
1. Aldomet
2. Alpha Methyl L Dopa
3. Alpha Methyldopa
4. Alpha-methyl-l-dopa
5. Alpha-methyldopa
6. Alphamethyldopa
7. Apo Methyldopa
8. Apo-methyldopa
9. Dopamet
10. Dopegit
11. Dopegyt
12. Dopergit
13. Hydopa
14. Meldopa
15. Methyldopate
16. Nu Medopa
17. Nu-medopa
18. Sembrina
1. 555-30-6
2. Alphamethyldopa
3. Alpha Medopa
4. Methyl Dopa
5. Methyldopa Anhydrous
6. Aldomet
7. Baypresol
8. L-alpha-methyldopa
9. Dopamet
10. Alpha-methyl Dopa
11. Hyperpax
12. Presolisin
13. Sedometil
14. Medomet
15. Alpha-methyldopa
16. Dopegyt
17. Methyl-l-dopa
18. L-(-)-alpha-methyldopa
19. L-methyl Dopa
20. Methyldopum
21. Metildopa
22. Medopren
23. Presinol
24. (s)-(-)-alpha-methyldopa
25. 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-l-alanine
26. L-(alpha-md)
27. 3-hydroxy-alpha-methyl-l-tyrosine
28. L-alpha-methyl Dopa
29. Sembrina
30. Alpha-methyl-l-dopa
31. Dopamethyperpax
32. Aldometil
33. Grospisk
34. Methoplain
35. Becanta
36. Dopatec
37. Hypolag
38. Medopa
39. Medopal
40. Alpha-methyldopa (van)
41. Aldoril
42. Alpha-methyldihydroxyphenylalanine
43. L-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylalanine
44. (s)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropanoic Acid
45. Alpha-methyl-l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
46. L-alpha-methyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
47. L-methyldopa
48. (-)-methyldopa
49. Anhydrous Methyldopa
50. Methyldopa [inn]
51. (2s)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropanoic Acid
52. Aldoril D30
53. Aldoril D50
54. Methyldopa (l,-)
55. Bayer 1440 L
56. Levo-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylalanine
57. Amd
58. C10h13no4
59. Methyldopa (levorotatory)
60. L-(-)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylalanine
61. Alpha-methyl-beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-l-alanine
62. L(-)-beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-methylalanine
63. L-(-)-alpha-methyl-beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine
64. Methyldopa (inn)
65. L-2-amino-2-methyl-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propionic Acid
66. Methyldopa, Anhydrous
67. Mk-351;methyldopa
68. Chebi:61058
69. Aldomet (tn)
70. Dopegit
71. (-)-.alpha.-methyldopa
72. Methyldopa Sesquihydrate
73. 41372-08-1
74. Lederdopa
75. Bayer-1440l
76. Mls000028644
77. M4r0h12f6m
78. Mk-351
79. Apo-methyldopa
80. Nu-medopa
81. Nsc-169916
82. Nsc-760080
83. J9.247i
84. L-.alpha.-methyldopa
85. Methyldopa Hydrate
86. Novomedopa
87. Smr000059170
88. .alpha.-methyl-l-dopa
89. L-tyrosine, 3-hydroxy-.alpha.-methyl-
90. Methyldopum [inn-latin]
91. Metildopa [inn-spanish]
92. (s)-(-)-.alpha.-methyldopa
93. Methyldopa (anhydrous)
94. 3-hydroxy-.alpha.-methyl-l-tyrosine
95. L-tyrosine, 3-hydroxy-alpha-methyl-
96. 27289-76-5
97. Ccris 4671
98. Hsdb 218
99. Sr-01000597712
100. Einecs 209-089-2
101. Nsc 169916
102. Unii-m4r0h12f6m
103. Medoba
104. L-a-methyldopa
105. A-methyl Dopa
106. Nsc169916
107. Tyrosine, 3-hydroxy-.alpha.-methyl-
108. A-methyl-l-dopa
109. 3,4-dihydroxy-2-methylphenylalanine #
110. Cas-555-30-6
111. Prestwick_732
112. (-)-a-methyldopa
113. A-methyldopa (van)
114. .alpha.-methyl-l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
115. Methyldopa (aldomet)
116. 88620-56-8
117. Alanine, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-, L-(-)-
118. Methyldopa 250 Tab
119. (-)-alpha-methyldopa
120. L-(-)--methyldopa
121. L(-)-a-methylalanine
122. L-(-)-a-methyldopa
123. Spectrum_000937
124. Tocris-0584
125. Mk-351; Methyldopa
126. Methyldopa [mi]
127. Nu-medopa Tab 125mg
128. Nu-medopa Tab 250mg
129. Nu-medopa Tab 500mg
130. L-(-)-?-methyldopa
131. (-)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-l-alanine Sesqui-hydrate
132. Novo-medopa Tab 125mg
133. Novo-medopa Tab 250mg
134. Novo-medopa Tab 500mg
135. Prestwick0_000326
136. Prestwick1_000326
137. Prestwick2_000326
138. Prestwick3_000326
139. Spectrum2_001068
140. Spectrum3_000501
141. Spectrum4_000054
142. Spectrum5_001295
143. Methyldopa [hsdb]
144. (s)-(-)-a-methyldopa
145. L(-)-alpha-methylalanine
146. Dsstox_cid_3295
147. Chembl459
148. Epitope Id:146097
149. L-(-)- Alpha-methyldopa
150. Apo Methyldopa Tab 125mg
151. Apo Methyldopa Tab 250mg
152. Apo Methyldopa Tab 500mg
153. Dsstox_rid_76962
154. Methyldopa [who-dd]
155. Dsstox_gsid_23295
156. L-(-)- Alpha -methyldopa
157. L-(a-md)
158. Lopac0_000853
159. Schembl34003
160. Bspbio_000331
161. Bspbio_002021
162. Kbiogr_000547
163. Kbioss_001417
164. Cid_38853
165. Mls006011978
166. Bidd:gt0620
167. Divk1c_000142
168. Methyldopa 125 Tab 125mg
169. Methyldopa 500 Tab 500mg
170. Spectrum1500403
171. Spbio_001056
172. Spbio_002252
173. Bpbio1_000365
174. Gtpl5217
175. Dtxsid5023295
176. Bdbm48449
177. Hms500h04
178. Kbio1_000142
179. Kbio2_001417
180. Kbio2_003985
181. Kbio2_006553
182. Kbio3_001521
183. Zinc20255
184. 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-l-alanine Sesquihydrate
185. 5-amino-2-fluorophenylboronicacid
186. Ninds_000142
187. Hms1569a13
188. Hms1920n09
189. Hms2090b11
190. Hms2091f04
191. Hms2096a13
192. Hms2235n11
193. Hms3262l07
194. Hms3372j14
195. Hms3411g18
196. Hms3675g18
197. Hms3713a13
198. Hms3887i15
199. Mk-35
200. Pharmakon1600-01500403
201. L-(-)-a-methyl-a-methyl-aldomin
202. Hy-b0225
203. Tox21_202610
204. Tox21_500853
205. Anhydrous Methyldopa [mart.]
206. Ccg-40120
207. Dl-443
208. Mfcd00004186
209. Nsc760080
210. S1642
211. A-methyl-l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
212. Akos015960582
213. Ac-8431
214. Db00968
215. Ks-1424
216. Lp00853
217. Sdccgsbi-0050829.p002
218. Idi1_000142
219. Ncgc00024667-01
220. Ncgc00024667-02
221. Ncgc00024667-03
222. Ncgc00024667-05
223. Ncgc00024667-06
224. Ncgc00024667-07
225. Ncgc00024667-08
226. Ncgc00024667-09
227. Ncgc00024667-10
228. Ncgc00024667-11
229. Ncgc00024667-13
230. Ncgc00024667-21
231. Ncgc00260158-01
232. Ncgc00261538-01
233. Ac-11671
234. As-13052
235. L-(-)-alpha-methyl-alpha-methyl-aldomin
236. Carbidopa Impurity A [ep Impurity]
237. L-a-methyl-(3, 4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine
238. D1817
239. Eu-0100853
240. 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-?-methyl-l-alanine
241. L-alpha-methyl-(3, 4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine
242. C07194
243. D08205
244. D82313
245. Ab00052043_09
246. Ab01275508-01
247. Ab01275508_02
248. 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-methyl-l-a Lanine
249. L-tyrosine, 3-hydroxy-alpha-methyl-, Homopolymer
250. Q412621
251. L-(-)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-alanine
252. Q-201392
253. Sr-01000597712-1
254. Sr-01000597712-3
255. W-105555
256. 3,4-dihydroxy-2-methylphenylalanine (acd/name 4.0)
257. (-)-.alpha.-methyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
258. L-.alpha.-methyl-3-(3,4)-dihydroxyphenylalanine
259. Z1565440340
260. (s)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropanoicacid
261. Methyldopa, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
262. (2s)-2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-propanoic Acid
263. (2s)-2-azaniumyl-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropanoate
264. Methyldopa, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
265. 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-l-alanine (h-l-ametyr(3-oh)-oh)
266. Methyldopa For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
267. L-(-)-afae'a Centa' Nota Inverted Exclamation Markafasa'a
268. Afae'adaggeratrade Mark?-methyldopa
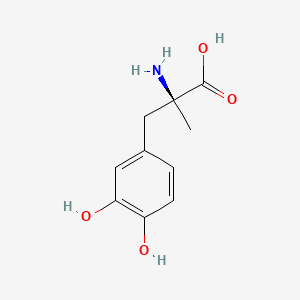
| Molecular Weight | 211.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H13NO4 |
| XLogP3 | -1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 211.08445790 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 211.08445790 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 246 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methyldopa |
| PubMed Health | Methyldopa (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Methyldopa is an antihypertensive and is the L-isomer of alpha-methyldopa. It is levo-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylalanine sesquihydrate. Methyldopa is supplied as tablets for oral administration, containing 125 mg, 250 mg and 500 mg of methyldopa... |
| Active Ingredient | Methyldopa |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Accord Hlthcare; Watson Labs; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Mylan |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Methyldopa |
| PubMed Health | Methyldopa (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Methyldopa is an antihypertensive and is the L-isomer of alpha-methyldopa. It is levo-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylalanine sesquihydrate. Methyldopa is supplied as tablets for oral administration, containing 125 mg, 250 mg and 500 mg of methyldopa... |
| Active Ingredient | Methyldopa |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Accord Hlthcare; Watson Labs; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Mylan |
Adrenergic alpha-Agonists; Antihypertensive Agents; Sympatholytics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Methyldopa is indicated in the treatment of moderate to severe hypertension, including that complicated by renal disease. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 2000
Methyldopa is an effective antihypertensive agent when given in conjunction with a diuretic.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 788
THE USUAL INITIAL DOSE OF METHYLDOPA IS 250 MG TWICE DAILY, AND THERE APPEARS TO BE LITTLE ADDNL EFFECT WITH DOSES OVER 2 G.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 788
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for METHYLDOPA (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Methyldopa should be used with caution in patients with a history of previous liver disease or dysfunction and is not recommended for use in patients with pheochromocytoma. Methyldopa is contraindicated in patients with active hepatic disease, such as acute hepatitis and active cirrhosis, and in patients in whom previous methyldopa therapy was associated with liver abnormalities or direct Coombs' positive hemolytic anemia. Methyldopa is contraindicated in patients receiving monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1512
Patients who are receiving methyldopa and who undergo dialysis may occasionally become hypertensive after the dialysis, since the drug is dialyzable.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1512
Positive direct antiglobulin (Coombs') test results have been reported in about 10-20% of patients receiving methyldopa, usually after 6-12 months of therapy. This phenomenon is dose related, with the lowest incidence in patients receiving 1 g or less of methyldopa daily. In most patients, a postive Coombs' test associated with mehtyldopa therapy is not clinically important. Reversal of the positive Coombs' test occurs within weeks to months after discontinuance of the drug and usually becomes negative within 6 months. Hemolytic anemia has only rarely occurred, although 2 deaths have been reported in patients with methyldopa-induced hemolytic anemia. If anemia or a positive Coombs' test occurs, appropriate laboratory studies should be performed to determine if hemolysis is present; if there is evidence of hemolytic anemia, the drug should be discontinued. Discontinuance of the drug alone or initiation of corticosteroid therapy has produced remission of methyldopa-induced hemolytic anemia.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1511
Nasal congestion occurs commonly in patients receiving methyldopa. Decreased libido and impotence frequently occur in males during therapy with the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1511
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for METHYLDOPA (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Methyldopa is indicated for the management of hypertension as monotherapy or in combination with hydrochlorothiazide. Methyldopa injection is used to manage hypertensive crises.
FDA Label
Antihypertensive effects of methyldopa are mostly mediated by its pharmacologically active metabolite, alpha-methylnorepinephrine, which works as an agonist at central inhibitory alpha-adrenergic receptors. Stimulation of alpha-adrenergic receptors leads to decreased peripheral sympathetic tone and reduced arterial pressure. Methyldopa causes a net reduction in the tissue concentration of serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. Overall, methyldopa lowers both standing blood pressure and especially supine blood pressure, with infrequent symptomatic postural hypotension. Methyldopa also reduces plasma renin activity but has negligible effects on glomerular filtration rate, renal blood flow, or filtration fraction. It also has no direct effect on cardiac function but in some patients, a slowed heart rate may occur. Following oral administration, blood-pressure-lowering effects are observed within 12 to 24 hours in most patients, and a maximum reduction in blood pressure occurs in 4 to 6 hours. Blood pressure returns to pre-treatment levels within 24 to 48 hours following drug discontinuation. Following intravenous administration, the blood-pressure-lowering effects of methyldopa last for about 10 to 16 hours.
Sympatholytics
Drugs that inhibit the actions of the sympathetic nervous system by any mechanism. The most common of these are the ADRENERGIC ANTAGONISTS and drugs that deplete norepinephrine or reduce the release of transmitters from adrenergic postganglionic terminals (see ADRENERGIC AGENTS). Drugs that act in the central nervous system to reduce sympathetic activity (e.g., centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, see ADRENERGIC ALPHA-AGONISTS) are included here. (See all compounds classified as Sympatholytics.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Compounds that bind to and activate ADRENERGIC ALPHA-2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C02 - Antihypertensives
C02A - Antiadrenergic agents, centrally acting
C02AB - Methyldopa
C02AB01 - Methyldopa (levorotatory)
Absorption
Methyldopa is incompletely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. In healthy individuals, the inactive D-isomer is less readily absorbed than the active L-isomer. The mean bioavailability of methyldopa is 25%, ranging from eight to 62%. Following oral administration, about 50% of the dose is absorbed and Tmax is about three to six hours.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 70% of absorbed methyldopa is excreted in the urine as unchanged parent drug (24%) and -methyldopa mono-O-sulfate (64%), with variability.3-O-methyl--methyldopa accounted for about 4% of urinary excretion products. Other metabolites like 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetone, -methyldopamine, and 3-O-methyl--methyldopamine are also excreted in urine. Unabsorbed drug is excreted in feces as the unchanged parent compound. After oral doses, excretion is essentially complete in 36 hours. Due to attenuated excretion in patients with renal failure, accumulation of the drug and its metabolites may occur, possibly leading to more profound and prolonged hypotensive effects in these patients.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution ranges between 0.19 and 0.32L/kg and the total volume of distribution ranges from 0.41 to 0.72L/kg. Since methyldopa is lipid-soluble, it crosses the placental barrier, appears in cord blood, and appears in breast milk.
Clearance
The renal clearance is about 130 mL/min in normal subjects and is decreased in patients with renal insufficiency.
(14)C-METHYLDOPA ADMIN ORALLY TO HYPERTENSIVE PT IS RECOVERED EQUALLY FROM URINE & FECES; PRODUCT IN FECES IS UNCHANGED METHYLDOPA, & IN URINE METHYLDOPA & ITS ETHEREAL SULFATE, TOGETHER WITH SMALL AMT OF 3-O-METHYL-METHYLDOPA & METHYLDOPAMINE.
Parke, D. V. The Biochemistry of Foreign Compounds. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1968., p. 180
METHYLDOPA CROSSES THE PLACENTA...
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 571
Methyldopa is partially absorbed from the GI tract. The degree of absorption varies among individuals and in the same patient from day to day, but generally about 50% of an oral dose is absorbed.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1510
Two isomers of methyldopa undergo different metabolic pathways. L--methyldopa is biotransformed to its pharmacologically active metabolite, alpha-methylnorepinephrine. Methyldopa is extensively metabolized in the liver to form the main circulating metabolite in the plasma, alpha ()-methyldopa mono-O-sulfate. Its other metabolites also include 3-O-methyl--methyldopa; 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetone; -methyldopamine; and 3-O-methyl--methyldopamine. These metabolites are further conjugated in the liver to form sulfate conjugates. After intravenous administration, the most prominent metabolites are alpha-methyldopamine and the glucuronide of dihydroxyphenylacetone, along with other uncharacterized metabolites. D--methyldopa, which is the inactive isomer of methyldopa, is also metabolized to 3-O-methyl--methyldopa and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetone to a minimal extent; however, there are no amines (-methyldopamine and 3-O-methyl--methyldopamine) formed.
METHYLDOPA YIELDS 3,4-DIHYDROXY-ALPHA-METHYLPHENETHYLAMINE, 3,4-DIHYDROXY-ALPHA-METHYL-L-PHENYLALANINE-O-SULFATE, & 4-HYDROXY-3-METHOXY-ALPHA-METHYL-L-PHENYLALANINE IN MAN. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. D-55
METHYLDOPA...UNDERGOES DECARBOXYLATION & BETA-HYDROXYLATION IN MOUSE & RABBIT BRAIN TO YIELD ALPHA-METHYLNORADRENALINE.
Parke, D. V. The Biochemistry of Foreign Compounds. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1968., p. 180
...ADMIN IP TO RATS (14)C-METHYLDOPA IS EXCRETED IN URINE AS...3-O-METHYL-METHYLDOPA (14%), METHYLDOPAMINE & ITS CONJUGATES (2%), 3-O-METHYL-METHYLDOPAMINE & ITS CONJUGATES (6%), 3-METHOXY-4-HYDROXYPHENYLACETONE (6%), & 3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYLACETONE (10%).
Parke, D. V. The Biochemistry of Foreign Compounds. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1968., p. 180
A REVIEW ON THE METAB OF ALPHA-METHYLDOPA.
MUSCHOLL E; ALPHA METHYLDOPA INT SYMP 20 (1981)
The plasma half-life of methyldopa is 105 minutes. Following intravenous injection, the plasma half-life of methyldopa ranges from 90 to 127 minutes.
The drug is ... eliminated with a half-life of about 2 hr. ... The half-life of methyldopa is prolonged to 4-6 hr in patients with renal failure.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 787
DISAPPEARANCE OF THE DRUG FROM PLASMA AFTER IV ADMIN IS BIPHASIC, & THE TERMINAL HALF-TIME OF ELIMINATION FROM PLASMA IS ABOUT 2 HOURS. RENAL EXCRETION ACCOUNTS FOR ABOUT TWO THIRDS OF THE CLEARANCE OF DRUG FROM PLASMA.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 795
IN PT WITH SEVERELY IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION, ONLY ABOUT 50% OF DRUG IS EXCRETED DURING EARLY PHASE (T/2= 3 1/2 HR), & SOME ACCUMULATION CAN OCCUR DURING CHRONIC ADMIN... BOTH TOTAL QUANTITY ABSORBED & DISTRIBUTION OF METABOLITES IN URINE CAN VARY CONSIDERABLY IN DIFFERENT INDIVIDUALS & IN SAME PT FROM DAY TO DAY.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 709
The exact mechanism of methyldopa is not fully elucidated; however, the main mechanisms of methyldopa involve its actions on alpha-adrenergic receptor and the aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase enzyme, to a lesser extent. The sympathetic outflow is regulated by alpha ()-2 adrenergic receptors and imidazoline receptors expressed on adrenergic neurons within the rostral ventrolateral medulla. Methyldopa is metabolized to methylnorepinephrine via dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity and, consequently, alpha-methylepinephrine via phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase activity. Mediating the therapeutic effects of methyldopa, methylnorepinephrine and -methylepinephrine active metabolites are agonists at presynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brainstem. Stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors results in the inhibition of adrenergic neuronal outflow and attenuation of norepinephrine release in the brainstem. Consequently, the output of vasoconstrictor adrenergic signals to the peripheral sympathetic nervous system is reduced, leading to a reduction in blood pressure. The L-isomer of alpha-methyldopa also reduces blood pressure by inhibiting aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, also known as DOPA decarboxylase, which is an enzyme responsible for the syntheses of dopamine and serotonin. Inhibiting this enzyme leads to depletion of biogenic amines such as norepinephrine. However, inhibition of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase plays a minimal role in the blood-pressurelowering effect of methyldopa.
METHYLDOPA...HAS HYPOTENSIVE ACTION INDEPENDENT OF ITS ANTIADRENERGIC ACTIONS; THIS IS PROBABLY PARTLY CENTRAL DEPRESSANT ACTION @ VASOMOTOR CENTER & PARTLY PERIPHERAL ACTION OF UNKNOWN MECHANISM.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 836
... Alpha-methylnorepinephrine acts in the brain to inhibit adrenergic neuronal outflow from the brainstem, and this central effect is principally responsible for its antihypertensive action.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 786
IN CONSCIOUS RENAL HYPERTENSIVE RATS ALPHA-METHYLDOPA PRODUCED A LONG-LASTING FALL IN BLOOD PRESSURE WHICH WAS PARTIALLY ATTENUATED BY PRETREATMENT WITH NALTREXONE (5 MG/KG SC). PRETREATMENT WITH ANTISERUM TO BETA-ENDORPHIN APPLIED LOCALLY, ALSO BLOCKED THE DEPRESSOR RESPONSE. THESE RESULTS SUGGEST THAT THE FALL IN BLOOD PRESSURE OBSERVED AFTER ALPHA-METHYLDOPA AND ITS ACTIVE METABOLITE ALPHA-METHYLNORADRENALINE INVOLVES A BETA-ENDORPHIN LIKE PEPTIDE; A POSSIBLE SITE OF ACTION IS THE NUCLEUS TRACTUS SOLITARII.
PETTY MA, DE JONG W; CLIN SCI SUPPL 63 (8): 293 (1982)
A REVIEW ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION.
KRONEBERG G; ALPHA-METHYLDOPA INT SYMP 6 (1981)