
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
EU WC
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
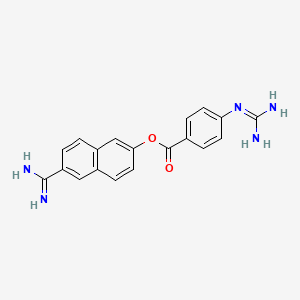

1. 6'-amidino-2-naphthyl 4-guanidinobenzoate
2. 6'-amidino-2-naphthyl 4-guanidinobenzoate, Dimethanesulfonate
3. Benzoic Acid, 4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-, 6-(aminoiminomethyl)-2-naphthalenyl Ester
4. Benzoic Acid, 4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-, 6-(aminoiminomethyl)-2-naphthalenyl Ester, Dihydrochloride
5. Benzoic Acid, 4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-, 6-(aminoiminomethyl)-2-naphthalenyl Ester, Dimethanesulfonate
6. Ckd-314
7. Ckd314
8. Fut 175
9. Fut-175
10. Nafamostat Dihydrochloride
11. Nafamostat Mesilate
12. Nafamostat Mesylate
13. Nafamstat Mesilate
14. Ronastat
1. 81525-10-2
2. Nafamostat [inn]
3. Nafamstat
4. (6-carbamimidoylnaphthalen-2-yl) 4-(diaminomethylideneamino)benzoate
5. Chembl273264
6. Y25lq0h97d
7. P-guanidinobenzoic Acid Ester With 6-hydroxy-2-naphthamidine
8. Nafamostat (inn)
9. Benzoic Acid, 4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-, 6-(aminoiminomethyl)-2-naphthalenyl Ester
10. 6-carbamimidoylnaphthalen-2-yl 4-guanidinobenzoate
11. Nafamostatum [latin]
12. Nafamostatum
13. Nafamostat Mesylate(fut-175)
14. 6-[amino(imino)methyl]-2-naphthyl 4-{[amino(imino)methyl]amino}benzoate Dimethanesulfonate
15. Ncgc00160398-01
16. 6-amidino2-naphthyl 4-guanidinobenzoate
17. Unii-y25lq0h97d
18. Nafabelltan
19. Ckd314
20. Ckd-314
21. Nafamostat [mi]
22. 6-(aminoiminomethyl)-2-naphthalenyl 4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)benzoate
23. Nafamostat [who-dd]
24. Bspbio_001194
25. Schembl135503
26. Gtpl4262
27. Dtxsid0048420
28. Amy8858
29. Chebi:135466
30. Hms3742k19
31. Albb-027243
32. Bcp13085
33. Hy-b0190
34. Zinc3874467
35. Bdbm50063698
36. Akos017259237
37. Db12598
38. 6-amidino-2-naphthyl P-guanidinobenzoate
39. Ncgc00160398-02
40. Ncgc00160398-03
41. Ncgc00160398-04
42. Ncgc00160398-13
43. Bs-17665
44. B1177
45. Ft-0629861
46. Fut-175; Fut 175; Fut175
47. D08240
48. Mls-0435512.0001
49. Ab01566816_01
50. 525n102
51. A840154
52. Q15409374
53. (6-carbamimidoyl-2-naphthyl) 4-guanidinobenzoate;nafamostat
54. (6-carbamimidoylnaphthalen-2-yl) 4-carbamimidamidobenzoate
55. 4-guanidino-benzoic Acid 6-carbamimidoyl-naphthalen-2-yl Ester
56. 6-carbamimidoylnaphthalen-2-yl 4-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]benzoate
57. 4-guanidino-benzoic Acid 6-carbamimidoyl-naphthalen-2-yl Ester(fut-175)
58. Benzoic Acid, 4-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-,6-(aminoiminomethyl)-2-naphthalenyl Ester
59. Benzoic Acid, 4-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-, 6-(aminoiminomethyl)-2-naphthalenyl Ester, Methanesulfonate (1:2)
| Molecular Weight | 347.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H17N5O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 347.13822480 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 347.13822480 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 141 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 552 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used as an anticoagulant in patients with disseminative blood vessel coagulation, hemorrhagic lesions, and hemorrhagic tendencies. It prevents blood clot formation during extracorporeal circulation in patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy and extra corporeal membrane oxygenation.
Nafamostat is a fast-acting proteolytic inhibitor used during hemodialysis to prevent the proteolysis of fibrinogen into fibrin by competitively inhibiting several serine proteases including thrombin. It improves acute pancreatitis and prevents blood clot formation during extracorporeal circulation and has an anti-inflammatory effect in vitro. A study suggets that nafamostat has a neuroprotective role during ischemia-induced brain injury from antithrombin activity.
Complement Inactivating Agents
Compounds that negatively regulate the cascade process of COMPLEMENT ACTIVATION. Uncontrolled complement activation and resulting cell lysis is potentially dangerous for the host. (See all compounds classified as Complement Inactivating Agents.)
Anticoagulants
Agents that prevent BLOOD CLOTTING. (See all compounds classified as Anticoagulants.)
Serine Proteinase Inhibitors
Exogenous or endogenous compounds which inhibit SERINE ENDOPEPTIDASES. (See all compounds classified as Serine Proteinase Inhibitors.)
Trypsin Inhibitors
Serine proteinase inhibitors which inhibit trypsin. They may be endogenous or exogenous compounds. (See all compounds classified as Trypsin Inhibitors.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Protease Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit or antagonize biosynthesis or actions of proteases (ENDOPEPTIDASES). (See all compounds classified as Protease Inhibitors.)
Route of Elimination
Two metabolites of NM, p-guanidinobenzoic acid (PGBA) and 6-amidino-2-naphthol (AN), are renally excreted. Nafamostat accumulates in the kidneys.
Nafamostat is mainly hydrolyzed by hepatic carboxyesterase and long-chain acyl-CoA hydrolase in human liver cytosol. Main metabolites are p-guanidinobenzoic acid (PGBA) and 6-amidino-2-naphthol (AN) as inactive protease inhibitors.
Approximately 8 minutes
Nafamostat mesilate inhibits various enzyme systems, such as coagulation and fibrinolytic systems (thrombin, Xa, and XIIa), the kallikreinkinin system, the complement system, pancreatic proteases and activation of protease-activated receptors (PARs). Nafamostat inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production, apoptosis, and interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 levels in cultured human trophoblasts. It is shown to act as an antioxidant in TNF--induced ROS production.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Market Place

ABOUT THIS PAGE
72
PharmaCompass offers a list of Nafamostat API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Nafamostat manufacturer or Nafamostat supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Nafamostat manufacturer or Nafamostat supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Nafamostat API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Nafamostat API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Nafamostat Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Nafamostat Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Nafamostat Mesylate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Nafamostat Mesylate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Nafamostat Mesylate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Nafamostat Mesylate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Nafamostat Mesylate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Nafamostat Mesylate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Nafamostat Mesylate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Nafamostat Mesylate finished formulations upon request. The Nafamostat Mesylate suppliers may include Nafamostat Mesylate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Nafamostat Mesylate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Nafamostat Mesylate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Nafamostat Mesylate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Nafamostat Mesylate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Nafamostat Mesylate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Nafamostat Mesylate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Nafamostat Mesylate USDMF includes data on Nafamostat Mesylate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Nafamostat Mesylate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Nafamostat Mesylate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Nafamostat Mesylate Drug Master File in Japan (Nafamostat Mesylate JDMF) empowers Nafamostat Mesylate API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Nafamostat Mesylate JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Nafamostat Mesylate JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Nafamostat Mesylate suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Nafamostat Mesylate Drug Master File in Korea (Nafamostat Mesylate KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Nafamostat Mesylate. The MFDS reviews the Nafamostat Mesylate KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Nafamostat Mesylate KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Nafamostat Mesylate KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Nafamostat Mesylate API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Nafamostat Mesylate suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Nafamostat Mesylate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Nafamostat Mesylate API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Nafamostat Mesylate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Nafamostat Mesylate and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Nafamostat Mesylate NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Nafamostat Mesylate suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Nafamostat Mesylate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Nafamostat Mesylate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Nafamostat Mesylate GMP manufacturer or Nafamostat Mesylate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Nafamostat Mesylate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Nafamostat Mesylate's compliance with Nafamostat Mesylate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Nafamostat Mesylate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Nafamostat Mesylate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Nafamostat Mesylate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Nafamostat Mesylate EP), Nafamostat Mesylate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Nafamostat Mesylate USP).
