
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
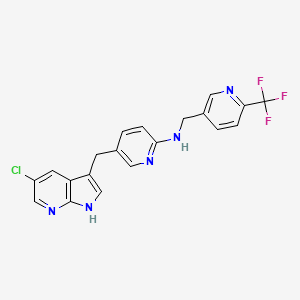

1. 5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-((6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)pyridin-2-amine
2. Pexidartinib Hydrochloride
3. Plx3397
4. Turalio
1. 1029044-16-3
2. Plx3397
3. Plx-3397
4. Pexidartinib (plx3397)
5. Turalio
6. Cml-261
7. Pexidartinib [inn]
8. Pexidartinib [usan]
9. 5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-((6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)pyridin-2-amine
10. Chembl3813873
11. 6783m2lv5x
12. 3-pyridinemethanamine, N-(5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-2-pyridinyl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)-
13. 5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-[[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]methyl]pyridin-2-amine
14. 5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-{[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]methyl}pyridin-2-amine
15. 5-({5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl}methyl)-n-{[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]methyl}pyridin-2-amine
16. Pexidartinibum
17. Unii-6783m2lv5x
18. 5-((5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-n-((6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)pyridin-2-amine
19. Pexidartinib [mi]
20. Pexidartinib(plx3397)
21. Pexidartinib (usan/inn)
22. Pexidartinib [usan:inn]
23. Pexidartinib [who-dd]
24. Gtpl8710
25. Schembl1267310
26. Ex-a589
27. Chebi:145373
28. Dtxsid301026482
29. Hms3886d19
30. Bcp15183
31. Plx 3397
32. Bdbm50177716
33. Mfcd28900745
34. Nsc789300
35. Nsc793434
36. Nsc800843
37. S7818
38. Akos026750359
39. Zinc115705166
40. Ccg-268862
41. Db12978
42. Nsc-789300
43. Nsc-793434
44. Nsc-800843
45. Sb19178
46. Ncgc00480774-01
47. Ncgc00480774-06
48. Ac-30300
49. As-74915
50. Da-48267
51. Hy-16749
52. Ft-0699505
53. Plx 3397;plx3397;pl-x3397
54. D11270
55. A856116
56. J-690008
57. Q25100640
58. B0084-470807
59. 2(s)-amino-3-(4-{2-amino-6-[2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(3'-fluoro-biphenyl-4-yl)-ethoxy]-pyrimidin-4-yl}-phenyl)-propionic Acid Hydrochloride
60. 5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-n-[[6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridyl]methyl]pyridin-2-amine
61. N-[5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-pyridinyl]-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinemethanamine
62. N-[5-[(5-chloro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2-pyridinyl]-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinemethanamine;pexidartinib
| Molecular Weight | 417.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H15ClF3N5 |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 417.0968077 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 417.0968077 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 66.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 537 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Pexidartinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) associated with severe morbidity or functional limitations and not amenable to improvement with surgery.
Treatment of tenosynovial giant cell tumour. ,
Pexidartinib works by suppressing the growth of tenosynovial giant cell tumors. In clinical trials comprising of patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor, pexidartinib had a higher overall response rate, characterized by improved patient symptoms and functional outcomes, compared to placebo. Pexidartinib works by inhibiting the activation and signaling of tumor-permissive cytokines and receptor tyrosine kinases that play a central role in tumor cell proliferation and survival.
L01XE
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX15 - Pexidartinib
Absorption
Following administration of single doses in healthy subjects and multiple doses in patients, the mean Cmax was 8625 ng/mL and the mean AUC was 77465 ngxh/mL. The median Tmax was 2.5 hours and the time to reach the steady state was approximately 7 days. Administration of pexidartinib with a high fat meal resulted in an increased drug Cmax and AUC by 100%, with a delay in Tmax by 2.5 hours.
Route of Elimination
Pexidartinib is predominantly excreted via feces, where fecal excretion accounts for 65% of total pexidartinib elimination. Via this route of elimination, about 44% of the compound found in feces is recovered as unchanged parent drug. The renal elimination accounts for 27% of pexidartinib elimination, where more than 10% of the compound is found as the N-glucuronide metabolite.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of pexidartinib is about 187 L. In rats, pexidartinib was shown to penetrate into the central nervous system.
Clearance
The apparent clearance is about 5.1 L/h.
Pexidartinib primarily undergoes oxidation mediated by hepatic CYP3A4 and glucuronidation by UGT1A4. Following UGT1A4-mediated glucuronidation, a major inactive N-glucuronide metabolite is formed with approximately 10% higher exposure than the parent drug after a single dose administration of pexidartinib. Based on the findings of _in vitro_ studies, CYP1A2 and CYP2C9 may also play a minor role in drug metabolism.
The elimination half-life is about 26.6 hours.
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor is a rare, non-malignant neoplasm that causes abnormal growth and damage to the synovium, bursae, or tendon sheaths. Recruitment of immune cells, specifically macrophages, is closely associated with the tumor mass formation in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Macrophages drive tumor-promoting inflammation and play a central role in every stage of tumor progression. As the most abundant immune cells in the tumor microenvironment of solid tumors, macrophages promote processes that enhance tumor survival, such as angiogenesis, tumor cell invasion, and intravasation at the primary site. They also modulate the immune response to tumors to inhibit tumor clearance and directly engage with tumor cells to activate pro-survival signaling pathways. The recruitment, proliferation, and irreversible differentiation of macrophages are regulated by colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1), which is a cytokine that is often translocated and highly expressed in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Elevated expression of CSF-1 and CSF-1 receptor (CSF1R) has also been implicated in various models of malignant cancers and tumors. Pexidartinib targets the CSF1/CSF1R pathway as a selective CSF1R inhibitor. It stimulates the autoinhibited state of the CSF1R by interacting with the juxtamembrane region of CSF1R, which is responsible for folding and inactivation of the kinase domain, and preventing the binding of CSF1 and ATP to the region. Without the binding of CSF1 to the receptor, CSF1R cannot undergo ligand-induced autophosphorylation. By inhibiting the CSF1R signaling pathway, pexidartinib works to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and downmodulate cells involved in the disease, such as macrophages. It was also shown to inhibit the CD117 or proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase (cKIT), mutant fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)-, which are all receptor tyrosine kinases that regulate critical cellular processes such as cell proliferation and survival.

0.0
<10
0.0
24.0
API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| UNITED STATES | 0.00 | 0.0 | <10 |
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

ABOUT THIS PAGE
87
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pexidartinib API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pexidartinib manufacturer or Pexidartinib supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Pexidartinib manufacturer or Pexidartinib supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Pexidartinib API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Pexidartinib API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Pexidartinib Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Pexidartinib Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Pexidartinib manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Pexidartinib, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Pexidartinib manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Pexidartinib API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Pexidartinib manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Pexidartinib supplier is an individual or a company that provides Pexidartinib active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Pexidartinib finished formulations upon request. The Pexidartinib suppliers may include Pexidartinib API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Pexidartinib suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Pexidartinib Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pexidartinib GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pexidartinib GMP manufacturer or Pexidartinib GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Pexidartinib CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Pexidartinib's compliance with Pexidartinib specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Pexidartinib CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Pexidartinib CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Pexidartinib may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Pexidartinib EP), Pexidartinib JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Pexidartinib USP).
