
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
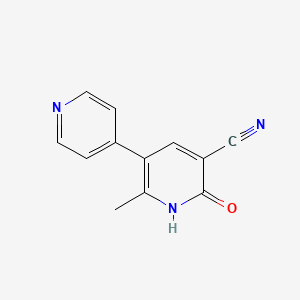

1. Corotrop
2. Corotrope
3. Lactate, Milrinone
4. Milrinone Lactate
5. Primacor
6. Win 47203
7. Win-47203
8. Win47203
1. 78415-72-2
2. Primacor
3. Milrinona
4. Milrinonum
5. Milrila
6. 2-methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-[3,4'-bipyridine]-5-carbonitrile
7. Win 47203
8. 6-methyl-2-oxo-5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-pyridine-3-carbonitrile
9. 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo(3,4'-bipyridine)-5-carbonitrile
10. Win-47203-2
11. 3-cyano-6-methyl-5-(4-pyridyl)-2-pyridone
12. Mfcd00133539
13. 2-methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-3,4'-bipyridine-5-carbonitrile
14. 6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile
15. Corotrope
16. 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo-(3,4'-bipyridine)-5-carbonitrile
17. Chembl189
18. Nsc-760072
19. Ju9yax04c7
20. Win 47,203-2
21. Chebi:50693
22. (3,4'-bipyridine)-5-carbonitrile, 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo-
23. Milrinonum [latin]
24. Ncgc00015675-08
25. Ncgc00164390-01
26. Milrinona [spanish]
27. [3,4'-bipyridine]-5-carbonitrile, 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo-
28. Cas-78415-72-2
29. Dsstox_cid_3324
30. Dsstox_rid_76978
31. Dsstox_gsid_23324
32. 2-hydroxy-6-methyl-5-pyridin-4-ylpyridine-3-carbonitrile
33. 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo-[3,4'-bipyridine]-5-carbonitrile
34. Ym 018
35. Smr000058475
36. Milrila (tn)
37. Win 47203-2
38. Ccris 3795
39. Sr-01000075524
40. Einecs 278-903-6
41. Unii-ju9yax04c7
42. Brn 3546821
43. Milrinone [usan:usp:inn:ban]
44. Milrinone- Bio-x
45. Milrinone(primacor)
46. 6-methyl-5-(4-pyridyl)-2-pyridone-3-carbonitrile
47. Milrinone (primacor)
48. Tocris-1504
49. 111ge027
50. Milrinone [inn]
51. Milrinone [jan]
52. (3,4'-bipyridine)-5-carbonitrile, 6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo-
53. Milrinone [mi]
54. Milrinone [usan]
55. 1,2-dihydro-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(4-pyridinyl)nicotinonitrile
56. Prestwick0_001065
57. Prestwick1_001065
58. Prestwick2_001065
59. Prestwick3_001065
60. Lopac-m-4659
61. Milrinone [vandf]
62. M1663
63. Milrinone [mart.]
64. M 4659
65. (non-labelled)milrinone-d3
66. Milrinone [usp-rs]
67. Milrinone [who-dd]
68. Milrinone (jan/usp/inn)
69. Lopac0_000737
70. Schembl36947
71. Bspbio_001050
72. Mls000028818
73. Mls001424052
74. Mls006011946
75. Bidd:gt0197
76. Spbio_002965
77. Bpbio1_001156
78. Gtpl5225
79. Schembl8309385
80. Dtxsid5023324
81. Bdbm15296
82. Milrinone [usp Monograph]
83. Hms1571e12
84. Hms2051l10
85. Hms2090j14
86. Hms2098e12
87. Hms2234a23
88. Hms3262c16
89. Hms3267p12
90. Hms3370h18
91. Hms3393l10
92. Hms3656g06
93. Hms3715e12
94. Hms3742g09
95. Pharmakon1600-01505489
96. Amy40564
97. Bcp02956
98. Zinc9224016
99. Tox21_112113
100. Tox21_400069
101. Tox21_500737
102. Milrinone, >=97% (tlc), Powder
103. Nsc760072
104. S2484
105. Milrinone - Cas 78415-72-2
106. 2-methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-3,4'-bipyridine-5-carbonitrile (milrinone)
107. Akos015836135
108. Tox21_112113_1
109. Ac-4730
110. Bcp9000926
111. Ccg-101020
112. Ccg-204822
113. Cs-1367
114. Db00235
115. Ks-1440
116. Lp00737
117. Nc00270
118. Nsc 760072
119. Sdccgsbi-0050715.p002
120. Ncgc00015675-01
121. Ncgc00015675-02
122. Ncgc00015675-03
123. Ncgc00015675-04
124. Ncgc00015675-05
125. Ncgc00015675-06
126. Ncgc00015675-07
127. Ncgc00015675-09
128. Ncgc00015675-11
129. Ncgc00015675-24
130. Ncgc00025189-01
131. Ncgc00025189-02
132. Ncgc00025189-03
133. Ncgc00261422-01
134. Bm164671
135. Hy-14252
136. Smr004703527
137. Sy028050
138. Bcp0726000256
139. Ab00514027
140. Eu-0100737
141. Ft-0630859
142. Sw197308-3
143. C07224
144. D00417
145. Ab00514027-02
146. Ab00514027-03
147. Ab00514027_04
148. Ab00514027_05
149. Ab00597139-08
150. 415m722
151. A839417
152. Q847399
153. Sr-01000075524-1
154. Sr-01000075524-3
155. Sr-01000075524-4
156. Sr-01000075524-6
157. W-104284
158. Brd-k67080878-001-05-5
159. Z1522568219
160. 1,2-dihydro-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(4 -pyridinyl)nicotinonitrile
161. 2-methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-[3,4']bipyridinyl-5-carbonitrile
162. Milrinone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
163. 1,2-dihydro-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-(4-pyridinyl)-nicotinonitrile
164. 6-methyl-2-oxidanylidene-5-pyridin-4-yl-1h-pyridine-3-carbonitrile
165. 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo-(3,4 Inverted Exclamation Mark -bipyridine)-5-carbonitrile
| Molecular Weight | 211.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H9N3O |
| XLogP3 | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 211.074561919 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 211.074561919 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 65.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 419 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Milrinone is indicated for the short-term (48 hours or less) treatment of patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Milrinone administration should occur together with close monitoring using appropriate electrocardiographic equipment and should occur in a facility equipped for the immediate treatment of potential cardiac events, including ventricular arrhythmias.
FDA Label
Milrinone is a bipyridine derivative with positive inotropic and lusitropic effects that also results in peripheral vasodilation with minimal chronotropic effects over a therapeutic range of 100 to 300 ng/mL. As such, milrinone is used in decompensated congestive heart failure. Studies have demonstrated that milrinone exhibits sigmoidal effects, such that increasing milrinone plasma concentrations beyond a certain level results in no further hemodynamic changes. Despite milrinone's benefits, both intravenous and oral use has been associated with increased frequency of ventricular arrhythmias, and long-term oral use has been associated with an increased risk of sudden death; in general, there are no data to support the safety or efficacy of milrinone use beyond 48 hours and patients should be monitored closely for cardiac dysfunction. Also, as milrinone is primarily excreted renally, dose adjustments may be required in patients with impaired renal function.
Phosphodiesterase 3 Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit PHOSPHODIESTERASE 3. (See all compounds classified as Phosphodiesterase 3 Inhibitors.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
C01CE02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01C - Cardiac stimulants excl. cardiac glycosides
C01CE - Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
C01CE02 - Milrinone
Absorption
When administered as an IV bolus dose of 10-100 g/kg, milrinone induces hemodynamic effects within 60 seconds reaching a peak effect by 2-5 minutes. The plasma AUC is significantly dose-dependent.
Route of Elimination
Milrinone is primarily excreted in the urine, with 60% of a dose recovered after two hours and 90% within eight hours. Approximately 83% of milrinone recovered in urine is unchanged while 12% is present as the main O-glucuronide metabolite.
Volume of Distribution
Milrinone administered intravenously to congestive heart failure patients had a volume of distribution of 0.38 L/kg (injections between 12.5-125 g/kg) and 0.45 L/kg (infusions between 0.2-0.7 g/kg/min.
Clearance
Milrinone administered intravenously to congestive heart failure patients had a clearance of 0.13 L/kg/hr (injections between 12.5-125 g/kg) and 0.14 L/kg/hr (infusions between 0.2-0.7 g/kg/min.
Animal studies suggest that two oxidative pathways are involved in milrinone metabolism, albeit only involving a small proportion of the administered dose. The major metabolite is the O-glucuronide metabolite.
Milrinone administered intravenously to congestive heart failure patients had a mean terminal elimination half-life of 2.3 hours (injections between 12.5-125 g/kg) and 2.4 hours (infusions between 0.2-0.7 g/kg/min.
Heart failure is a condition characterized by the heart's inability to provide adequate perfusion to the peripheral tissues, resulting in systemic symptoms including pulmonary, gastrointestinal, renal, and cerebral dysfunction. Although the biochemical and physiological processes underlying heart failure complex and variable, one such physiological response regulated by the sympathetic nervous system involves the eventual downregulation of cardiac -receptors, decreased catecholamine sensitivity, and a corresponding decrease in adenylyl-cyclase-mediated signalling pathways. Increased intracellular cAMP, mainly acting through protein kinase A, increases sarcolemmal calcium release through L-type calcium channels as well as calcium re-uptake mediated by phospholamban and troponin I; these actions correspond to positive inotropic and lusitropic effects, respectively. Milrinone is a partial competitive inhibitor of phosphodiesterase III (PDE-III), with a measured IC50 value of between 0.66 and 1.3 M. As a PDE-III inhibitor, milrinone results in an increase in intracellular cAMP, responsible for its pharmacological effects, including positive inotropy, positive lusitropy, and vasodilation. As milrinone affects cAMP levels through PDE-III and not through -adrenergic receptors, it is effective in patients who have downregulated or otherwise desensitized -adrenergic receptors and can be administered together with -agonists/antagonists.

API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?