
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
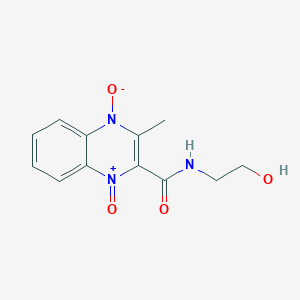

1. 2-(n-2'-hydroxyethylcarbamoyl)-3-methylquinoxaline- Di-n-oxide
2. Bay Va 9391
3. Bayo-n-ox
4. Bisergon
5. Olanquindox
1. 23696-28-8
2. Bayernox
3. Bisergon
4. Bayonox
5. 2-((2-hydroxyethyl)carbamoyl)-3-methylquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide
6. Bay Va 9391
7. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-2-quinoxalinecarboxamide 1,4-dioxide
8. 2-quinoxalinecarboxamide, N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-, 1,4-dioxide
9. Olachindox
10. Bay-va-9391
11. Olaquindox (inn)
12. Nsc634933
13. Ncgc00164265-01
14. Olaquindox [inn]
15. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-4-oxido-1-oxoquinoxalin-1-ium-2-carboxamide
16. Dsstox_cid_20726
17. Dsstox_rid_79573
18. Dsstox_gsid_40726
19. Olaquindox [ban:inn]
20. Cas-23696-28-8
21. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-1,4-dioxidoquinoxaline-1,4-diium-2-carboxamide
22. Olaquindox [mi]
23. Olaquindox [hsdb]
24. Olaquindox-(ethylene-d4)
25. Olaquindox [mart.]
26. G3law9u88t
27. Schembl557579
28. Olaquindox [veterinary] (tn)
29. Chembl1649716
30. Dtxsid3040726
31. Chebi:177538
32. Act06680
33. Hy-n0465
34. Zinc1624227
35. Tox21_112095
36. Mfcd00210341
37. Akos015895584
38. Akos037514759
39. Olaquindox 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
40. Tox21_112095_1
41. Nsc-634933
42. Ncgc00164265-02
43. Ac-13888
44. As-12544
45. Olaquindox 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
46. Db-046225
47. Cs-0008992
48. Ft-0630505
49. Ft-0673254
50. N2086
51. A14807
52. D08292
53. Olaquindox, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
54. J-015187
55. Q27278699
56. 2-(2-hydroxyethylcarbamoyl)-3-methylquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide
57. 2-(n-(2-hydroxyethyl)carbamoyl)-3-methylquinoxaline1,4-dioxide
58. 2-[(2-hydroxyethyl)carbamoyl]-3-methyl-1-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1
59. E?-quinoxalin-1-ylium-4-olate
60. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-1,4-dioxido-quinoxaline-1,4-diium-2-carboxamide
61. 1,4-dihydroxy-n-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-1.lambda.~5~,4.lambda.~5~-quinoxaline-2-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 263.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H13N3O4 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 263.09060590 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 263.09060590 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 421 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
The compound /olaquindox/ is used as a growth promoter in pigs.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Food Additives; Toxicological Evaluation of Certain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food, WHO Food Additive Series 27: Olaquindox (1991). Available from, as of November 5, 2015: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Experiments with (3-1)4C-olaquindox intraduodenally administered to rats with bile duct fistulas suggested that around 18% of the dose was excreted in the bile. Similar findings were made after intravenous dosing. Distribution occurred in a generalized manner throughout the body after oral dosing and most of the radioactivity had disappeared by 24 hours. Autoradiography revealed the highest amount in the rat kidney at 4 hours, indicative of the extent of urinary excretion already noted. Slightly elevated concentrations were also observed in liver, testes, adrenals and hair follicles.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Food Additives; Toxicological Evaluation of Certain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food, WHO Food Additive Series 27: Olaquindox (1991). Available from, as of November 5, 2015: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
After pigs were given diets containing up to 45 ppm olaquindox for the duration of the fattening period, the highest levels were found in the liver (0.14 ppm) and kidney (0.28 ppm) 6 hours after withdrawal. By 24 hours the levels were below the limit of detection (0.1 ppm). Similar results were noted when pigs were given diets containing 10 ppm olaquindox.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Food Additives; Toxicological Evaluation of Certain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food, WHO Food Additive Series 27: Olaquindox (1991). Available from, as of November 5, 2015: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
When pigs were dosed at levels in the range of those recommended in use (up to 100 ppm in the diet) for up to 20 weeks, relatively high levels were found in the kidney (around 2000 ppb) with relatively moderate levels in the liver (300 ppb) when the animals were killed six hours after drug withdrawal. When killed 2 days after withdrawal, levels had fallen to below the limits of detection (50 ppb) in liver, kidney and muscle. Pigs given diets containing olaquindox at levels in excess of those recommended (160 or 250 ppm) for up to 4 weeks also had high initial levels in kidney, liver and muscle but these had fallen to below the limits of detection by day 2 after withdrawal.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Food Additives; Toxicological Evaluation of Certain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food, WHO Food Additive Series 27: Olaquindox (1991). Available from, as of November 5, 2015: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Olaquindox was rapidly absorbed when given orally to pigs. Over 90% of an oral dose of 2 mg/kg bw was eliminated in the urine within 24 hours, which is indicative of rapid and extensive absorption. The remainder was excreted in the feces. Maximum plasma levels were attained within 1-2 hours of dosing (1-2 ppm). This was followed by a rapid decline in plasma levels reaching around 0.03 ppm by 24 hours and 0.005-0.01 ppm by 48 hours. Radioactivity was present in all tissues when examined 2 days after dosing, but the levels were extremely low. In the kidney and liver, levels of 110 and 52 ppb were found, while levels in muscle were only 9 ppb. After 8 days, levels in liver and kidney had fallen to 27 and 12 ppb, respectively, while those in muscle were in the range of 2.5 ppb. By 28 days after dosing only low levels were found in kidney and muscle (0.9 and 0.5-0.8 ppb, respectively) with slightly higher concentrations in the liver (2 ppb).
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Food Additives; Toxicological Evaluation of Certain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food, WHO Food Additive Series 27: Olaquindox (1991). Available from, as of November 5, 2015: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for OLAQUINDOX (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The biotransformation of olaquindox has been investigated only in the pig. The majority of an oral dose of olaquindox (70%) was excreted in the urine unchanged. The major metabolites appeared to be the reduced compounds, the 1- or 4-mono-N-oxides (16%). Three other compounds thought to be carboxylic acid derivatives made up the remainder. Later work led to the elucidation of the structures of these metabolites in the pig. Again the major urinary component after oral dosing was olaquindox with about 7% present as the 4-mono-N-oxide. Omega oxidation produced the 2-carboxymethylaminocarbonyl compound and its 4-mono-N-oxide derivative (6%). Some of the corresponding 1-mono-N-oxide moiety of the 2-carboxymethylaminocarbonyl was also noted (1%). The remaining metabolite was the di-desoxy derivative of 2-carboxymethylaminocarbonyl compound, 2-carboxymethylaminocarbonyl-3- methyl quinoxaline (>1%).
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Food Additives; Toxicological Evaluation of Certain Veterinary Drug Residues in Food, WHO Food Additive Series 27: Olaquindox (1991). Available from, as of November 5, 2015: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
ABOUT THIS PAGE
77
PharmaCompass offers a list of Olaquindox API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Olaquindox manufacturer or Olaquindox supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Olaquindox manufacturer or Olaquindox supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Olaquindox API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Olaquindox API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Olaquindox Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Olaquindox Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Olaquindox manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Olaquindox, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Olaquindox manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Olaquindox API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Olaquindox manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Olaquindox supplier is an individual or a company that provides Olaquindox active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Olaquindox finished formulations upon request. The Olaquindox suppliers may include Olaquindox API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Olaquindox suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Olaquindox Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Olaquindox GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Olaquindox GMP manufacturer or Olaquindox GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Olaquindox CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Olaquindox's compliance with Olaquindox specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Olaquindox CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Olaquindox CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Olaquindox may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Olaquindox EP), Olaquindox JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Olaquindox USP).
