
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
API
0
FDF
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
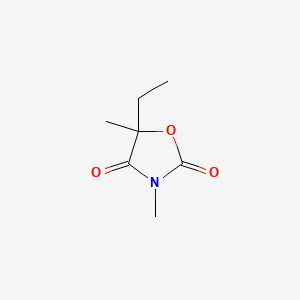

1. 5-ethyl-3,5-dimethyloxazolinedione
1. Parametadione
2. Paradione
3. 115-67-3
4. Isoethadione
5. Paramethadionum
6. 5-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-2,4-dione
7. 2,4-oxazolidinedione, 5-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-
8. 3,5-dimethyl-5-ethyloxazolidine-2,4-dione
9. 5-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione
10. 5-ethyl-3,5-dimethyloxazolidine-2,4-dione
11. A 348
12. Paramethadione (inn)
13. Isoethadione; Paradione
14. Nsc-760129
15. Chebi:7921
16. Z615frw64n
17. Parametadione [dcit]
18. Parametadiona
19. Parametadiona [inn-spanish]
20. Paramethadionum [inn-latin]
21. Paramethadione [inn]
22. Paradione (tn)
23. Hsdb 3245
24. Einecs 204-098-8
25. Brn 0127715
26. Unii-z615frw64n
27. Paramethadione [usp:inn:ban]
28. Paramethadione [mi]
29. Chembl1100
30. Schembl34857
31. Paramethadione [hsdb]
32. 4-27-00-03255 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
33. Paramethadione [vandf]
34. Paramethadione [mart.]
35. Gtpl7261
36. Paramethadione [who-dd]
37. Dtxsid8023420
38. Hms3264i11
39. Pharmakon1600-01505456
40. Hy-b1721
41. Paramethadione [orange Book]
42. Nsc760129
43. Akos006239791
44. Ccg-213441
45. Db00617
46. Nsc 760129
47. Ncgc00183600-01
48. Ncgc00183600-04
49. Sbi-0206930.p001
50. A-348
51. Cs-0013725
52. C07411
53. D00495
54. Ab01563081_01
55. 115p673
56. Sr-05000002060
57. Q3895202
58. Sr-05000002060-1
59. 5-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-2,4-dione #
60. Brd-a22128695-001-01-8
61. Z2327506990
62. 128557-52-8
| Molecular Weight | 157.17 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H11NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 157.07389321 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 157.07389321 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 214 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anticonvulsants
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
/PARAMETHADIONE & TRIMETHADIONE/...WERE MAJOR AGENTS FOR TREATMENT OF PETIT MAL EPILEPSY & ATYPICAL SPIKE-AND-WAVE ABSENCE ATTACKS BEFORE INTRODUCTION OF ETHOSUXIMIDE. THOUGH EFFECTIVE, THEIR SIDE EFFECTS MAKE THEM DRUGS OF SECOND CHOICE.
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 597
MEDICATION (VET): ANTICONVULSANT. USE: NOW RARE, TO CONTROL CONVULSIONS IN ANIMALS.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 413
Paramethadione and trimethadione are indicated in the control of absence (petit mal) seizures that are refractory to treatment with other medications. /Included in US product labeling./
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 243
... Its pharmacological properties, therapeutic uses, dosage, and toxicity are similar to those of trimethadione.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 478
ALTHOUGH IT IS SLIGHTLY LESS POTENT, DOES NOT INDUCE MYASTHENIA GRAVIS-LIKE SYNDROME, & INDUCES PHOTOPHOBIA & SKIN RASHES IN SOMEWHAT FEWER PATIENTS, IT HAS SAME LIMITATIONS & EXHIBITS SAME SIDE REACTIONS AS.../TRIMETHADIONE/.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1016
AS WITH TRIMETHADIONE, THERE IS SUGGESTIVE EVIDENCE THAT USE OF PARAMETHADIONE DURING PREGNANCY IS ASSOCIATED WITH INCR IN INCIDENCE OF CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES. ACCORDINGLY, PARAMETHADIONE SHOULD BE AVOIDED IN PREGNANT WOMEN IF POSSIBLE.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 466
NEPHROPATHIES HAVE DEVELOPED...ESP IN PATIENTS RECEIVING...PARAMETHADIONE. THESE REACTIONS MAY DEVELOP INSIDIOUSLY, & URINALYSES SHOULD BE MADE BEFORE & PERIODICALLY DURING TREATMENT. DEVELOPMENT OF ANY SIGNIFICANT RENAL ABNORMALITY IS INDICATION FOR DISCONTINUING THE DRUG.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 458
SINCE EARLY RECOGNITION OF /BLOOD/ DYSCRASIA & DISCONTINUANCE OF...DRUG ARE ESSENTIAL, PT SHOULD BE ADVISED TO REPORT PROMPTLY SUCH SYMPTOMS AS SORE THROAT, FEVER, EASY BRUISING, PETECHIAE, EPISTAXIS, OR OTHER SIGNS OF INFECTION OR BLEEDING TENDENCY. /ANTICONVULSANTS /
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 458
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PARAMETHADIONE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used for the control of absence (petit mal) seizures that are refractory to treatment with other medications.
Paramethadione is an oxazolidinedione anticonvulsant similar to trimethadione that acts on the central nervous system (CNS) to reduce the number of absence seizures (often seen in epileptics). Absence seizures involve an interruption to consciousness where the person experiencing the seizure seems to become vacant and unresponsive for a short period of time (usually up to 30 seconds). Paramethadione acts on thalamic neurons in the thalamic reticular nucleus (which studies have shown to be associated with absence seizures, von Krosigk et al., 1993).
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AC - Oxazolidine derivatives
N03AC01 - Paramethadione
Absorption
Rapid via the digestive tract.
PARAMETHADIONE IS COMPLETELY N-DEMETHYLATED TO 5-ETHYL-5-METHYL-OXAZOLIDINE-2,4-DIONE AND SLOWLY EXCRETED BY KIDNEYS.
Thienes, C., and T.J. Haley. Clinical Toxicology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1972., p. 78
Primarily hepatic (mainly via cytochrome P450 isozyme 2C9), paramethadione is completely demethylated to 5-ethyl-5-methyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione, the active metabolite.
PARAMETHADIONE IS COMPLETELY N-DEMETHYLATED TO 5-ETHYL-5-METHYL-OXAZOLIDINE-2,4-DIONE...
Thienes, C., and T.J. Haley. Clinical Toxicology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1972., p. 78
PARAMETHADIONE IS N-DEMETHYLATED BY HEPATIC MICROSOMAL ENZYMES TO ACTIVE METABOLITE THAT IS SLOWLY EXCRETED IN URINE...
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 216
PARAMETHADIONE IS N-DEMETHYLATED BY HEPATIC MICROSOMAL ENZYMES TO ACTIVE METABOLITE... METABOLITE ACCUMULATES DURING CHRONIC MEDICATION & IS PROBABLY RESPONSIBLE FOR MOST OF ANTICONVULSANT ACTIVITY OF PARENT DRUG...
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 216
12 to 24 hours (however the half-life for the active metabolite is not known)
Paramethadion - 12 to 24 hours; active metabolite - unknown.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 243
Dione anticonvulsants such as paramethadione reduce T-type calcium currents in thalamic neurons (including thalamic relay neurons). This inhibits corticothalamic transmission and raises the threshold for repetitive activity in the thalamus. This results in a dampening of the abnormal thalamocortical rhythmicity proposed to underlie the 3-Hz spike-and-wave discharge seen on electroencephalogram (EEG) during absence seizures.
Dione anticonvulsants reduce T-type calcium currents in thalamic neurons, including thalamic relay neurons. this raises the threshold for repetitive activity in the thalamus, and inhibits corticothalamic transmission. Thus, the abnormal thalamocortical rhythmicity, which is thought to underlie the 3-Hz spike-and-wave discharge seen on electroencephalogram (EEG) with absence seizures, is dampened. The maximal seizure pattern in patients undergoing electroconvulsive therapy is not modified. /Dione anticonvulsants/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 243
ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?