
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
VMF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
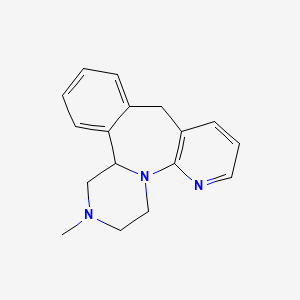

1. (n-methyl-11c)mirtazapine
2. (s)-mirtazapine
3. 6 Azamianserin
4. 6-azamianserin
5. Esmirtazapine
6. Norset
7. Org 3770
8. Org 50081
9. Org-3770
10. Org3770
11. Remergil
12. Remeron
13. Rexer
14. Zispin
1. 85650-52-8
2. Remeron
3. 61337-67-5
4. 6-azamianserin
5. Zispin
6. Mepirzepine
7. Remergil
8. Rexer
9. Promyrtil
10. Remergon
11. Norset
12. Mirtazepine
13. Avanza
14. Remeron Soltab
15. Mepirzapin
16. Mirtazipine
17. Org 3770
18. Mirtazapina
19. Mirtazapinum
20. Mirtazapinum [inn-latin]
21. Mirtazapina [inn-spanish]
22. Mirtazapin
23. Org-3770
24. 2-methyl-1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydropyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c][2]benzazepine
25. Mirataz
26. 2-methyl-1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydrobenzo[c]pyrazino[1,2-a]pyrido[3,2-f]azepine
27. Org3770
28. Mirtazapine Anhydrous
29. 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c][2]benzazepine
30. 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino(2,1-a)pyrido(2,3-c)benzazepine
31. Chembl654
32. Mirtazapine (remeron, Avanza)
33. Chebi:6950
34. (r)-org3770;(r)-6-azamianserin
35. (s)-org3770;(s)-6-azamianserin
36. Pyrazino(2,1-a)pyrido(2,3-c)(2)benzazepine, 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methyl-
37. A051q2099q
38. Ncgc00025346-02
39. Pyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c][2]benzazepine, 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methyl-
40. Azamianserin
41. Mirtazapine [usan:ban:inn]
42. Smilon
43. 2-methyl-1,2,3,4,9,13b-hexahydro-2,4a,5-triaza-tribenzo[a,c,e]cycloheptene
44. 5-methyl-2,5,19-triazatetracyclo[13.4.0.02,7.08,13]nonadeca-1(15),8,10,12,16,18-hexaene
45. Smr000466347
46. Remeron (tn)
47. Sr-01000597530
48. Einecs 288-060-6
49. Mepirzapine
50. Unii-a051q2099q
51. 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c](2)benzazepine
52. Mirtazapine [usan:usp:inn:ban]
53. Mirtazapine Solution
54. Mirtazapine- Bio-x
55. Mfcd00865427
56. Reflex (tn)
57. (1)-1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino(2,1-a)pyrido(2,3-c)(2)benzazepine
58. Mianserin, 6-aza-
59. 5-methyl-2,5,19-triazatetracyclo[13.4.0.0^{2,7}.0^{8,13}]nonadeca-1(15),8(13),9,11,16,18-hexaene
60. Me-2040
61. Mirtazapine [mi]
62. Mirtazapine [inn]
63. Mirtazapine [jan]
64. Dsstox_cid_3325
65. Mirtazapine [usan]
66. Mirtazapine [vandf]
67. Dsstox_rid_76979
68. Dsstox_gsid_23325
69. Schembl35408
70. Mirtazapine [usp-rs]
71. Mirtazapine [who-dd]
72. Mls000759460
73. Mls001076676
74. Mls001424294
75. Mls006011449
76. Mirtazapine (jan/usp/inn)
77. Gtpl7241
78. Dtxsid0023325
79. Mirtazapine [green Book]
80. Mirtazapine, (+/-)-
81. Mirtazapine, >=98% (hplc)
82. Mirtazapine [orange Book]
83. Hms2052h03
84. Hms2233k03
85. Hms3268f21
86. Hms3370b05
87. Hms3374j01
88. Hms3394h03
89. Hms3413c11
90. Hms3657m13
91. Hms3677c11
92. Hms3713p13
93. Hms3884o18
94. Mirtazapine [ep Monograph]
95. Mirtazapine [usp Monograph]
96. Bcp14560
97. Bcp22244
98. Hy-b0352
99. Mirtazapine 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
100. Tox21_110965
101. Bdbm50115644
102. Pdsp1_001529
103. Pdsp2_001513
104. S2016
105. Stk711107
106. Akos005530681
107. Bcp9000930
108. Ccg-101154
109. Ccg-220556
110. Db00370
111. Ks-1086
112. Nc00404
113. (14br)-2-methyl-1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydropyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c][2]benzazepine
114. Ncgc00025346-01
115. Ncgc00025346-08
116. 5-methyl-2,5,19-triazatetracyclo[13.4.0.0^{2,7}.0^{8,13}]nonadeca-1(19),8(13),9,11,15,17-hexaene
117. Ac-15480
118. Bm164672
119. Cas-61337-67-5
120. Ft-0601544
121. Ft-0628951
122. Ft-0672414
123. M-130
124. M2151
125. Sw197784-4
126. En300-49851
127. C07570
128. D00563
129. Ab00698265_08
130. 337m675
131. A914630
132. L001294
133. Q421930
134. Sr-01000597530-1
135. Sr-01000597530-4
136. Brd-a64977602-001-01-9
137. Brd-a64977602-001-04-3
138. Z2327131613
139. Mirtazapine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
140. Mirtazapine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
141. (+/-)-12-methyl-1,2,3,4,9,13b-hexahydro-2,4a,5-triaza-tribenzo[a,c,e]cycloheptene
142. 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c][2]benzazepine.
143. 2-methyl-1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydrobenzo-[c]pyrazino[1,2-a]pyrido[3,2-f]azepine
144. Mirtazapine For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
145. Mirtazapine Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
146. 5-methyl-2,5,19-triazatetracyclo[13.4.0.0?,?.0?,??]nonadeca-1(15),8,10,12,16,18-hexaene
147. Pyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c][2]benzazepine, 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methyl-, (.+/-.)-
| Molecular Weight | 265.35 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H19N3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 265.157897619 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 265.157897619 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 19.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 345 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mirtazapine |
| PubMed Health | Mirtazapine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidepressant |
| Drug Label | Mirtazapine Tablets USP are an orally administered drug. Mirtazapine has a tetracyclic chemical structure and belongs to the piperazino-azepine group of compounds. It is designated 1,2,3,4,10,14b-Hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c]benzazep... |
| Active Ingredient | Mirtazapine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 7.5mg; 30mg; 15mg; 45mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Actavis Labs Fl; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Mylan |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Remeron |
| PubMed Health | Mirtazapine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidepressant |
| Drug Label | REMERON (mirtazapine) Tablets are an orally administered drug. Mirtazapine has a tetra-cyclic chemical structure and belongs to the piperazino-azepine group of compounds. It is designated 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino [2,1-a] pyrido [2,... |
| Active Ingredient | Mirtazapine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg; 45mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Organon Usa |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Remeron soltab |
| Active Ingredient | Mirtazapine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg; 45mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Organon Usa |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mirtazapine |
| PubMed Health | Mirtazapine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidepressant |
| Drug Label | Mirtazapine Tablets USP are an orally administered drug. Mirtazapine has a tetracyclic chemical structure and belongs to the piperazino-azepine group of compounds. It is designated 1,2,3,4,10,14b-Hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c]benzazep... |
| Active Ingredient | Mirtazapine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 7.5mg; 30mg; 15mg; 45mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Actavis Labs Fl; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Mylan |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Remeron |
| PubMed Health | Mirtazapine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidepressant |
| Drug Label | REMERON (mirtazapine) Tablets are an orally administered drug. Mirtazapine has a tetra-cyclic chemical structure and belongs to the piperazino-azepine group of compounds. It is designated 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino [2,1-a] pyrido [2,... |
| Active Ingredient | Mirtazapine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg; 45mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Organon Usa |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Remeron soltab |
| Active Ingredient | Mirtazapine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, orally disintegrating |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg; 45mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Organon Usa |
This drug is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder and its associated symptoms. Mirtazapine has been used off-label for a variety of conditions including panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, dysthymia, tension headaches, hot flushes, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), sleep disorders, substance abuse disorders, and sexual disorders, among others.
FDA Label
For bodyweight gain in cats experiencing poor appetite and weight loss resulting from chronic medical conditions.
**General effects and a note on suicidality** Mirtazapine is effective in treating moderate to severe depression and treats many symptoms normally associated with this condition. These symptoms may include disturbed sleep, lack of appetite, and anhedonia, in addition to anxiety.. It is important to note that suicidal ideation and behavior may emerge or increase during treatment with mirtazapine, as with any other antidepressant. This risk is especially pronounced in younger individuals. Patients, medical professionals, and families should monitor for suicidal thoughts, worsening depression, anxiety, agitation, sleep changes, irritable behavior, aggression, impulsivity, restlessness, and other unusual behavior when this drug is taken or the dose is adjusted. Do not administer mirtazapine to children. When deciding to prescribe this drug, carefully consider the increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior, especially in young adults. **Effects on appetite and weight gain** In addition to the above effects, mirtazapine exerts stimulating effects on appetite, and has been used for increasing appetite and decreasing nausea in cancer patients. Some studies and case reports have shown that this drug improves eating habits and weight gain in patients suffering from anorexia nervosa when administered in conjunction with psychotherapy and/or other psychotropic drugs. In a clinical trial, women with depression experienced a clinically significant mean increase in body weight, fat mass, and concentrations of leptin when treated with mirtazapine for a 6-week period, with a lack of effect on glucose homeostasis. **Effects on sleep** The use of mirtazapine to treat disordered sleep has been leveraged from its tendency to cause somnolence, which is a frequently experienced adverse effect by patients taking this drug. Mirtazapine has been shown to exert beneficial effects on sleep latency, duration, and quality due to its sedating properties. Insomnia is a common occurrence in patients with depression, and mirtazapine has been found to be efficacious in treating this condition.
Anti-Anxiety Agents
Agents that alleviate ANXIETY, tension, and ANXIETY DISORDERS, promote sedation, and have a calming effect without affecting clarity of consciousness or neurologic conditions. ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS are commonly used in the symptomatic treatment of anxiety but are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Anxiety Agents.)
Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate SEROTONIN 5-HT2 RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of SEROTONIN or SEROTONIN 5-HT2 RECEPTOR AGONISTS. Included under this heading are antagonists for one or more specific 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists.)
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to and block the activation of ADRENERGIC ALPHA-2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Antagonists.)
Antidepressive Agents
Mood-stimulating drugs used primarily in the treatment of affective disorders and related conditions. Several MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS are useful as antidepressants apparently as a long-term consequence of their modulation of catecholamine levels. The tricyclic compounds useful as antidepressive agents (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) also appear to act through brain catecholamine systems. A third group (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, SECOND-GENERATION) is a diverse group of drugs including some that act specifically on serotonergic systems. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents.)
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate SEROTONIN 5-HT3 RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of SEROTONIN or SEROTONIN 5-HT3 RECEPTOR AGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists.)
QN06AX11
N06AX11
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06A - Antidepressants
N06AX - Other antidepressants
N06AX11 - Mirtazapine
Absorption
The absorption of this drug is rapid and complete. Due to first pass metabolism in the liver and metabolism in the gut wall, absolute bioavailability is about 50%. Peak blood concentrations are attained within about 2 hours after an oral dose. Food has little effect on the absorption of mirtazapine, and no dose adjustment is required if it is taken with food. Steady-state levels are achieved by about 5 days after the initial dose. Mirtazapine pharmacokinetics vary across gender and age range. Females and the elderly population have been shown to have higher blood concentrations in comparison to males and younger adults.
Route of Elimination
This drug is mainly excreted by the kidney. It is 75% eliminated in the urine and 15% eliminated in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution after an oral steady-state dose was measured to be 107 42L in a pharmacokinetic study.
Clearance
Total body clearance in males was found to be 31 L/h in a clinical pharmacokinetics study after intravenous administration. **Clearance in elderly patients*
Mirtazapine clearance is slower in the elderly than in younger subjects. Exercise caution when this drug is given to elderly patients. In a clinical trial, elderly males showed a marked decrease in mirtazapine clearance when compared to young males taking the same dose. This difference was less significant when clearance was compared between elderly females and younger females taking mirtazapine. **Clearance in hepatic and renal impairment** Patients with hepatic and renal impairment have decreased rates of clearance and dosage adjustments may be necessary for these patients. Moderate renal impairment and hepatic impairment cause about a 30% decrease in mirtazapine clearance. Severe renal impairment leads to a 50% decrease in mirtazapine clearance.
Mirtazapine is heavily metabolized in humans. Demethylation and hydroxylation and subsequent glucuronide conjugation are the major pathways by which mirtazapine is metabolized. Data from in vitro studies on human liver microsomes show that cytochrome 2D6 and 1A2 lead to the formation of the _8-hydroxy metabolite_ of mirtazapine. The CYP3A enzyme metabolizes this drug into its _N-desmethyl and N-oxide_ metabolites. There are various other unconjugated metabolites of this drug that are pharmacologically active, but are measured in the blood at limited concentrations.
Mirtazapine has known human metabolites that include 8-hydroxy-mirtazapine, Mirtazapine N-oxide, and N-Desmethylmirtazapine.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
20-40 hours
**Summary** The mechanism of action of mirtazapine is not fully understood but may be explained by its effects on central adrenergic and serotonergic activity. This drug exhibits a fast onset of action, a high level of response, a manageable side-effect profile, and dual noradrenergic and serotonergic effects that are unique from the effects of other antidepressants. **Effects on various receptors** It has been shown that both noradrenergic and serotonergic activity increase following mirtazapine administration. The results of these studies demonstrate mirtazapine exerts antagonist activity at presynaptic 2-adrenergic inhibitory autoreceptors and heteroreceptors in the central nervous system. This is thought to lead to enhanced noradrenergic and serotonergic activity, which are known to improve the symptoms of depression and form the basis of antidepressant therapy. Mirtazapine is a strong antagonist of serotonin 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. It has not been found to bind significantly to the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors but indirectly increases 5-HT1A transmission. In addition to the above effects, mirtazapine is a peripheral 1-adrenergic antagonist. This action may explain episodes of orthostatic hypotension that have been reported after mirtazapine use. Mirtazapine is a potent histamine (H1) receptor antagonist, which may contribute to its powerful sedating effects. The pain-relieving effects of mirtazapine may be explained by its effects on opioid receptors.
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 10457
Submission : 1993-08-30
Status : Active
Type : II
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 16007
Submission : 2002-06-11
Status : Active
Type : II
GDUFA
DMF Review : Complete
Rev. Date : 2023-12-28
Pay. Date : 2023-11-24
DMF Number : 30850
Submission : 2016-09-07
Status : Active
Type : II
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 24022
Submission : 2010-08-04
Status : Active
Type : II
 TAPI, a leading global supplier of APIs, provides over 350 products and customized CDMO solutions for every stage of development.
TAPI, a leading global supplier of APIs, provides over 350 products and customized CDMO solutions for every stage of development.
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 15323
Submission : 2001-03-02
Status : Active
Type : II
GDUFA
DMF Review : Complete
Rev. Date : 2024-12-13
Pay. Date : 2024-11-22
DMF Number : 31322
Submission : 2017-01-19
Status : Active
Type : II
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 37013
Submission : 2022-03-30
Status : Active
Type : II
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 16014
Submission : 2002-06-20
Status : Inactive
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 8357
Submission : 1989-08-21
Status : Inactive
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : Complete
Rev. Date : 2013-04-30
Pay. Date : 2013-04-17
DMF Number : 15749
Submission : 2001-12-05
Status : Active
Type : II

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
19
PharmaCompass offers a list of Mirtazapine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Mirtazapine manufacturer or Mirtazapine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Mirtazapine manufacturer or Mirtazapine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Mirtazapine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Mirtazapine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Mirtazapine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Mirtazapine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Mirtazapine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Mirtazapine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Mirtazapine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Mirtazapine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Mirtazapine supplier is an individual or a company that provides Mirtazapine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Mirtazapine finished formulations upon request. The Mirtazapine suppliers may include Mirtazapine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Mirtazapine DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Mirtazapine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Mirtazapine DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Mirtazapine USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Mirtazapine DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Mirtazapine USDMF includes data on Mirtazapine's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Mirtazapine USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Mirtazapine Drug Master File in Japan (Mirtazapine JDMF) empowers Mirtazapine API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Mirtazapine JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Mirtazapine JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Mirtazapine Drug Master File in Korea (Mirtazapine KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Mirtazapine. The MFDS reviews the Mirtazapine KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Mirtazapine KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Mirtazapine KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Mirtazapine API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Mirtazapine CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Mirtazapine Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Mirtazapine CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Mirtazapine EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Mirtazapine to their clients by showing that a Mirtazapine CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Mirtazapine CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Mirtazapine CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Mirtazapine CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Mirtazapine DMF.
A Mirtazapine CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Mirtazapine CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Mirtazapine written confirmation (Mirtazapine WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Mirtazapine manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Mirtazapine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Mirtazapine APIs or Mirtazapine finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Mirtazapine WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Mirtazapine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Mirtazapine API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Mirtazapine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Mirtazapine and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Mirtazapine NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Mirtazapine suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Mirtazapine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Mirtazapine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Mirtazapine GMP manufacturer or Mirtazapine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Mirtazapine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Mirtazapine's compliance with Mirtazapine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Mirtazapine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Mirtazapine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Mirtazapine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Mirtazapine EP), Mirtazapine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Mirtazapine USP).

