Gtpl7087
131. Mestranol [orange Book]
132. 17-ethynyl-3-methoxyestra-1(10),2,4-trien-17beta-ol
133. Chembl1201151
134. Dtxsid0020814
135. Mestranol [ep Monograph]
136. Enovid Component Mestranol
137. Ovulen Component Mestranol
138. 17-ethynyl-3-methoxyoestra-1(10),2,4-trien-17beta-ol
139. Mestranol [usp Monograph]
140. 3-methoxy-19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17beta-ol
141. Hms1570j13
142. Hms2051j22
143. Hms2097j13
144. Hms2230l20
145. Hms3714j13
146. Hy-b0390
147. Zinc3815424
148. Mestranol Component Of Enovid
149. Mestranol Component Of Ovulen
150. Tox21_111200
151. Tox21_301837
152. 17-alpha-19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-methoxy-
153. 19-nor-17alpha-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-methoxy-
154. Akos005267152
155. Tox21_111200_1
156. Ccg-101067
157. Db01357
158. Nc00317
159. Ncgc00093347-03
160. Ncgc00093347-05
161. Ncgc00093347-07
162. Ncgc00179410-01
163. Ncgc00255342-01
164. Ac-13293
165. As-56063
166. S2125
167. Mestranol, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
168. C07618
169. C76306
170. D00575
171. 003m689
172. Q904308
173. Sr-01000695429
174. Sr-01000695429-4
175. Brd-k31920458-001-03-8
176. Brd-k31920458-001-23-6
177. Mestranol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
178. (17beta)-17-ethynyl-3-methoxyestra-1(10),2,4-trien-17-ol
179. Mestranol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
180. 17.alpha.-19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-meth
181. (+)-17alpha-ethynyl-17beta-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1,3,5(10)-estratriene
182. (+)-17alpha-ethynyl-17beta-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1,3,5(10)-oestratriene
183. (+ )-17.alpha.-ethynyl-17.beta.-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1,3, 5(10)-oestratriene
184. (+)-17.alpha.-ethynyl-17.beta.-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1,3, 5(10)-estratriene
185. 3-methoxy-19-nor-17.alpha.-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol.
186. (1s,10r,11s,14r,15s)-14-ethynyl-5-methoxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2(7),3,5-trien-14-ol
187. (8r,13s,17r)-17-ethynyl-3-methoxy-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-ol
| Molecular Weight | 310.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H26O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 310.193280068 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 310.193280068 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 519 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Estrogens
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Mestranol /is indicated in combination with an oral progestin/ for the prevention of pregnancy in women who elect to use this product as a method of contraception. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information NECON (norethindrone and mestranol) kit (January 200). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=9157
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular side effects from oral contraceptive use. This risk increases with age and with heavy smoking (15 or more cigarettes per day) and is quite marked in women over 35 years of age. Women who use oral contraceptives are strongly advised not to smoke.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information NECON (norethindrone and mestranol) kit (January 200). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=9157
Patients who are fully breast-feeding should not take Norinyl-1 tablets since, in common with other combined oral contraceptives, the estrogen component may reduce the amount of milk produced. In addition, active ingredients or their metabolites have been detected in the milk of mothers taking oral contraceptives.
Datapharm Communications Ltd; Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC), Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) for Norinyl-1 Tablets (Last updated May 2007). Available from, as of March 22, 2011: https://www.medicines.org.uk/EMC/medicine/1920/SPC/Norinyl-1+Tablets/
Oral contraceptives should not be used in women who have the following conditions: thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders; a past history of deep vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders; cerebral vascular or coronary artery disease; known or suspected carcinoma of the breast; carcinoma of the endometrium or other known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia; undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding; cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior pill use; hepatic adenomas, carcinomas or benign liver tumors.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information NECON (norethindrone and mestranol) kit (January 200). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=9157
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: X /CONTRAINDICATED IN PREGNANCY. Studies in animals and or humans, or investigational or post-marketing reports, have demonstrated positive evidence of fetal abnormalities or risk which clearly outweighs any possible benefit to the patient.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information NECON (norethindrone and mestranol) kit (January 200). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=9157
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MESTRANOL (37 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Mestranol was used as one of the first oral contraceptives.
Contraceptives, Oral, Hormonal
Oral contraceptives which owe their effectiveness to hormonal preparations. (See all compounds classified as Contraceptives, Oral, Hormonal.)
Estrogens
Compounds that interact with ESTROGEN RECEPTORS in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of ESTRADIOL. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female SEX CHARACTERISTICS. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. (See all compounds classified as Estrogens.)
Mestranol binds poorly to the estrogen receptor and its estrogenic effect is due to its rapid demethylation in the liver to form ethinylestradiol; however, demethylation is not complete and more mestranol must be administered than ethinylestradiol to achieve similar effects.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V91 145 (2007)
The excretion of metabolites in urine ranged from 10-27%; that of ethinyloestradiol metabolites ranges from 36-54%. When position 2 or 4 of the mestranol molecule is tritiated or marked with (14)C, between 14-45% of the radioactivity is released into the body water.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V21 270 (1979)
Mestranol is rapidly absorbed and extensively metabolised to ethinylestradiol. Ethinylestradiol is rapidly and well absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract but is subject to some first-pass metabolism in the gut-wall. Compared to many other estrogens it is only slowly metabolized in the liver. Excretion is via the kidneys with some appearing also in the feces.
Datapharm Communications Ltd; Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC), Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) for Norinyl-1 Tablets (Last updated May 2007). Available from, as of March 22, 2011: https://www.medicines.org.uk/EMC/medicine/1920/SPC/Norinyl-1+Tablets/
In the body it undergoes rapid hepatic demethylation to ethinyl estradiol, which is its active form. /Estrogens/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 1420
Mestranol, the 3-methyl ether of ethinyloestradiol, is more lipophilic than ethinyloestradiol and has a greater affinity for adipose tissues, as shown by experiments in rats. Mestranol itself does not bind significantly to estrogen receptors at the sites of their antifertility action; its hormonal effectiveness relies on transformation to ethinyloestradiol. About 35% of a mestranol dose is transformed into ethinyloestradiol in rats, 61% in mice, 56% in rabbits and 54% in man. The demethylated portion then follows the pathways for ethinyloestradiol that are typical for the particular species, e.g., 2-hydroxylation in rats and D-homoannulation in rabbits and guinea-pigs. Mestranol is also demethylated to ethinylestradiol in non-human primates.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V21 269 (1979)
The metabolism of mestranol in humans is closely related to that of ethinyloestradiol. Mestranol is transformed to ethinyloestradiol by demethylation: after i.v. administration of (14)C-mestranol to human volunteers, about 50% of the dose is demethylated to ethinylestradiol. The main compound found in plasma is ethinyloestradiol-3-sulfate.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V21 270 (1979)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for MESTRANOL (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Mestranol has known human metabolites that include ethinylestradiol.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Mestranol is the 3-methyl ether of ethinylestradiol. Ethinylestradiol, is a synthetic derivative of estradiol. Ethinylestradiol is orally bio-active and the estrogen used in almost all modern formulations of combined oral contraceptive pills. It binds to (and activates) the estrogen receptor. Mestranol is a biologically inactive prodrug of ethinylestradiol to which it is demethylated in the liver with a conversion efficiency of 70%. Estrogens diffuse into their target cells and interact with a protein receptor. Target cells include the female reproductive tract, the mammary gland, the hypothalamus, and the pituitary. Estrogens increase the hepatic synthesis of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), thyroid-binding globulin (TBG), and other serum proteins and suppress follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary. The combination of an estrogen with a progestin suppresses the hypothalamic-pituitary system, decreasing the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
The mode of action of Norinyl-1 is similar to that of other progestogen/estrogen oral contraceptives and includes the inhibition of ovulation, the thickening of cervical mucus so as to constitute a barrier to sperm and the rendering of the endometrium unreceptive to implantation. Such activity is exerted through a combined effect on one or more of the following: hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, ovary, endometrium and cervical mucus.
Datapharm Communications Ltd; Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC), Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) for Norinyl-1 Tablets (Last updated May 2007). Available from, as of March 22, 2011: https://www.medicines.org.uk/EMC/medicine/1920/SPC/Norinyl-1+Tablets/
Estrogens have an important role in the reproductive, skeletal, cardiovascular, and central nervous systems in women, and act principally by regulating gene expression. Biologic response is initiated when estrogen binds to a ligand-binding domain of the estrogen receptor resulting in a conformational change that leads to gene transcription through specific estrogen response elements (ERE) of target gene promoters; subsequent activation or repression of the target gene is mediated through 2 distinct transactivation domains (ie, AF-1 and AF-2) of the receptor. The estrogen receptor also mediates gene transcription using different response elements (ie, AP-1) and other signal pathways. Recent advances in the molecular pharmacology of estrogen and estrogen receptors have resulted in the development of selective estrogen receptor modulators (eg, clomiphene, raloxifene, tamoxifen, toremifene), agents that bind and activate the estrogen receptor but that exhibit tissue-specific effects distinct from estrogen. Tissue-specific estrogen-agonist or -antagonist activity of these drugs appears to be related to structural differences in their estrogen receptor complex (eg, specifically the surface topography of AF-2 for raloxifene) compared with the estrogen (estradiol)-estrogen receptor complex. A second estrogen receptor also has been identified, and existence of at least 2 estrogen receptors (ER-alpha, ER-beta) may contribute to the tissue-specific activity of selective modulators. While the role of the estrogen receptor in bone, cardiovascular tissue, and the CNS continues to be studied, emerging evidence indicates that the mechanism of action of estrogen receptors in these tissues differs from the manner in which estrogen receptors function in reproductive tissue. /Estrogen General Statement/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 3130
Intracellular cytosol-binding proteins for estrogens have been identified in estrogen-responsive tissues including the female genital organs, breasts, pituitary, and hypothalamus. The estrogen-binding protein complex (ie, cytosol-binding protein and estrogen) distributes into the cell nucleus where it stimulates DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. The presence of these receptor proteins is responsible for the palliative response to estrogen therapy in women with metastatic carcinoma of the breast. /Estrogen General Statement/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 3130
Estrogens have generally favorable effects on blood cholesterol and phospholipid concentrations. Estrogens reduce LDL-cholesterol and increase HDL-cholesterol concentrations in a dose-related manner. The decrease in LDL-cholesterol concentrations associated with estrogen therapy appears to result from increased LDL catabolism, while the increase in triglyceride concentrations is caused by increased production of large, triglyceride-rich, very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs); changes in serum HDL-cholesterol concentrations appear to result principally from an increase in the cholesterol and apolipoprotein A-1 content of HDL2- and a slight increase in HDL3-cholesterol. /Estrogen General Statement/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 3130
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for MESTRANOL (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
78
PharmaCompass offers a list of Mestranol API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Mestranol manufacturer or Mestranol supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Mestranol manufacturer or Mestranol supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Mestranol API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Mestranol API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Mestranol Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Mestranol Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Mestranol manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Mestranol, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Mestranol manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Mestranol API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Mestranol supplier is an individual or a company that provides Mestranol active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Mestranol finished formulations upon request. The Mestranol suppliers may include Mestranol API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Mestranol suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Mestranol DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Mestranol active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Mestranol DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Mestranol USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Mestranol DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Mestranol USDMF includes data on Mestranol's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Mestranol USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Mestranol suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
Mestranol Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Mestranol GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Mestranol GMP manufacturer or Mestranol GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Mestranol CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Mestranol's compliance with Mestranol specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Mestranol CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Mestranol CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Mestranol may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Mestranol EP), Mestranol JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Mestranol USP).
