
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
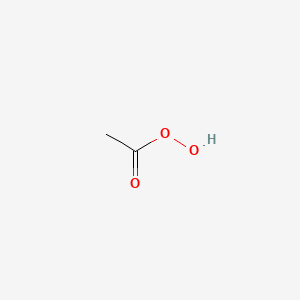

1. Acetyl Hydroperoxide
2. Acid, Peracetic
3. Acid, Peroxyacetic
4. Acid, Peroxyethanoic
5. Desoxone 1
6. Desoxone-1
7. Desoxone1
8. Dialax
9. Peracetate, Sodium
10. Peracetate, Zinc
11. Peracetic Acid, Sodium Salt
12. Peroxyacetic Acid
13. Peroxyethanoic Acid
14. Sodium Peracetate
15. Zinc Peracetate
1. Peroxyacetic Acid
2. Ethaneperoxoic Acid
3. 79-21-0
4. Estosteril
5. Acetic Peroxide
6. Peroxoacetic Acid
7. Acetyl Hydroperoxide
8. Monoperacetic Acid
9. Osbon Ac
10. Proxitane 4002
11. Desoxon 1
12. Ethaneperoxic Acid
13. Hydroperoxide, Acetyl
14. Acide Peracetique
15. Acido Peroxiacetico
16. Peroxy Acetic Acid
17. I6kpi2e1hd
18. Chembl444965
19. Ncgc00166305-01
20. Caswell No. 644
21. Acecide
22. Proxitane
23. Acide Peracetique [french]
24. Acide Peroxyacetique
25. F50
26. Ccris 686
27. Acide Peroxyacetique [french]
28. Acido Peroxiacetico [spanish]
29. Kyselina Peroxyoctova [czech]
30. Kyselina Peroxyoctova
31. Lcap
32. Hsdb 1106
33. Einecs 201-186-8
34. Unii-i6kpi2e1hd
35. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 063201
36. Brn 1098464
37. Aceticperoxide
38. Peractic Acid
39. Per-acetic Acid
40. Peroxacetic Acid
41. Acetic Acid Oxide
42. Peroxy-acetic Acid
43. Acooh
44. Acecide (tn)
45. Ch3co2oh
46. Ethaneperoxoic Acid, 9ci
47. Ch3c(o)ooh
48. Dsstox_cid_5853
49. Ec 201-186-8
50. Dsstox_rid_77948
51. Peracetic Acid [mi]
52. Dsstox_gsid_25853
53. 4-02-00-00390 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
54. Peracetic Acid [hsdb]
55. Peracetic Acid [mart.]
56. Dtxsid1025853
57. Peracetic Acid [who-dd]
58. Chebi:42530
59. Tox21_112402
60. Bdbm50266095
61. Mfcd00002128
62. Peroxyacetic Acid, >43% And With >6% Hydrogen Peroxide [forbidden]
63. Zinc38141555
64. Akos015837803
65. Db14556
66. Cas-79-21-0
67. Peracetic Acid 35-40% Wt In Acetic Acid
68. Peracetic Acid Solution, 8.7% In Acetic Acid
69. D03467
70. Q375140
71. Peracetic Acid Solution, 36-40 Wt. % In Acetic Acid
72. Peracetic Acid Solution 32 Wt. % In Dilute Acetic Acid
73. Peracetic Acid Solution, 32 Wt. % In Dilute Acetic Acid
74. Peroxyacetic Acid, >43% And With >6% Hydrogen Peroxide
75. Peracetic Acid Solution, Purum, ~39% In Acetic Acid (rt)
76. Peracetic Acid Solution, Purum, ~40% In Acetic Acid: Water
| Molecular Weight | 76.05 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2H4O3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 76.016043985 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 76.016043985 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 40.2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Peracetic acid-ethanol sterilization (PES) with a preceding delipidation step is an effective sterilization method for allograft bone ... The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of different incubation times of water, hydrogen peroxide and alcohol cleansing procedures combined with PES on biomechanical properties of freeze-dried cortical bone ... /The/ in vitro study indicates that the cleansing procedure proposed combined with PES affects the biomechanical properties of cortical bone only on a limited scale.
PMID:17892947 Haimi S et al; Biologicals 36 (2): 99-104 (2008)
Sterilization of allografts for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction has become an important prerequisite to prevent disease transmission. However, current sterilization techniques impair the biological or mechanical properties of such treated grafts. Peracetic acid (PAA) has been successfully used to sterilize bone allografts without these disadvantages and does not impair the mechanical properties of soft tissue grafts in vitro ... Whether PAA sterilization would influence recellularization, restoration of crimp length and pattern, and revascularization of ACL grafts during early healing /was examined using/an in vivo sheep model for open ACL reconstruction ... The histologic findings /were correlated/ with the restoration of anteroposterior stability and structural properties during load-to-failure testing. PAA slowed remodeling activity at 6 and 12 weeks compared to nonsterilized allografts and autografts. The mechanical properties of PAA grafts were also reduced compared to these control groups at both time points. /It was concluded that/ PAA sterilization currently should not be used to sterilize soft tissue grafts typically used in ACL reconstruction.
PMID:18491201 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2584264 Scheffler SU et al; Clin Orthopedics Related Res 466 (8): 1810-8 (2008)
Oxidants
Electron-accepting molecules in chemical reactions in which electrons are transferred from one molecule to another (OXIDATION-REDUCTION). (See all compounds classified as Oxidants.)
Disinfectants
Substances used on inanimate objects that destroy harmful microorganisms or inhibit their activity. Disinfectants are classed as complete, destroying SPORES as well as vegetative forms of microorganisms, or incomplete, destroying only vegetative forms of the organisms. They are distinguished from ANTISEPTICS, which are local anti-infective agents used on humans and other animals. (From Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, 11th ed) (See all compounds classified as Disinfectants.)
An in vitro dermal penetration assay at 37 C using 0.8 % PAA (non-corrosive) indicated a low dermal uptake of peracetic acid through the intact skin of pigs. When the skin of rats was exposed to a corrosive concentration of (14)C-labelled PAA, a considerable uptake of (14)C was found but it is unknown if the (14)C was present as peracetic acid, acetic acid, or CO2. It is expected that corrosive concentrations of PAA would compromise the normal barrier function of the skin.
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; SIDS Initial Assessment Profile (SIAP) for Peracetic acid (79-21-0), p.2 (SIAM 26, April 2008). Available from, as of October 5, 2010: https://webnet.oecd.org/Hpv/ui/SponsoredSubstances.aspx
Two reliable in vitro studies, using different analytical methods, showed a rapid degradation of peracetic acid in rat blood. When rat blood was diluted 1000 times, the half-life of peracetic acid was < 5 minutes. In undiluted blood the half-life is expected to be several seconds or less. For this reason the distribution of peracetic acid is probably very limited and it is not expected to be systemically available after exposure to peracetic acid solutions.
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; SIDS Initial Assessment Profile (SIAP) for Peracetic acid (79-21-0), p.2 (SIAM 26, April 2008). Available from, as of October 5, 2010: https://webnet.oecd.org/Hpv/ui/SponsoredSubstances.aspx
Degradation products have not been identified during kinetic studies. However, based on the structure of the substance the following degradation products are expected: acetic acid, oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and water. Hydrogen peroxide is also presumed to be rapidly degraded into oxygen and water.
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; SIDS Initial Assessment Profile (SIAP) for Peracetic acid (79-21-0), p.2 (SIAM 26, April 2008). Available from, as of October 5, 2010: https://webnet.oecd.org/Hpv/ui/SponsoredSubstances.aspx
When rat blood was diluted 1000 times, the half-life of peracetic acid was < 5 min. In undiluted blood the half-life is expected to be several seconds or less.
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; SIDS Initial Assessment Profile (SIAP) for Peracetic acid (79-21-0), p.2 (SIAM 26, April 2008). Available from, as of October 5, 2010: https://webnet.oecd.org/Hpv/ui/SponsoredSubstances.aspx
To explore possible mechanisms of the arachidonic acid deficiency of the RBC membrane in alcoholics, the effect of ethanol and its oxidized products, acetaldehyde and peracetic acid, with other peroxides on the accumulation of 14(C)arachidonate into RBC membrane lipids in vitro was compared. Incubation of erythrocytes with 50 mM ethanol or 3 mM acetaldehyde had no effect on arachidonate incorporation. Pretreatment of erythrocytes with 10 mM hydrogen peroxide, 0.1 mM cumene hydroperoxide or 0.1 mM t-butyl hydroperoxide had little effect on 14(C)arachidonate incorporation in the absence of azide. However, pretreatment of cells with N-ethylmaleimide, 0.1 mM peracetic acid or performic acid, with or without azide, inhibited arachidonate incorporation into phospholipids but not neutral lipids. In chase experiments, peracetate also inhibited transfer of arachidonate from neutral lipids to phospholipids. To investigate a possible site of this inhibition of arachidonate transfer into phospholipids by percarboxylic acids, a repair enzyme, arachidonoyl CoA: 1-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine acyl transferase was assayed. As in intact cells, phospholipid biosynthesis was inhibited more by N-ethylmalemide and peracetic acid than by hydrogen peroxide, cumene hydroperoxide, and t-butyl hydroperoxide. Peracetic acid was the only active inhibitor among ethanol and its oxidized products studied and may deserve further examination in ethanol toxicity.
PMID:1900205 Allen DW et al; Biochim Biophys Acta 1081 (3): 267-73 (1991)
ABOUT THIS PAGE
71
PharmaCompass offers a list of Peroxyacetic Acid API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Peroxyacetic Acid manufacturer or Peroxyacetic Acid supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Peroxyacetic Acid manufacturer or Peroxyacetic Acid supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Peroxyacetic Acid API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Peroxyacetic Acid API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Peroxyacetic Acid Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Peroxyacetic Acid Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Peroxyacetic Acid manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Peroxyacetic Acid, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Peroxyacetic Acid manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Peroxyacetic Acid API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Peroxyacetic Acid supplier is an individual or a company that provides Peroxyacetic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Peroxyacetic Acid finished formulations upon request. The Peroxyacetic Acid suppliers may include Peroxyacetic Acid API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Peroxyacetic Acid Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Peroxyacetic Acid GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Peroxyacetic Acid GMP manufacturer or Peroxyacetic Acid GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Peroxyacetic Acid CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Peroxyacetic Acid's compliance with Peroxyacetic Acid specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Peroxyacetic Acid CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Peroxyacetic Acid CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Peroxyacetic Acid may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Peroxyacetic Acid EP), Peroxyacetic Acid JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Peroxyacetic Acid USP).
