
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
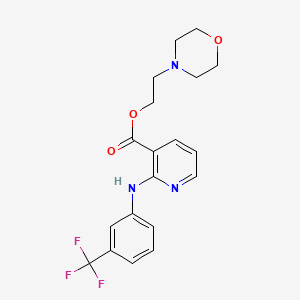

1. Beta-morpholinoethyl Niflumate
2. Niflumic Acid Beta-morpholinoethyl Ester
1. 65847-85-0
2. Up 164
3. Flomax;up 164
4. 2-morpholin-4-ylethyl 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]pyridine-3-carboxylate
5. R133mwh7x1
6. 2-morpholinoethyl 2-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)nicotinate
7. Up-164
8. Morniflumate (usan)
9. Morniflumatum
10. Morniflumate [usan]
11. Morniflumato
12. 2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl 2-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}pyridine-3-carboxylate
13. 3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid, 2-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)-, 2-(4-morpholinylethyl) Ester
14. Morniflumate [usan:inn]
15. Morniflumatum [inn-latin]
16. Morniflumato [inn-spanish]
17. Unii-r133mwh7x1
18. Nifluminsaeure 2-morpholinoethylester
19. Niflumic Acid Beta-morpholinoethyl Ester
20. Morniflumate [inn]
21. Dsstox_cid_31587
22. Dsstox_rid_97471
23. Dsstox_gsid_57798
24. Schembl50683
25. Morniflumate [mart.]
26. Morniflumate [who-dd]
27. 2-morpholinoethyl 2-(3-trifluoromethylanilino)nicotinat
28. Chembl2105059
29. Dtxsid6057798
30. Chebi:136018
31. Tox21_113913
32. Zinc21999791
33. 2-morpholinoethyl 2-(alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-m-toluidino)nicotinate
34. Akos015918126
35. Db09285
36. Ncgc00262915-01
37. As-15259
38. Hy-17488
39. Cas-65847-85-0
40. Db-054848
41. Cs-0009223
42. Ft-0628990
43. D05078
44. 847m850
45. A835248
46. Niflumic Acid .beta.-morpholinoethyl Ester
47. 2,4-dimethyl-thiazole-5-carboxylicacidamide
48. Q-201412
49. Q6912761
50. Niflumic Acid .beta.-morpholinoethyl Ester [mi]
51. 2-morpholinoethyl 2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenylamino)nicotinate
52. 2-morpholinoethyl2-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)nicotinate
53. 2-morpholinoethyl 2-(a,a,a-trifluoro-m-toluidino)nicotinate
54. 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]-3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid 2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl Ester
55. 2-morpholin-4-ylethyl 2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]pyridine-3-carboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 395.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H20F3N3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 395.14567599 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 395.14567599 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 501 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Morniflumate is indicated for the treatment of inflammatory conditions affecting the airways, ENT system, urogenital tract and bone and joint systems in adults. In Italy, morniflumate is also indicated for the treatment of pain associated with ear, nose, throat (ENT) and gastrointestinal inflammatory conditions in children. Morniflumate is a well established NSAID that has been in use for over three decades in Italy (particularly for the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections in children), France, Belgium, Austria, Switzerland, Spain and Portugal; it has a generally favorable tolerability profile.
Morniflumate, given at therapeutic dosages to healthy human volunteers, on leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and thromboxane (TXB2) synthesis, both in purified PMNs (polymorphnuclear neutrophils) and in whole blood. In whole blood experiments, morniflumate reduced blood leukotriene B4 (LTB4) synthesis induced by Ca-ionophore A23187 Bx approximately 50%, both after a single dose and at steady state; the level of inhibition showed a pattern similar to the plasma levels of the bioactive metabolite of morniflumate (M1). The inhibition of serum thromboxane B2 (TXB2) levels was higher than 85%. Hence, morniflumate is demonstrated to reduce arachidonic acid metabolism, by exerting its effects on cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase. This characteristic might provide a better approach for anti-inflammatory therapy. In several animal models orally administered morniflumate, the beta-morpholinoethyl ester of niflumic acid, proved almost equal to the parent compound in anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity with the absence of gastric irritating/ulcerogenic effects of its acidic parent compound.
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AX - Other antiinflammatory and antirheumatic agents, non-steroids
M01AX22 - Morniflumate
Route of Elimination
0.12 L /kg on average
Clearance
45 ml/min
The pharmacokinetic availability of niflumic acid in two different pharmaceutical preparations have been studied in 12 subjects after oral administration. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics studies after oral and intravenous (IV) administration demonstrate that morniflumate is absorbed as from the gastrointestinal tract, followed by rapid hydrolysis in the plasma, releasing the free acidic form, the molecule responsible for its anti-inflammatory effects. The ester displays gastroprotective effect against the ulcerogenic effects of niflumic acid.
2h
The primary mechanism of niflumic acid and its ester is action is inhibition of enzymes involved in the synthesis of inflammatory prostaglandins. This medication inhibits cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase pathways, which lead to fever and inflammation. Niflumic acid, a calcium-activated Cl- channel blocker, is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent used in the treatment of inflammatory conditions. Niflumic acid does directly inhibit calcium channels or activate potassium channels. Niflumic acid selectively reduces noradrenaline- and 5-HT-induced pressor responses by inhibiting a mechanism which leads to the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels. Niflumic acid (NFA) produces biphasic behavior on human CLC-K channels that suggests the presence of two functionally different binding sites: an activating site and a blocking site.
Global Sales Information

ABOUT THIS PAGE
14
PharmaCompass offers a list of Morniflumate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Morniflumate manufacturer or Morniflumate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Morniflumate manufacturer or Morniflumate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Morniflumate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Morniflumate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Morniflumate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Morniflumate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Morniflumate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Morniflumate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Morniflumate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Morniflumate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Morniflumate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Morniflumate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Morniflumate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Morniflumate finished formulations upon request. The Morniflumate suppliers may include Morniflumate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Morniflumate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Morniflumate Drug Master File in Korea (Morniflumate KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Morniflumate. The MFDS reviews the Morniflumate KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Morniflumate KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Morniflumate KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Morniflumate API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Morniflumate suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
Morniflumate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Morniflumate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Morniflumate GMP manufacturer or Morniflumate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Morniflumate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Morniflumate's compliance with Morniflumate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Morniflumate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Morniflumate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Morniflumate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Morniflumate EP), Morniflumate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Morniflumate USP).
