
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
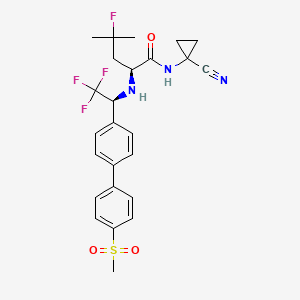

1. L-1037536
2. Mk-0822
1. 603139-19-1
2. Mk-0822
3. Odanacatib (mk-0822)
4. Mk0822
5. Mk 0822
6. Odanacatib (mk0822)
7. Odanacatib (mk 0822)
8. Chembl481611
9. N673f6w2vh
10. (s)-n-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-4-methyl-2-(((s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4'-(methylsulfonyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)ethyl)amino)pentanamide
11. (2s)-n-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-4-methyl-2-[[(1s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-[4-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl)phenyl]ethyl]amino]pentanamide
12. (2s)-n-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-4-methyl-2-[[(1s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-[4'-(methylsulfonyl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]ethyl]amino]pentanamide
13. (s)-n-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-4-methyl-2-((s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4'-(methylsulfonyl)biphenyl-4-yl)ethylamino)pentanamide
14. Odanacatib [usan]
15. Odanacatib [usan:inn]
16. Unii-n673f6w2vh
17. (2s)-n-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-4-methyl-2-(((1s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4'-(methylsulfonyl)(1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl)ethyl)amino)pentanamide
18. Mk-0822a
19. Odanacatib [mi]
20. Odanacatib [inn]
21. Odanacatib [jan]
22. Odanacatib (jan/usan)
23. Odanacatib [mart.]
24. Odanacatib [who-dd]
25. Mls006010197
26. Gtpl6478
27. L-1037536
28. Schembl1496266
29. Dtxsid40209075
30. Ex-a552
31. Bcpp000141
32. Cas:603139-19-1;odanacatib
33. Bdbm50255753
34. Mfcd11042419
35. Nsc766811
36. S1115
37. Zinc42893657
38. Akos015900719
39. Bcp9001020
40. Ccg-269888
41. Cs-0277
42. Db06670
43. Nsc-766811
44. Ncgc00346637-01
45. Ac-27468
46. As-19562
47. Hy-10042
48. Smr004676504
49. Sw219669-1
50. D08955
51. Mk-0822;mk 0822;mk0822
52. 139m191
53. J-690332
54. Q2014070
55. N-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-n2-{(1s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-[4'-(methylsulfonyl)biphenyl-4-yl]ethyl}-l-leucinamide
56. N1-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-n2-{(1s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-[4'-(methyl Sulfonyl)-1,1'-biphenyl-4-yl]ethyl}-l-leucinamide
57. N1-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-n2-{(1s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-[4'-(methylsulfonyl)-1,1'-biphenyl-4-yl]ethyl}-l-leucinamide
58. Pentanamide, N-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-4-fluoro-4-methyl-2-(((1s)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4'-(methylsulfonyl)(1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl)ethyl)amino)-, (2s)-
| Molecular Weight | 525.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H27F4N3O3S |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 525.17092555 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 525.17092555 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 107 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 934 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in osteoporosis.
Treatment of osteoporosis
Increases bone mineral density and reduces risk of fractures in osteoporosis.
Absorption
Tmax of 2-6h. The absolute bioavailabilities observed with 30mg and 50 mg doses are 70% and 30% respectively. When taken with high fat meals the 50mg dose's bioavailability increases to 49% and tmax increases to 10.5h.
Route of Elimination
16.9% excreted in urine. 74.5% excreted in feces.
Volume of Distribution
100L
Clearance
Total clearance of 0.8L/h.
The major metabolite is the product of hydroxylation by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8. This metabolite is active but is 25 times less effective at inhibiting cathepsin K than odanacatib. The other metabolites are produced through glutathione conjugation, hydrolysis, dealkylation, glucuronidation, oxidation, and cyclization.
Apparent half life observed to be 87.3-94.7h.
Odanacatib inhibits cathepsin K, likely by binding to its active site. Cathepsin K is a cysteine protease enzyme which is secreted by osteoclasts. Cathepsin K is responsible for the breakdown of collagen in the bone matrix as part of bone resorption. The inhibition of this enzyme results in decreased bone resorption without affecting bone deposition resulting in increased bone mineral density. This increased bone mineral density strengthens the bone which leads to fewer fractures in osteoporosis.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
45
PharmaCompass offers a list of Odanacatib API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Odanacatib manufacturer or Odanacatib supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Odanacatib manufacturer or Odanacatib supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Odanacatib API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Odanacatib API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Odanacatib Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Odanacatib Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Odanacatib manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Odanacatib, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Odanacatib manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Odanacatib API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Odanacatib manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Odanacatib supplier is an individual or a company that provides Odanacatib active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Odanacatib finished formulations upon request. The Odanacatib suppliers may include Odanacatib API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Odanacatib suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Odanacatib Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Odanacatib GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Odanacatib GMP manufacturer or Odanacatib GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Odanacatib CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Odanacatib's compliance with Odanacatib specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Odanacatib CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Odanacatib CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Odanacatib may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Odanacatib EP), Odanacatib JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Odanacatib USP).
