
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Fc-1271a
2. Osphena
3. Senshio
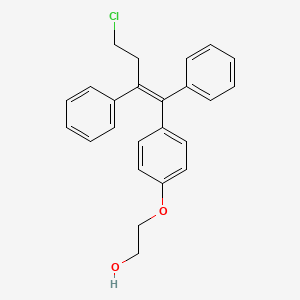
4. Z-2-(4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-but-1-enyl)phenoxy)ethanol
1. 128607-22-7
2. Fc-1271a
3. Osphena
4. Senshio
5. Deamino-hydroxytoremifene
6. Fc-1271
7. 2-(4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-but-1-enyl)phenoxy)ethanol
8. Tore Iii
9. 2-(p-((z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)ethanol
10. Ccris 9205
11. (deaminohydroxy) Toremifene
12. B0p231ilbk
13. Chebi:73275
14. Ethanol, 2-[4-[(1z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-buten-1-yl]phenoxy]-
15. Ethanol, 2-[4-[(1z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl]phenoxy]-
16. 2-[4-[(z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl]phenoxy]ethanol
17. (z)-2-(4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-en-1-yl)phenoxy)ethan-1-ol
18. 2-{4-[(1z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-en-1-yl]phenoxy}ethanol
19. Ospemifene [inn]
20. Unii-b0p231ilbk
21. Ophena
22. Ospemifene [usan:inn:ban]
23. Deaminotoremifene
24. Ethanol, 2-(4-((1z)-4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy)-
25. Osphena (tn)
26. Deaminohydroxytoremifene
27. Ospemifene [mi]
28. Ospemifene [usan]
29. Ospemifene, Fc-1271a
30. Ospemifene [vandf]
31. Ospemifene [mart.]
32. Ospemifene [who-dd]
33. Ospemifene (inn/usan/ban)
34. Schembl948118
35. Gtpl7349
36. Chembl2105395
37. Ospemifene [orange Book]
38. Hsdb 8281
39. Dtxsid101025426
40. Z-2-(4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-but-1-enyl)phenoxy)ethanol
41. Bcp20981
42. Hy-b0723
43. Zinc1550766
44. Mfcd00871890
45. S4285
46. Akos025401964
47. Ccg-268392
48. Cs-5961
49. Db04938
50. Ncgc00386347-01
51. Ac-27645
52. O0441
53. Sw219657-1
54. A14261
55. D08958
56. J-005613
57. Q7107372
58. Z-2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenyl-but-1-enyl)-phenoxy]-ethanol
59. 2-[4-[(z)-4-chloro-1,2-di(phenyl)but-1-enyl]phenoxy]ethanol
| Molecular Weight | 378.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H23ClO2 |
| XLogP3 | 6.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 378.1386577 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 378.1386577 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 441 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Osphena |
| PubMed Health | Ospemifene (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | OSPHENA is anestrogen agonist/antagonist.The chemical structure of ospemifene is shown in Figure 1.Figure 1: Chemical structureThe chemical designation is Z-2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethanol, and has the empirical formula C24H... |
| Active Ingredient | Ospemifene |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shionogi |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Osphena |
| PubMed Health | Ospemifene (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | OSPHENA is anestrogen agonist/antagonist.The chemical structure of ospemifene is shown in Figure 1.Figure 1: Chemical structureThe chemical designation is Z-2-[4-(4-chloro-1,2-diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenoxy]ethanol, and has the empirical formula C24H... |
| Active Ingredient | Ospemifene |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Shionogi |
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Ospemifene is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of September 30, 2015: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search/intervention=ospemifene%20OR%20Fc-1271
Osphena is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe dyspareunia, a symptom of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, due to menopause. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
/BOX WARNING/ There is a reported increased risk of stroke and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) who received daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) (0.625 mg)-alone therapy over 7.1 years as part of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI). In the clinical trials for Osphena (duration of treatment up to 15 months), the incidence rates of thromboembolic and hemorrhagic stroke were 0.72 and 1.45 per thousand women, respectively in Osphena 60 mg treatment group and 1.04 and 0 in placebo. The incidence of DVT was 1.45 per thousand women in Osphena 60 mg treatment group and 1.04 per thousand women in placebo. Osphena should be prescribed for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
/BOX WARNING/ Osphena is an estrogen agonist/antagonist with tissue selective effects. In the endometrium, Osphena has estrogen agonistic effects. There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a woman with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy reduces the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed and random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
/BOX WARNING/ What is the most important information I should know about Osphena? Osphena is a medicine that works like estrogen in the lining of the uterus (womb), but can work differently in other parts of the body. Taking estrogen-alone or Osphena may increase your chance of getting cancer of the lining of the uterus (womb). Vaginal bleeding after menopause may be a warning sign of cancer of the lining of the uterus (womb). Your healthcare provider should check any unusual vaginal bleeding to find out the cause. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any unusual vaginal bleeding while you are taking Osphena. Osphena may increase your chance of getting strokes and blood clots. You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with Osphena.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
The pharmacokinetics of ospemifene has not been studied in women with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C); therefore, Osphena should not be used in women with severe hepatic impairment.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Ospemifene (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Ospemifene is used for the treatment of moderate to dyspareunia, a symptom of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, due to menopause.
FDA Label
Senshio is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe symptomatic vulvar and vaginal atrophy (VVA) in post-menopausal women.
The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) for estrogen receptor (ER) alpha and beta are 0.8 M and 1.7 M, respectively. Ospemifene has potential uses in the management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. It interacts with osteoblasts and osteoclasts in such a way that it reduces bone turnover. It also has potential uses in the prevention of breast cancer. Studies suggest that ospemifene, in a dose-dependent manner, reduces the incidence of tumours.
G03XC05
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G03 - Sex hormones and modulators of the genital system
G03X - Other sex hormones and modulators of the genital system
G03XC - Selective estrogen receptor modulators
G03XC05 - Ospemifene
Absorption
When a single oral dose of ospemifene 60 mg is given to postmenopausal women under fasted conditions, the pharmacokinetic parameters are as follows: Tmax = 2 hours (range of 1 - 8 hours); Cmax = 533 ng/mL; AUC (0-inf) = 4165 nghr/mL. When the same aforementioned dose is given to postmenopausal women under fed conditions, the pharmacokinetic parameters are as follows: Tmax = 2.5 hours (1 - 6 hours); Cmax = 1198 ng/mL; AUC (0-inf) = 7521 nghr/mL. Accumulation occurs following repeated doses. Time to steady state = 9 days. Although the bioavailability of ospemifene has not been formally evaluated, it is expected to have a low bioavailability because of its lipophilic nature.
Route of Elimination
Following an oral administration of ospemifene, approximately 75% and 7% of the dose was excreted in feces and urine, respectively. Less than 0.2% of the ospemifene dose was excreted unchanged in urine.
Volume of Distribution
448 L
Clearance
Total body clearance = 9.16 L/hr.
/MILK/ Human lacatation data is not available, however, the prodrug is rapidly metabolized upon absorption, and this agent is concentrated in the breast milk.
Briggs, G.G., Freeman, R.K., Yaffee, S.J.; Drugs in Pregancy and Lactation Nineth Edition. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA. 2011, p. 839
/MILK/ It is not known whether Osphena is excreted in human breast milk. In a nonclinical study, ospemifene was excreted in rat milk and detected at concentrations higher than that in maternal plasma.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
Following a single oral administration of Osphena 60 mg tablet in postmenopausal women under fasted condition, peak median serum concentrations was reached at approximately 2 hours (range: 1 to 8 hours) post-dose. Mean ospemifene C max and AUC 0-inf were 533 ng/mL and 4165 ng/hr/mL, respectively. After a single oral administration of Osphena 60 mg tablet in postmenopausal women with a high fat/high calorie (860 kcal) meal, C max was reached at approximately 2.5 hours (range: 1 to 6 hours) post-dose. Mean ospemifene C max and AUC 0-inf were 1198 ng/mL and 7521 ng/hr/mL, respectively. The absolute bioavailability of ospemifene was not evaluated. Ospemifene exhibits less than dose-proportional pharmacokinetics from 25 to 200 mg with ospemifene capsule formulation. Accumulation of ospemifene with respect to AUC 0-inf was approximately 2 after twelve weeks of daily administration. Steady-state was reached after nine days of ospemifene administration. Osphena is highly (>99 percent) bound to serum proteins. The apparent volume of distribution is 448 L. The apparent terminal half-life of ospemifene in postmenopausal women is approximately 26 hours. Following an oral administration of ospemifene, approximately 75% and 7% of the dose was excreted in feces and urine, respectively. Less than 0.2% of the ospemifene dose was excreted unchanged in urine.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
Ospemifene is hepatically metabolized via CYP3A4, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2B6. The major metabolite was 4-hydroxyospemifene, 25% of the parent compound will undergo this biotransformation. Other metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-ospemifene, <7% of the parent compound will undergo this biotransformation. In order of decreasing potency, ospemifene was suggested to be a weak inhibitor for CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2C8, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4.
The objective of these investigations was to determine the possible effects of the novel selective estrogen receptor modulator, ospemifene, on cytochrome P450 (CYP)-mediated drug metabolism. Ospemifene underwent testing for possible effects on CYP enzyme activity in human liver microsomes and in isolated human hepatocytes. Based on the results obtained in vitro, three Phase 1 crossover pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in healthy postmenopausal women to assess the in vivo effects of ospemifene on CYP-mediated drug metabolism. Ospemifene and its main metabolites 4-hydroxyospemifene and 4'-hydroxyospemifene weakly inhibited a number of CYPs (CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2C8, and CYP2D6) in vitro. However, only CYP2C9 activity was inhibited by 4-hydroxyospemifene at clinically relevant concentrations. Induction of CYPs by ospemifene in cultured human hepatocytes was 2.4-fold or less. The in vivo studies showed that ospemifene did not have significant effects on the areas under the plasma concentration-time curves of the tested CYP substrates warfarin (CYP2C9), bupropion (CYP2B6) and omeprazole (CYP2C19), demonstrating that pretreatment with ospemifene did not alter their metabolism. Therefore, the risk that ospemifene will affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs that are substrates for CYP enzymes is low.
PMID:23880855 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3742231 Turpeinen M et al; Int J Mol Sci 14(7): 14064-75 (2013).
Ospemifene and its main metabolites 4-hydroxyospemifene and 4'-hydroxyospemifene weakly inhibited a number of CYPs (CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2C8, and CYP2D6) in vitro.
PMID:23880855 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3742231 Turpeinen M et al; Int J Mol Sci 14(7): 14064-75 (2013).
In vitro experiments with human liver microsomes indicated that ospemifene primarily undergoes metabolism via CYP3A4, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19. The major metabolite was 4-hydroxyospemifene. The apparent total body clearance is 9.16 L/hr using a population approach.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
Terminal half-life = 26 hours .
The apparent terminal half-life of ospemifene in postmenopausal women is approximately 26 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287
Ospemifene is a next generation SERM (selective estrogen receptor modulator) that selectively binds to estrogen receptors and either stimulates or blocks estrogen's activity in different tissue types. It has an agonistic effect on the endometrium.
OSPHENA is an estrogen agonist/antagonist with tissue selective effects. Its biological actions are mediated through binding to estrogen receptors. This binding results in activation of estrogenic pathways in some tissues (agonism) and blockade of estrogenic pathways in others (antagonism).
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Osphena (Ospemifene) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: August 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=8462d6ab-e3cd-4efa-a360-75bf8f917287

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
87
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ospemifene API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ospemifene manufacturer or Ospemifene supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ospemifene manufacturer or Ospemifene supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ospemifene API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ospemifene API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ospemifene Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ospemifene Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Osphena manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Osphena, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Osphena manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Osphena API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Osphena manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Osphena supplier is an individual or a company that provides Osphena active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Osphena finished formulations upon request. The Osphena suppliers may include Osphena API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Osphena suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Osphena DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Osphena active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Osphena DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Osphena USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Osphena DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Osphena USDMF includes data on Osphena's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Osphena USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Osphena suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Osphena written confirmation (Osphena WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Osphena manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Osphena active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Osphena APIs or Osphena finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Osphena WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Osphena suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Osphena as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Osphena API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Osphena as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Osphena and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Osphena NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Osphena suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Osphena Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Osphena GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Osphena GMP manufacturer or Osphena GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Osphena CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Osphena's compliance with Osphena specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Osphena CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Osphena CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Osphena may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Osphena EP), Osphena JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Osphena USP).
