
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
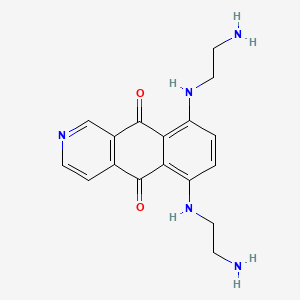

1. 5,8-bis((2-aminoethyl)amino)-2-aza-anthracene-9,10-dione
2. 5,8-bis(2-aminoethylamino)-2-azaanthracene-9,10-dione
3. 6,9-aea-biqdo
4. 6,9-bis((2-aminoethyl)amino)benzo(g)isoquinoline-5,10-dione
5. Bbr 2778
6. Bbr-2778
7. Bbr2778
1. 144510-96-3
2. 6,9-bis(2-aminoethylamino)benzo[g]isoquinoline-5,10-dione
3. Pixantrone Dimaleate
4. Bbr 2778
5. F5sxn2knmr
6. Bbr-2778
7. Pixuvri (tn)
8. 6,9-bis((2-aminoethyl)amino)benzo(g)isoquinoline-5,10-dione
9. 144675-97-8
10. 6,9-bis((2-aminoethyl)amino)benzo[g]isoquinoline-5,10-dione
11. Benz(g)isoquinoline-5,10-dione, 6,9-bis((2-aminoethyl)amino)-
12. 6,9-aea-biqdo
13. Unii-f5sxn2knmr
14. 6,9-bis[(2-aminoethyl)amino]benzo[g]isoquinoline-5,10-dione
15. Pixantrone [usan:inn:ban]
16. Benz[g]isoquinoline-5,10-dione, 6,9-bis[(2-aminoethyl)amino]-
17. Pixantrone [mi]
18. Pixantrone [inn]
19. Pixantrone (usan/inn)
20. Pixantrone [usan]
21. Pixantrone [mart.]
22. Schembl7825
23. Pixantrone (bbr 2778)
24. Pixantrone [who-dd]
25. Chembl167731
26. Gtpl7544
27. Dtxsid10162744
28. Chebi:135945
29. 5,8-bis((2-aminoethyl)amino)-2-aza-anthracene-9,10-dione
30. 6,9-bis((2-aminoethyl)amino)benz(g)isoquinoline-5,10-dione
31. Bcp05981
32. Zinc1535903
33. Akos005145782
34. Am84406
35. Db06193
36. Sb16817
37. Ncgc00274280-01
38. Ac-26441
39. Hy-13727
40. Ft-0673961
41. Ft-0689753
42. D05522
43. 510p963
44. A808224
45. Q7199690
46. 6,9-bis(2-azanylethylamino)benzo[g]isoquinoline-5,10-dione
47. (6,9-bis[(2-aminoethyl)amino]benzo[g]isoquinoline-5,10-dione)
| Molecular Weight | 325.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H19N5O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 325.15387487 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 325.15387487 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 123 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 472 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Currently in Phase III investigation for treatment of relapsed or refractory aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in patients who have failed two prior lines of therapy. Presently, no standard therapy exists for patients with relapsed or refractory NHL. [2] After first line therapy has been initiated, most patients have received their lifetime limit of doxorubicin and further use of anthracyclines may potentially lead to anthracycline-induced congestive heart failure (CHF). Pixantrone is an attractive alternative as a second line agent, due to its lack of cardiac toxicity. [2] The phase III trial, PIX-R, is ongoing and will compare pixantrone multidrug therapy with an equivalent regimen in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (the most common type of NHL). Previous study results have also suggested the possibility that pixantrone may be safe and effective in doxorubicin naive patients. In myocardial strips which are doxorubicin naive, pixantrone is taken up to a higher degree than in myocardial strips which are doxorubicin exposed, and once absorbed exhibits redox inactivity. [3] Pixantrone dimaleate has also been investigated as a treatment for acute myelogenous leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, metastatic breast cancer, low grade small lymphocytic lymphomas and general metastatic cancers.
Pixuvri is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with multiply relapsed or refractory aggressive non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas (NHL). The benefit of pixantrone treatment has not been established in patients when used as fifth-line or greater chemotherapy in patients who are refractory to last therapy.
Treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Pixantrone has a wide range of antitumor activity, especially in terms of treating leukemias and lymphomas [3]. Pixantrone lacks cardio-toxic effects. It has postulated that his is because of its redox inactivity and lack and inhibition of doxorubicinol formation in human myocardium. [3]
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
L01DB11
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01D - Cytotoxic antibiotics and related substances
L01DB - Anthracyclines and related substances
L01DB11 - Pixantrone
Absorption
Intravenous administration results in a rapid distribution followed by a slow elimination. [2] In ex vivo myocardial strips, pixantrone is taken up to a higher degree than mitoxantrone. In myocardial strips which are doxorubicin naive pixantrone displays higher uptake than in DOX-loaded myocardial strips. DOX clearance causes membrane effects which may be responsible for this observation. DOX clearance involves rapid passive diffusion through one side of the membrane followed by "flip flop" reorientation of the lipid bilayer. This disorganization of lipids is believed to impair membrane penetration by pixantrone. [3]
Route of Elimination
Fecally and renally excreted. Urinary elimination of unchanged drug is less than 10%. [2]
Volume of Distribution
9.7-29.7 L/kg. [2]
Clearance
Plasma clearance is 0.75 - 1.31 L/h/kg. [2]
Pixantrone does not form secondary alcohol metabolites. [2] Pixantrone hydrolyzes extensively to CT-45886 which is believed to inhibit doxol formation by displacing DOX from the active site of reductases. CT4889 and CT-45890 are also formed.[3]
Half life is 12 hours. [2]
Pixantrone is an aza-anthracenedione which acts as a DNA intercalator. By intercalating between DNA, with modest affinity, it stimulates DNA cleavage by topoisomerase II. (Pixantrone acts as a poison to topoisomerase II by stabilizing protein-DNA complexes which are usually transient, giving rise to double stranded DNA breaks.) However, pixantrone is believed to have additional mechanisms of action as its potency does not correlate to the degree of double stranded DNA breaks observed. It has been postulated that this second mechanism may be pixantrone-DNA adduct formation. [1] It is important to note that the formation of a pixtantrone-DNA adduct requires pixantrone activation by formaldehyde. Formadehyde may be generated in vitro by hydrogen peroxide, and is derived by various sources in biological systems. It is present in low levels as a result of normal metabolism, and may be present in elevated levels in some haematolgical malignancies. [1] The formation of pixantrone-DNA adducts is thus feasible, and it is believed that a long pixantrone-DNA adduct half life has the potential to maximize DNA damage. It may do so by enhancing the disruption of DNA replication and transcription, and potentially by encourage apoptosis. [1] In explanation of pixantrones lack of cardiotoxicity, it has been elucidated that pixantrone is structurally similar to mitoxantrone; however, instead of a 5,8-dihydroxyphenyl ring (thought to be responsible for cardiotoxicity) it has a nitrogen heteroatom. This nitrogen heteroatom helps to create additional hydrogen bonding sites amd increases pixantrone interaction with DNA and topoisomerase II. [2] Pixantrone's lack of a hydroquinone is believed to render it resistant to one electron reduction. In contrast, doxorubicin - which contains a hydroquinone - experiences one electron redox cycling and ROS formation via NADH dehydrogenase. [3] Pixantrone also does not bind iron, and thus does not produce ROS by redox cycling between oxidative states of iron, as other anthracyclines do. [2] The first line agent doxorubicin is cardiotoxic, in part, due to its ability to redox activate the superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide, and form a long-lived secondary alcohol metabolite: doxorubicinol. [3] Clearance of doxorubicin from myocardial tissue is incomplete, and it can be found months or years after the last administration. [3] In doxorubicin treated ex vivo cardiac strips, pixantrone formed an N-dealkylated product that inhibited metabolism of residual doxorubicin into doxorubicinol. Additionally, in ex vivo human myocardial strips (doxorubicin naive, and doxorubicin pretreated) pixantrone showed high cardiac uptake without formation of superoxide anion or hydrogen peroxide. Pixantrones lack of cardiotoxicity is thus attributed to its redox inactivity and inhibition of doxorubicinol formation. [3]
ABOUT THIS PAGE
72
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pixantrone API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pixantrone manufacturer or Pixantrone supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Pixantrone manufacturer or Pixantrone supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Pixantrone API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Pixantrone API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Pixantrone Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Pixantrone Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Pixantrone manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Pixantrone, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Pixantrone manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Pixantrone API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Pixantrone manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Pixantrone supplier is an individual or a company that provides Pixantrone active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Pixantrone finished formulations upon request. The Pixantrone suppliers may include Pixantrone API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Pixantrone suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Pixantrone Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pixantrone GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pixantrone GMP manufacturer or Pixantrone GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Pixantrone CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Pixantrone's compliance with Pixantrone specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Pixantrone CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Pixantrone CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Pixantrone may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Pixantrone EP), Pixantrone JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Pixantrone USP).
