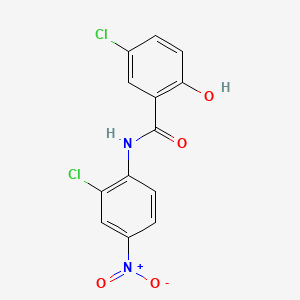

1. Bayer 2353
2. Bayer 73
3. Bayluscide
4. Clonitralide
5. Fenasal
6. Niclocide
7. Niclosamide, 2-aminoethanol (1:1)
8. Phenasal
9. Radewerm
10. Trdmine
11. Yomesan
1. 50-65-7
2. 5-chloro-n-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)-2-hydroxybenzamide
3. Niclocide
4. Bayluscid
5. Phenasal
6. Tredemine
7. Fenasal
8. Yomesan
9. Dichlosale
10. Helmiantin
11. Atenase
12. Cestocid
13. Devermin
14. Devermine
15. Iomesan
16. Iomezan
17. Mansonil
18. Radeverm
19. Sagimid
20. Vermitid
21. Lintex
22. Nasemo
23. Sulqui
24. 2',5-dichloro-4'-nitrosalicylanilide
25. Mato
26. Fedal-telmin
27. Bayer 73
28. Zestocarp
29. Bayer 2353
30. Bay 2353
31. Chemagro 2353
32. Benzamide, 5-chloro-n-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)-2-hydroxy-
33. Wr 46234
34. 5-chloro-2'-chloro-4'-nitrosalicylanilide
35. Nicolsamide
36. Niclosamide (anhydrous)
37. Hl 2447
38. Ent 25823
39. 2-hydroxy-5-chloro-n-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)benzamide
40. N-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)-5-chlorosalicylamide
41. Niclosamide Anhydrous
42. 2-chloro-4-nitrophenylamide-6-chlorosalicylic Acid
43. Niclosamide, Anhydrous
44. Salicylanilide, 2',5-dichloro-4'-nitro-
45. 2',5-dichlor-4'-nitro-salizylsaeureanilid
46. Nsc-178296
47. 5-chloro-n-(2'-chloro-4'-nitrophenyl)salicylamide
48. 8kk8cq2k8g
49. Sr 73
50. Radewerm
51. N-(2'-chlor-4'-nitrophenyl)-5-chlorsalicylamid
52. Bay-2353
53. Cas-50-65-7
54. Ncgc00015735-07
55. Niclosamide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
56. C13h8cl2n2o4
57. Dsstox_cid_20362
58. Dsstox_rid_79485
59. Dsstox_gsid_40362
60. N-(2'-chloro-4'-nitrophenyl)-5-chlorosalicylamide
61. Niclosamida
62. Niclosamidum
63. Cestocide
64. Niclosamidum [inn-latin]
65. Niclosamida [inn-spanish]
66. Nitrophenyl Chlorsalicylamide
67. Niclosamide [iso]
68. Niclosamide [usan:inn:ban]
69. Ccris 3437
70. Hsdb 1572
71. Sr-01000076024
72. Niclosamide [bsi:iso]
73. Einecs 200-056-8
74. Unii-8kk8cq2k8g
75. Nsc 178296
76. Brn 2820605
77. Yomensan
78. Niclo-samide
79. Ai3-25823
80. 5-chlorosalicyloyl-(o-chloro-p-nitranilide)
81. B 2353
82. Niclocide (tn)
83. Prestwick_354
84. 2',5-dichlor-4'-nitro-salizylsaeureanilid [german]
85. Mfcd00057597
86. Niclosamidum Anhydrous
87. Mollutox (salt/mix)
88. N-(2'-chlor-4'-nitrophenyl)-5-chlorsalicylamid [german]
89. Spectrum_000239
90. Niclosamide (niclocide)
91. Clonitralid (salt/mix)
92. Clonitralide (salt/mix)
93. Niclosamide [mi]
94. Prestwick0_000040
95. Prestwick1_000040
96. Prestwick2_000040
97. Prestwick3_000040
98. Spectrum2_001183
99. Spectrum3_000667
100. Spectrum4_000196
101. Spectrum5_001083
102. Lopac-n-3510
103. Niclosamide [inn]
104. Niclosamide (usan/inn)
105. Niclosamide [hsdb]
106. Niclosamide [usan]
107. Niclosamide [vandf]
108. Chembl1448
109. Niclosamide [mart.]
110. Lopac0_000866
111. Oprea1_259151
112. Schembl67182
113. Bspbio_000139
114. Bspbio_002333
115. Kbiogr_000771
116. Kbioss_000719
117. Niclosamide [who-dd]
118. Mls002154181
119. Divk1c_000709
120. Spectrum1503265
121. Spbio_001225
122. Spbio_002060
123. Bpbio1_000153
124. Chebi:7553
125. Gtpl8494
126. Dtxsid7040362
127. Niclosamide [green Book]
128. Schembl18563900
129. Wln: Wnr Cg Dmvr Bq Eg
130. Bdbm11242
131. Hms502d11
132. Kbio1_000709
133. Kbio2_000719
134. Kbio2_003287
135. Kbio2_005855
136. Kbio3_001553
137. 5-chloro-n-(2-chloro-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-hydroxy-benzamide
138. Niclosamide - Cas 50-65-7
139. Niclosamide [orange Book]
140. Ninds_000709
141. Bdbm513089
142. Hms1568g21
143. Hms2093a21
144. Hms2095g21
145. Hms2231h06
146. Hms3262n13
147. Hms3373p08
148. Hms3712g21
149. Kuc107299n
150. Niclosamide [ep Monograph]
151. Pharmakon1600-01503265
152. Bcp22958
153. Hy-b0497
154. Zinc3874496
155. Tox21_110209
156. Tox21_300749
157. Tox21_500866
158. Bbl004110
159. Ccg-39641
160. Nsc178296
161. Nsc758440
162. S3030
163. Salicylanilide,5-dichloro-4'-nitro-
164. Stk396676
165. 2,5-dichloro-4-nitrosalicylanilide ?
166. Akos003589004
167. Niclosamide Anhydrous [who-ip]
168. Tox21_110209_1
169. At15436
170. Bcp9000068
171. Db06803
172. Ks-5210
173. Lp00866
174. Nsc-758440
175. Sb19414
176. Sdccgsbi-0050841.p004
177. 2',5'-dichloro-4'-nitrosalicylanilide
178. Idi1_000709
179. Smp2_000228
180. 5-chloro-n-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)-
181. Ncgc00015735-01
182. Ncgc00015735-02
183. Ncgc00015735-03
184. Ncgc00015735-04
185. Ncgc00015735-05
186. Ncgc00015735-06
187. Ncgc00015735-08
188. Ncgc00015735-09
189. Ncgc00015735-11
190. Ncgc00015735-12
191. Ncgc00015735-24
192. Ncgc00094190-01
193. Ncgc00094190-02
194. Ncgc00094190-03
195. Ncgc00094190-04
196. Ncgc00254654-01
197. Ncgc00261551-01
198. Ksc-18-157-2
199. Smr000058390
200. Sbi-0050841.p003
201. Db-051812
202. Vu0243604
203. Ab00052340
204. Eu-0100866
205. Ft-0603220
206. Niclosamide, Anhydrous [ep Impurity]
207. Niclosamidum Anhydrous [who-ip Latin]
208. En300-92958
209. D00436
210. N 3510
211. Ab00052340_08
212. Ab00052340_09
213. A828227
214. Q418523
215. Q-201469
216. Sr-01000076024-1
217. Sr-01000076024-3
218. Sr-01000076024-6
219. Brd-k35960502-001-06-9
220. Brd-k35960502-001-11-9
221. Z57902203
222. 5-chloro-n-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl) -2-hydroxybenzamide
223. 5-chloranyl-n-(2-chloranyl-4-nitro-phenyl)-2-oxidanyl-benzamide
224. Niclosamide (anhydrous), European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 327.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H8Cl2N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 325.9861121 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 325.9861121 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 404 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anticestodal Agents; Antinematodal Agents; Molluscacides
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
THERE ARE NO CONTRAINDICATIONS TO THE USE OF NICLOSAMIDE AS A TENIACIDE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 965
MEDICATION (VET): Niclosamide can also be used to treat tapeworm infections of lab animals /eg mice, rabbits, monkeys, or reptiles/. ... Niclosamide is admin orally in tablet form to dogs and cats ... It is usually admin to ruminants /eg cattle, sheep and goats/ ... as a drench ...
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 857
Therapeutic Use Niclosamide in the free-base form only is used primarily as a cestocide and to a lesser extent as a trematocide. The drug is formulated as a chewable tablet containing 500 mg of niclosamide. It is very effective against tapeworrn infections caused by Taenia saginata, Taenia solium, and Diphyllobothrium latum; tapeworms such as Hymenolepis diminuta, Hymenolepis nana, and Dipylidium caninum are somewhat more recalcitrant. For infections of Taenia saginata, Taenia solium, and Diphyllobothrium latum, single oral dosages of 2 gm (adult), 1.5 gm (child > 34 kg), and 1.0 gm (child 11-34 kg) are recommended. 0ther tapeworms may require repeated treatment for example, 2 gm/day in single daily doses for 7 days (adults), 1.5 gm given in a single dose on the first day followed by 1 gm/day for the next 6 days (child > 34 kg), and 1 gm given in a single dose on the first day followed by 500 mg/day for next 6 days (child 11-34 kg). Safety for use in children under 2 years of age has not been established. Since niclosamide is active only against intestinal cestodes, it is not effective for treatment of cysticercosis. As a trematocide, niclosamide is active mainly against flukes such as Fasciolopsis buski in the intestines.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 1498
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for NICLOSAMIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
SINCE TAPEWORM INFECTIONS GENERALLY ARE NOT LIFE THREATENING, IT IS RECOMMENDED THAT TREATMENT OF PREGNANT WOMEN BE POSTPONED UNTIL AFTER DELIVERY.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 1753
VET: DO NOT TREAT LACTATING ANIMALS.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 384
... It is important to note that the lethal action of the drug against the adult worn does not extend to the ova. Thus, use of niclosamide in Taenia solium infections may expose the patient to the risk of cysticercosis, since, following digestion of the dead segments, viable ova will be liberated into the lumen of the gut. It is desirable to give an adequate purge within 3 to 4 hours after the drug has been given, to clear the bowel of all dead segments before they can be digested.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 965
The drug causes segments to disintegrate, releasing viable eggs; hence, if used against pork tapeworm, a purge should be given 1 or 2 hr after treatment. Untoward effects occur only occasionally; nausea and abdominal pain have been reported.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1182
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for NICLOSAMIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of tapeworm and intestinal fluke infections: Taenia saginata (Beef Tapeworm), Taenia solium (Pork Tapeworm), Diphyllobothrium latum (Fish Tapeworm), Fasciolopsis buski (large intestinal fluke). Niclosamide is also used as a molluscicide in the control of schistosomiasis.
Niclosamide is an antihelminth used against tapeworm infections. It may act by the uncoupling of the electron transport chain to ATP synthase. The disturbance of this crucial metabolic pathway prevents creation of adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP), an essential molecule that supplies energy for metabolism.
Antinematodal Agents
Substances used in the treatment or control of nematode infestations. They are used also in veterinary practice. (See all compounds classified as Antinematodal Agents.)
Molluscacides
Agents destructive to snails and other mollusks. (See all compounds classified as Molluscacides.)
Anticestodal Agents
Agents used to treat tapeworm infestations in man or animals. (See all compounds classified as Anticestodal Agents.)
P02DA01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P02 - Anthelmintics
P02D - Anticestodals
P02DA - Salicylic acid derivatives
P02DA01 - Niclosamide
Absorption
Niclosamide appears to be minimally absorbed from the gastrointestinal tractneither the drug nor its metabolites have been recovered from the blood or urine.
VERY LITTLE IS ABSORBED FROM THE GI TRACT ... .
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 965
EXPOSING RAINBOW TROUT TO (14)C-BAYER 73 CAUSED BILE TO WATER (14)C RATIO OF 10,000:1. AFTER 24 HR OF EXPOSURE, THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF UNFRACTIONATED BILE FROM FISH SHOWED 1 MAJOR RADIOACTIVE PEAK. UNCHANGED BAYER 73 WAS FOUND IN BILE.
STATHAM CN ET AL; PHARMACOLOGIST 16 (2): 327 (1974)
Niclosamide is excreted in feces.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 44
When male and female volunteers each were treated orally with 2000 mg of radiocarbon-labeled niclosamide, between 2 and 25% of the dose was eliminated in the urine over a 4-day period; the remainder was found in the feces. Elimination of niclosamide equivalents was essentially complete after 1-2 days. Maximal niclosamide equivalents in serum ranged from 0.25 to 6.0 ppm; the variation associated with this parameter was attrributed to differential rates of absorption among the individual.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 1499
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for NICLOSAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
ANTHELMINTIC NICLOSAMIDE...REDUCED TO CORRESPONDING AMINO DERIVATIVE BY BOTH MOUSE- & SHEEP-LIVER ENZYME PREPARATIONS & BY ENZYMES FROM CESTODES & NEMATODES. ...NICLOSAMIDE WAS NOT HYDROLYZED EITHER BY MAMMALIAN & HELMINTH ENZYME PREPN OR BY WHOLE HELMINTHS.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 5: A Review of the Literature Published during 1976 and 1977. London: The Chemical Society, 1979., p. 372
In warm-blooded organisms, the nitro group is reduced to an amino group (5,2'-dichloro-4-aminosalicylanilide).
Hartley, D. and H. Kidd (eds.). The Agrochemicals Handbook. Old Woking, Surrey, United Kingdom: Royal Society of Chemistry/Unwin Brothers Ltd., 1983., p. A297/Oct 83
Pregnant rats were treated orally with niclosamide at 1000 mg/kg on day 13, 19, or 20 of gestation, and rats were sacrificed at 4, 8, 16, or 24 hr posttreatment. Highest concentrations of niclosamide and 2,5'-dichloro-4'-aminosalicylanilide were detected in liver and kidney 8 hr after treatment. Niclosamide, but not its amino metabolite, was present in fetuses from rats treated on day 13, whereas both compounds were found in fetuses from rats treated on day 19 or 20. It was suggested that 19- and 20-day-old fetuses, but not 13-day-old fetuses, were able to metabolize niclosamide.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 1497
Niclosamide ... is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and mutagenic metabolites are excreted in the free form and as conjugated glucuronides. as in the case of other secondary amides, phase I metabolism of niclosamide may result in hydrolytic cleavage of the amide bond, giving rise to 5-chlorosalicylic acid and 2-chloro-4-nitroaniline. ...
PMID:1944396 Espinosa-Aguirre JJ et al; Mutat Res 264 (3): 139-45 (1991)
Niclosamide works by killing tapeworms on contact. Adult worms (but not ova) are rapidly killed, presumably due to uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation or stimulation of ATPase activity. The killed worms are then passed in the stool or sometimes destroyed in the intestine. Niclosamide may work as a molluscicide by binding to and damaging DNA.
Niclosamide has prominent activity against most of the cestodes that infect man; Enterobius (Oxyuris) vermicularis is also susceptible. At low concn, niclosamide stimulates oxygen uptake by Hymenolepis diminuta, but at higher concn respiration is inhibited and glucose uptake is blocked. The principal action of the drug may be to inhibit anaerobic phosphorylation of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) by the mitochondria of the parasite, an energy producing process that is dependent on CO2 fixation ... .
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 965
Cestocidal activity is due to inhibition of absorption of glucose by the tapeworm and uncoupling of the oxidative phosphorylation process in the mitochondria of cestodes. Resultant blocking of the Krebs cycle leads to accumulation of lactic acid, which kills the tapeworm. ... overstimulation of adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activity of the mitochondria may be related to cestodal action of niclosamide.
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 857