
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
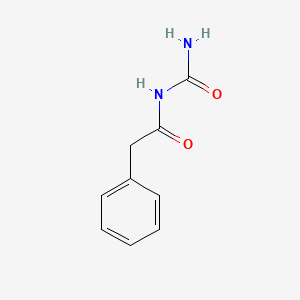

1. (phenylacetyl)urea
2. Phenuron
1. Phenylacetylurea
2. 63-98-9
3. Phenurone
4. Phenacetylurea
5. Cetylureum
6. Phenuron
7. N-carbamoyl-2-phenylacetamide
8. Fenacemid
9. Neophedan
10. Phenacalum
11. Phenacetur
12. Phenicarb
13. Phetylureum
14. Phacetur
15. Phenacetylcarbamide
16. Fenacetamide
17. Acetylureum
18. Carbanmide
19. Comitiadone
20. Epiclase
21. Fenacemide
22. Fenostenyl
23. Fenurone
24. Neophenal
25. Phenacereum
26. Phenarone
27. Phenutal
28. Phenyrit
29. Epheron
30. Felurea
31. Fenilep
32. Fenised
33. Fenural
34. Fenurea
35. Fenytan
36. Efron
37. (phenylacetyl)urea
38. Eferon
39. Fenacetil-karbamide
40. Phenylacetyluree
41. Carbamide Phenylacetate
42. Fenylacetylmocovina
43. Benzeneacetamide, N-(aminocarbonyl)-
44. Urea, (phenylacetyl)-
45. (2-phenylacetyl)urea
46. N-(aminocarbonyl)benzeneacetamide
47. A-1348
48. Nsc 39458
49. .alpha.-phenylacetylurea
50. Nsc-39458
51. Chebi:8049
52. Pai7j52v09
53. Phenacemidum
54. Phenacerum
55. Fenacemide [dcit]
56. Ncgc00094754-01
57. Fenacemida
58. Dsstox_cid_3442
59. Dsstox_rid_77032
60. Phenylacetyluree [french]
61. Dsstox_gsid_23442
62. Fenacemida [inn-spanish]
63. Phenacemidum [inn-latin]
64. Fenylacetylmocovina [czech]
65. Cas-63-98-9
66. Phenurone (tn)
67. Hsdb 3380
68. Phenacemide (jan/inn)
69. Einecs 200-570-2
70. Brn 2048735
71. Unii-pai7j52v09
72. Phenacemide [usp:inn:ban]
73. N-(aminocarbonyl)-2-phenylacetamide
74. N-(phenylacetyl)urea
75. Spectrum_000923
76. N-(phenylacetyl)urea #
77. Phenacemide [mi]
78. Spectrum2_001019
79. Spectrum3_000679
80. Spectrum4_000473
81. Spectrum5_001240
82. Phenacemide [inn]
83. Phenacemide [jan]
84. Wln: Zvmv1r
85. Phenacemide [hsdb]
86. Chembl918
87. Phenacemide [vandf]
88. Phenacemide [mart.]
89. Schembl35118
90. Bspbio_002377
91. Kbiogr_000946
92. Kbioss_001403
93. Phenacemide [who-dd]
94. 4-09-00-01636 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
95. Divk1c_000320
96. Spectrum1500472
97. Spbio_001177
98. Gtpl7265
99. Zinc1916
100. Dtxsid6023442
101. Hms500p22
102. Kbio1_000320
103. Kbio2_001403
104. Kbio2_003971
105. Kbio2_006539
106. Kbio3_001597
107. Phenacemide [orange Book]
108. Ninds_000320
109. Hms1920f16
110. Hms2091n16
111. Pharmakon1600-01500472
112. Nsc39458
113. Tox21_111325
114. Ccg-40237
115. Mfcd00007948
116. Nsc757266
117. Akos009156469
118. Tox21_111325_1
119. Db01121
120. Nsc-757266
121. Idi1_000320
122. Ncgc00094754-02
123. Ncgc00094754-03
124. Ncgc00094754-05
125. Sbi-0051478.p003
126. Db-054589
127. Ft-0631283
128. C07428
129. D00504
130. Ab00052068_02
131. 063p989
132. Sr-05000001694
133. Q3742404
134. Sr-05000001694-1
135. 1-[(c-hydroxycarbonimidoyl)imino]-2-phenylethan-1-ol
136. Brd-k40905133-001-02-3
137. Brd-k40905133-001-03-1
| Molecular Weight | 178.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H10N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 178.074227566 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 178.074227566 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 72.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 198 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anticonvulsants
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
PHENACEMIDE SHOULD BE USED ONLY IN THERAPY OF TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSY REFRACTORY TO OTHER AGENTS, IN ASSOCIATION WITH OTHER DRUGS, & ONLY IF ADEQUATE SUPERVISION & MONITORING ARE POSSIBLE.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 218
PHENACEMIDE IS EFFECTIVE ANTICONVULSANT THAT MAY BE USEFUL IN...GENERALIZED TONIC-CLONIC, ABSENCE, & MIXED SEIZURES.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 470
MEDICATION (VET): ANTICONVULSANT. USE/D/ IN CHOREA & VARIOUS EPILEPTIFORM CONVULSIVE DISORDERS OF DOGS USUALLY IN COMBINATION WITH SMALL DOSES OF PHENOBARBITAL.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 436
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PHENACEMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Phenacemide has produced hepatitis and jaundice which have proceeded to fatal liver necrosis. Severe bone marrow depression, including fatalities resulting from aplastic anemia or agranulocytosis has also occurred in association with phenacemide therapy. Leukopenia (leukocyte count of 4000/cu mm or less) has been the most commonly observed effect.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1639
Phenacemide has also produced acute psychoses, often with suicidal tendencies. Phenacemide-induced psychological disturbances subside promptly when the drug is discontinued. Some authorities believe that phenacemide merely exacerbates or intensifies previously existing personality disorders.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1640
Phenacemide has occasionally produced nephritis characterized by marked albuminuria. A substantial increase in serum creatinine concentration in the absence of elevated BUN or any other evidence of renal disease may also occur in some patients receiving phenacemide.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1640
Other adverse reactions which have occurred during phenacemide therapy are anorexia and weight loss, drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, insomnia, headache, paresthesia, fever, muscle pain, palpitations, and rashes.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1640
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PHENACEMIDE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used to control certain seizures in the treatment of epilepsy.
Phenacemide is a ureal anticonvulsant indicated for control of severe epilepsy, particularly mixed forms of complex partial (psychomotor or temporal lobe) seizures, refractory to other anticonvulsants. Phenacemide elevates the threshold for minimal electroshock convulsions and abolishes the tonic phase of maximal electroshock seizures. It also prevents or modifies seizures induced by pentylenetetrazol or other convulsants.
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AX - Other antiepileptics
N03AX07 - Phenacemide
Absorption
Almost completely absorbed.
PHENACEMIDE IS ALMOST COMPLETELY ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT. ... UNCHANGED DRUG IS NOT EXCRETED IN URINE... PLASMA CONCN ASSOCIATED WITH EFFICACY & SAFETY HAVE NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 218
COMPARISON OF EXCRETION OF (14)C-PHENACETYLUREA IN DIFFERENT SPECIES SHOWED DIFFERENCES IN BIOTRANSFORMATION. AFTER ORAL DOSE, RATS EXCRETED 63% OF (14)C IN 48-HR URINE, GUINEA-PIGS 56%, RABBITS 87%, & MICE 62%.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 54
Metabolized in the liver by hepatic microsomal enzymes, where it is inactivated by p-hydroxylation.
BIOTRANSFORMATION OF PHENACETYLUREA IN RABBITS GAVE PHENYLACETIC ACID & PHENACETURIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF UREIDO-GROUP, & 4-HYDROXYPHENACETYLUREA & 3-METHOXY-4-HYDROXYPHENACETYLUREA BY SUCCESSIVE RING-HYDROXYLATION & METHYLATION OF PHENOLIC HYDROXY-GROUP. PHENACETYLUREA N-GLUCURONIDE...DID NOT APPEAR TO BE FORMED...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 178
BIOTRANSFORMATION BY HEPATIC MICROSOMAL ENZYMES INCL INACTIVATION BY PARAHYDROXYLATION OF PHENYL SUBSTITUENT; RING CLOSURE TO FORM HYDANTOIN DOES NOT OCCUR.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 218
22-25 hours.
In one study using 1 control subject and 3 epileptic patients, the half-life of phenacemide was demonstrated to be 22 to 25 hours.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 2315
Phenacemide binds to and blocks neuronal sodium channels or voltage sensitive calcium channels. This blocks or suppresses neuronal depolarization and hypersynchronization. Hypersynchronization is what often causes seizures.
IT ACTS BOTH TO INCR THRESHOLD FOR CONVULSIVE STIMULI REACHING CNS AS WELL AS PREVENTING SPREAD OF SEIZURE DISCHARGE FROM INITIATING FOCI.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1016
...HAS BROAD SPECTRUM OF ANTICONVULSANT ACTIVITY IN EXPTL ANIMALS. IN NONTOXIC DOSES, IT ABOLISHES TONIC EXTENSOR PHASE OF MAX ELECTROSHOCK SEIZURES, ELEVATES THRESHOLD FOR ELECTROSHOCK CONVULSIONS IN NORMAL & HYPONATREMIC ANIMALS, & PREVENTS OR MODIFIES PENTYLENETETRAZOL SEIZURES...
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 218
The mechanism of action in humans has not been established. However, in animals, at doses well below those causing neurological signs, phenacemide elevates the threshold for minimal electroshock convulsions and abolishes the tonic phase of maximal electroshock seizures. It also prevents or modified seizures induced by pentylenetetrazol or other convulsants.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 2315
ABOUT THIS PAGE
78
PharmaCompass offers a list of Phenacemide API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Phenacemide manufacturer or Phenacemide supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Phenacemide manufacturer or Phenacemide supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Phenacemide API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Phenacemide API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Phenacemide Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Phenacemide Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Phenacemide manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Phenacemide, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Phenacemide manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Phenacemide API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Phenacemide supplier is an individual or a company that provides Phenacemide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Phenacemide finished formulations upon request. The Phenacemide suppliers may include Phenacemide API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Phenacemide Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Phenacemide GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Phenacemide GMP manufacturer or Phenacemide GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Phenacemide CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Phenacemide's compliance with Phenacemide specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Phenacemide CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Phenacemide CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Phenacemide may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Phenacemide EP), Phenacemide JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Phenacemide USP).
