
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
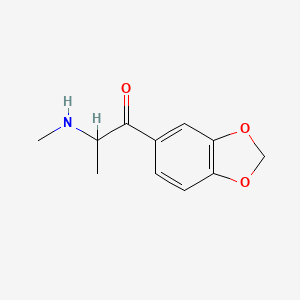

1. 3,4-methylenedioxy-n-methylcathinonmethylone
2. Beta-keto-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine
1. 186028-79-5
2. 2-methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propan-1-one
3. Bk-mdma
4. .beta.k-mdma
5. Unii-l4i4b1r01f
6. 3,4-methylenedioxy-n-methylcathinone
7. L4i4b1r01f
8. Methylenedioxymethcathinone
9. Hsdb 7997
10. M1 (psychedelic)
11. Beta-keto-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine
12. J899.632f
13. 3,4-methylenedioxy-n-methylcathinonmethylone
14. 1-propanone, 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(methylamino)-
15. Chembl3604010
16. 2-(methylamino)-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-propanone
17. 1-(2h-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(methylamino)propan-1-one
18. Mdmc
19. 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(methylamino)propan-1-one
20. (rs)-methylone
21. Betak-mdma
22. Dea No. 7540
23. Schembl1826389
24. Dtxsid80870167
25. Chebi:182618
26. Bdbm50114073
27. Ns00002964
28. C20126
29. Q4046265
| Molecular Weight | 207.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H13NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | Da |
| Monoisotopic Mass | Da |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 47.6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 244 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
In recent years, a new class of designer drugs has appeared on the drugs of abuse market in many countries, namely, the so-called beta-keto (bk) designer drugs such as mephedrone (bk-4-methylmethamphetamine), butylone (bk-MBDB), and methylone (bk-MDMA). The aim of the present study was to identify the metabolites of mephedrone in rat and human urine using GC-MS techniques and to include mephedrone, butylone, and methylone within the authors' systematic toxicological analysis (STA) procedure. Six phase I metabolites of mephedrone were detected in rat urine and seven in human urine suggesting the following metabolic steps: N-demethylation to the primary amine, reduction of the keto moiety to the respective alcohol, and oxidation of the tolyl moiety to the corresponding alcohols and carboxylic acid. The STA procedure allowed the detection of mephedrone, butylone, methylone, and their metabolites in urine of rats treated with doses corresponding to those reported for abuse of amphetamines. Besides macro-based data evaluation, an automated evaluation using the automated mass spectral deconvolution and identification system was performed. Mephedrone and butylone could be detected also in human urine samples submitted for drug testing. Assuming similar kinetics in humans, the described STA procedure should be suitable for proof of an intake of the bk-designer drugs in human urine.
PMID:20333362 Meyer MR et al; Anal Bioanal Chem 397 (3): 1225-33 (2010)
The urinary metabolites of methylone in humans and rats were investigated by analysing urine specimens from its abuser and after administrating to rats with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC-ESI MS), using authentic standards. The time-course excretion profiles of methylone and its three metabolites in rats were further investigated after a single intraperitoneal dosing of 5 mg/ kg methylone hydrochloride. Two major metabolic pathways were revealed for both humans and rats as follows: (1) side-chain degradation by N-demethylation to the corresponding primary amine methylenedioxycathinone (MDC), partly conjugated; and (2) demethylenation followed by O-methylation of either a 3- or 4-OH group on the benzene ring to produce 4-hydroxy-3-methoxymethcathinone (HMMC) or 3-hydroxy-4-methoxymethcathinone (3-OH-4-MeO-MC), respectively, mostly conjugated. Of these metabolites, HMMC was the most abundant in humans and rats. The cumulative amount of urinary HMMC excreted within the first 48 hr in rats was approximately 26% of the dose, and the amount of the parent methylone was not more than 3%. These results demonstrate that the analysis of HMMC will be indispensable for proof of the use of methylone in forensic urinalysis.
PMID:16891251 Kamata HT et al; Xenobiotica 36 (8): 709-23 (2006)
A reproducible, simple, and small-scale method for determining the re-uptake and release of monoamines (dopamine, serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine) using rat brain synaptosomes /was developed/. These assays were then applied to study the effects of different kinds of non-medically used psychoactive drugs on monoamine re-uptake and release. The phenethylamine derivatives, 4-fluoroamphetamine, 2-methylamino-3,4-methylene-dioxy-propiophenone (methylone), 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-butanamine (BDB), and N-methyl-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-butanamine (MBDB), had strong inhibitory effects on the re-uptake of dopamine, 5-HT and norepinephrine. 4-Fluoroamphetamine, methylone and BDB also strongly increased the release of the three monoamines, but MBDB increased 5-HT and norepinephrine release, but had little effect on dopamine release. However, 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (2C-I), 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenethylamine (2C-E), 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenethylamine (2C-C), 2,4,5-trimethoxyamphetamine (TMA-2) and 2,4,6-trimethoxyamphetamine (TMA-6), which are methoxylated phenethylamine derivatives, slightly influenced the re-uptake and release of monoamines. Alpha-metyltryptamine (AMT), a tryptamine derivative, was one of the strongest re-uptake inhibitors and releasers of the three monoamines. The tryptamine derivative, 5-methoxy-alpha-methyltryptamine (5-MeO-AMT), also strongly inhibited re-uptake and increased the release of the three monoamines. N,N-dipropyltryptamine (DPT), 5-methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (5-MeO-DIPT), 5-methoxy-N,N-methylisopropyltryptamine (5-MeO-MIPT), and 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT) inhibited monoamine re-uptake, but had a few effects on monoamine release. 1-(3-Chlorophenyl)piperazine (3CPP) and 1-(methoxyphenyl)piperazine (4MPP), which are piperazine derivatives, inhibited monoamine re-uptake and accelerated their release. The results suggest that some designer drugs strongly act on the central nerve system to the same extent as restricted drugs.
PMID:17223101 Nagai F et al; Eur J Pharmacol 559 (2-3): 132-7 (2007)
Methcathinone and methylone, the beta-ketone analogues of methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), respectively, were tested for neurotransmitter uptake inhibition in vitro. The beta-ketones were threefold less potent than the nonketo drugs at inhibiting platelet serotonin accumulation, with IC(50)'s of 34.6+/-4.8uM and 5.8+/-0.7 uM, respectively. Methcathinone and methylone were similar in potency to methamphetamine and MDMA at catecholamine transporters individually expressed in transfected glial cells. For dopamine uptake, IC(50)'s were 0.36+/-0.06 uM and 0.82+/-0.17 uM, respectively; for noradrenaline uptake, IC(50) values were 0.51+/-0.10 uM and 1. 2+/-0.1 microM, respectively. In chromaffin granules, IC(50)'s for serotonin accumulation were 112+/-8.0 uM for methcathinone and 166+/-12 uM for methylone, 10-fold higher than the respective values for methamphetamine and MDMA. Our results indicate that methcathinone and methylone potently inhibit plasma membrane catecholamine transporters but only weakly inhibit the vesicle transporter.
PMID:10528135 Cozzi NV et al; Eur J Pharmacol 381 (1): 63-9 (1999)
Methylone (2-methylamino-1-[3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl]propane-1-one) is a synthetic hallucinogenic amphetamine analog, like MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxy- methamphetamine), considered to act on monoaminergic systems. However, the psychopharmacological profile of its cytotoxicity as a consequence of monoaminergic deficits remains unclear. We examined here the effects of methylone on the transporters for dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, using a heterologous expression system in CHO cells, in association with its cytotoxicity. Methylone inhibited the activities of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, but not GABA transporter-1 (GAT1), in a concentration-dependent fashion with a rank order of norepinephrine > dopamine > serotonin. Methylone was less effective at inhibiting dopamine and norepinephrine, but more effective against serotonin, than was methamphetamine. Methylone alone was not toxic to cells except at high concentrations, but in combination with methamphetamine had a synergistic effect in CHO cells expressing the monoamine transporters but not in control CHO cells or cells expressing GAT1. The ability of methylone to inhibit monoamine transporter function, probably by acting as a transportable substrate, underlies the synergistic effect of methylone and methamphetamine.
PMID:21886563 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3137202 Sogawa C et al; Curr Neuropharmacol 9 (1): 58-62 (2011)
ABOUT THIS PAGE
