


1. 33-epi-chloro-33-desoxyascomycin
2. Asm 981
3. Elidel
4. Sdz Asm 981
5. Sdz-asm-981
1. Elidel
2. 137071-32-0
3. Sdz-asm 981
4. Sdz-asm-981
5. Sdz Asm 981
6. 33-epi-chloro-33-desoxyascomycin
7. Asm 981
8. 7kyv510875
9. Elidel (tn)
10. Pimecrolimus [usan:inn:ban]
11. 1000802-56-1
12. 33-epichloro-33-desoxyascomycin
13. Pimecrolimus (jan/usan/inn)
14. Unii-7kyv510875
15. Asm-981
16. Asm-998
17. Ncgc00167506-01
18. Pimecrolimus (elidel)
19. Pimecrolimus [mi]
20. (-)-pimecrolimus
21. Pimecrolimus [inn]
22. Pimecrolimus [jan]
23. Pimecrolimus [usan]
24. Pimecrolimus [vandf]
25. Pimecrolimus [mart.]
26. Pimecrolimus [who-dd]
27. Schembl438880
28. Sdz Asm-981
29. Gtpl6783
30. Schembl3000675
31. Chembl1200686
32. Pimecrolimus, >=97% (hplc)
33. Chebi:135888
34. Pimecrolimus [orange Book]
35. Ex-a2138
36. Bdbm50248356
37. Mfcd00901792
38. S5004
39. Zinc85536990
40. Akos015895946
41. Ccg-270502
42. Db00337
43. Ncgc00167506-04
44. Hy-13723
45. B1817
46. D05480
47. Ab01566841_01
48. 071p320
49. Q417489
50. Q-201579
51. Brd-k92107055-001-01-9
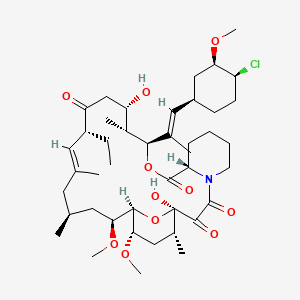
52. (1r,9s,12s,13r,14s,17r,18e,21s,23s,24r,25s,27r)-12-[(1e)-1-[(1r,3r,4s)-4-chloro-3-methoxycyclohexyl]prop-1-en-2-yl]-17-ethyl-1,14-dihydroxy-23,25-dimethoxy-13,19,21,27-tetramethyl-11,28-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[22.3.1.0?,?]octacos-18-ene-2,3,10,16-tetrone
53. (3s,4r,5s,8r,9e,12s,14s,15r,16s,18r,19r,26as)-3-((e)-2-((1r,3r,4s)-4-chloro-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylvinyl)-8-ethyl-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-epoxy-3h-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclotricosine-1,17,20,21(4h,23h)-tetrone
54. 15,19-epoxy-3h-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4h,23h)-tetrone, 3-((1e)-2-((1r,3r,4s)-4-chloro-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethenyl)-8-ethyl-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-, (3s,4r,5s,8r,9e,12s,14s,15r,16s,18r,19r,26as)-
55. 15,19-epoxy-3h-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4h,23h)-tetrone, 3-(2-(4-chloro-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethenyl)-8-ethyl-, 5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-, (3s-(3r*(e(1s*,3s*,4r*)),4s*,5r*,8s*,9e,12r*,14r*,15s*,16r*,18s*,19s*,26ar*))-
| Molecular Weight | 810.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C43H68ClNO11 |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 809.4480897 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 809.4480897 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 158 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 56 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1440 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 14 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Elidel |
| PubMed Health | Pimecrolimus (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | ELIDEL (pimecrolimus) Cream 1% contains the compound pimecrolimus, the immunosuppressant 33-epi-chloro-derivative of the macrolactam ascomycin.Chemically, pimecrolimus is (1R,9S,12S,13R,14S,17R,18E,21S,23S,24R,25S,27R)-12-[(1E)-2-{(1R,3R,4S)-4-chl... |
| Active Ingredient | Pimecrolimus |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Bermuda |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Elidel |
| PubMed Health | Pimecrolimus (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | ELIDEL (pimecrolimus) Cream 1% contains the compound pimecrolimus, the immunosuppressant 33-epi-chloro-derivative of the macrolactam ascomycin.Chemically, pimecrolimus is (1R,9S,12S,13R,14S,17R,18E,21S,23S,24R,25S,27R)-12-[(1E)-2-{(1R,3R,4S)-4-chl... |
| Active Ingredient | Pimecrolimus |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Bermuda |
For treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.
FDA Label
Pimecrolimus is a chemical that is used to treat atopic dermatitis (eczema). Atopic dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by redness, itching, scaling and inflammation of the skin. The cause of atopic dermatitis is not known; however, scientists believe that it may be due to activation of the immune system by various environmental or emotional triggers. Scientists do not know exactly how pimecrolimus reduces the manifestations of atopic dermatitis, but pimecrolimus reduces the action of T-cells and mast cells which are part of the immune system and contribute to responses of the immune system. Pimecrolimus prevents the activation of T-cells by blocking the effects of chemicals (cytokines) released by the body that stimulate T-cells. Pimecrolimus also reduces the ability of mast cells to release chemicals that promote inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Calcineurin Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit or block the PHOSPHATASE activity of CALCINEURIN. (See all compounds classified as Calcineurin Inhibitors.)
Dermatologic Agents
Drugs used to treat or prevent skin disorders or for the routine care of skin. (See all compounds classified as Dermatologic Agents.)
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D11 - Other dermatological preparations
D11A - Other dermatological preparations
D11AH - Agents for dermatitis, excluding corticosteroids
D11AH02 - Pimecrolimus
Absorption
Because of the low systemic absorption of pimecrolimus following topical application the calculation of standard pharmacokinetic measures such as AUC, Cmax, half-life, etc. cannot be reliably done.
Route of Elimination
80% of the drug is excreted in the feces.
No drug metabolism was observed in human skin in vitro. Oral administration yielded metabolites produced from O-demethylation and oxygenation reactions.
Pimecrolimus binds with high affinity to macrophilin-12 (FKBP-12) and inhibits the calcium-dependent phosphatase, calcineurin. As a consequence, it inhibits T cell activation by blocking the transcription of early cytokines. In particular, pimecrolimus inhibits at nanomolar concentrations Interleukin-2 and interferon gamma (Th1-type) and Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-10 (Th2-type) cytokine synthesis in human T cells. Also, pimecrolimus prevents the release of inflammatory cytokines and mediators from mast cells in vitro after stimulation by antigen/lgE.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?
