
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
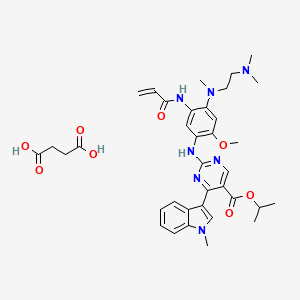

1. 2389149-74-8
2. Mobocertinib (succinate)
3. Tak-788 Succinate
4. Ap32788 Succinate
5. Ap-32788 Succinate
6. 53qia92zee
7. Unii-53qia92zee
8. Exkivity
9. Propan-2-yl 2-(5-(acryloylamino)-4-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(methyl)amino)-2-methoxyanilino)-4-(1-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate Succinate
10. Mobocertinib Succinate (jan)
11. Mobocertinib Succinate [jan]
12. Butanedioic Acid;propan-2-yl 2-[4-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl-methylamino]-2-methoxy-5-(prop-2-enoylamino)anilino]-4-(1-methylindol-3-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
13. 788succinic Acid
14. Exkivity (tn)
15. Tak788 Succinate
16. Tak 788 Succinate
17. Ap 32788 Succinate
18. Mobocertinib (succinate)?
19. Chembl4802239
20. Schembl25406916
21. Wlz3772
22. Glxc-25145
23. Bcp33315
24. Ex-a3982
25. At30194
26. Hy-135815a
27. Mobocertinib Succinate [who-dd]
28. Da-65572
29. Ms-31177
30. Tak-788 Succinate; Ap32788 Succinate
31. Mobocertinib Succinate [orange Book]
32. Cs-0114257
33. D11969
34. Isopropyl 2-((5-acrylamido-4-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(methyl)amino)-2-methoxyphenyl)amino)-4-(1-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate Succinic Acid
35. Propan-2-yl 2-(4-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(methyl)amino)-2-methoxy-5-(prop-2-enamido)anilino)-4-(1-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate Monosuccinate
36. Propan-2-yl 2-[4-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl-methylamino]-2-methoxy-5-(prop-2-enoylamino)anilino]-4-(1-methylindol-3-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate Succinate
37. Tak-788 Succinate; Ap32788 Succinate;tak 788 Succinate; Ap 32788 Succinate;tak788 Succinate; Ap-32788 Succinate
| Molecular Weight | 703.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C36H45N7O8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 16 |
| Exact Mass | Da |
| Monoisotopic Mass | Da |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 188 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 51 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1030 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
