
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Canada
0
Australia
0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
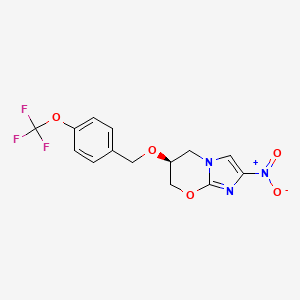

1. 2-nitro-6-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyloxy)-6,7-dihydro-5h-imidazo(2,1-b)(1,3)oxazine
2. Pa 824
3. Pa-824
4. Pa824 Cpd
1. Pa-824
2. 187235-37-6
3. Pa 824
4. Pa824
5. (s)-2-nitro-6-((4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyl)oxy)-6,7-dihydro-5h-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine
6. (s)-pa 824
7. 2xoi31yc4n
8. Chembl227875
9. Mmv688755
10. (6s)-2-nitro-6-[[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methoxy]-6,7-dihydro-5h-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine
11. (6s)-2-nitro-6-{[4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyl]oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5h-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine
12. (6s)-2-nitro-6-{[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methoxy}-5h,6h,7h-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine
13. Pretomanid [usan:inn]
14. Unii-2xoi31yc4n
15. Pretomanid (tn)
16. Pa-824(pretomanid)
17. Pretomanid [mi]
18. Pretomanid [inn]
19. Pretomanid (usan/inn)
20. Pretomanid [usan]
21. Pretomanid [who-dd]
22. Mls006011141
23. Schembl2983011
24. Dtxsid8041163
25. Pretomanid [orange Book]
26. Gtpl11172
27. Ex-a1749
28. Zinc3821675
29. Bdbm50363237
30. Cs1245
31. Mfcd06809939
32. S1162
33. Akos024464713
34. Ccg-268145
35. Db05154
36. Ds-7321
37. 2-nitro-6-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyloxy)-6,7-dihydro-5h-imidazo(2,1-b)(1,3)oxazine
38. Ncgc00346682-01
39. Ncgc00346682-02
40. Ac-25501
41. Hy-10844
42. Smr004702918
43. P2718
44. Sw220281-1
45. D10722
46. A855886
47. Sr-05000022748
48. Q7118312
49. Sr-05000022748-1
50. (3s)-3-(4-trifluoromethoxybenzyloxy)-6-nitro-2h-3,4-dihydroimidazo(2,1-b)oxazine
51. (s)-2-nitro-6-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyloxy)-6,7-dihydro-5h-imidazo(2,1-b)(1,3)oxazine
52. {4-[((3s)-6-nitro(2h,3h,4h-imidazolo[2,1-b]1,3-oxazaperhydroin-3-yloxy))methyl]phenoxy}trifluoromethane
53. 5h-imidazo(2,1-b)(1,3)oxazine, 6,7-dihydro-2-nitro-6-((4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)methoxy)-, (6s)-
54. Pretomanid;(6s)-6,7-dihydro-2-nitro-6-[[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methoxy]-5h-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine
| Molecular Weight | 359.26 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H12F3N3O5 |
| XLogP3 | 2.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 359.07290498 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 359.07290498 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 91.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 468 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Pretomanid is indicated for adults in combination with bedaquiline and linezolid for the treatment of pulmonary forms of nonresponsive multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and treatment-intolerant forms of pulmonary tuberculosis (TB). It is important to note that the following conditions are not approved indications for pretomanid therapy, according to the FDA: Drug-sensitive (DS) tuberculosis, latent tuberculosis caused by M.tuberculosis, extra-pulmonary tuberculosis caused by M.tuberculosis, and multidrug-resistant TB that is not treatment-intolerant or nonresponsive to conventional TB therapy.
Dovprela is indicated in combination with bedaquiline and linezolid, in adults, for the treatment of pulmonary extensively drug resistant (XDR), or treatment-intolerant or nonresponsive multidrug-resistant (MDR) tuberculosis (TB).
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Treatment of multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis
Pretomanid kills the actively replicating bacteria causing tuberculosis, known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and shortens the duration of treatment in patients who suffer from resistant forms of pulmonary TB by killing dormant bacteria. In rodent models of tuberculosis infection, pretomanid administered in a regimen with bedaquiline and linezolid caused a significant reduction in pulmonary bacterial cell counts. A decrease in the frequency of TB relapses at 2 and 3 months after treatment was observed after the administration of this regimen, when compared to the administration of a 2-drug regimen. Successful outcomes have been recorded for patients with XDR and MDR following a clinical trial of the pretomanid regimen, demonstrating a 90% cure rate after 6 months. **A note on cardiac QT prolongation, hepatotoxicity, and myelosuppression** This drug has the propensity to caused cardiac QT interval prolongation and significant hepatotoxicity, as well as myelosuppression. Caution must be observed during the administration of this drug.
J04
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J04 - Antimycobacterials
J04A - Drugs for treatment of tuberculosis
J04AK - Other drugs for treatment of tuberculosis
J04AK08 - Pretomanid
Absorption
This drug is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The steady-state Cmax of pretomanid was estimated to be 1.7 g/mL after a single 200mg oral dose. In a separate pharmacokinetic modeling study, the Cmax of a 200mg dose was 1.1 g/ml. Tmax in a study of healthy subjects in the fed or unfed state was achieved within 4 to 5 hours. The AUC in the same study was found to be about 28.1 ghr/mL in the fasted state and about 51.6 ghr/mL in the fed state, showing higher absorption when taken with high-calorie and high-fat food.
Route of Elimination
Healthy adult male volunteers were administered a 1,100 mg oral dose of radiolabeled pretomanid in one pharmacokinetic study. An average of about 53% of the radioactive dose was found to be excreted in the urine. Approximately 38% was measured mainly as metabolites in the feces. A estimated 1% of the radiolabeled dose was measured as unchanged drug in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
A pharmacokinetic modeling study estimated the volume of distribution at 130 5L. A pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers determined a volume of distribution of about 180 51.3L in fasted state and 97.0 17.2L in the fed state.
Clearance
The clearance of pretomanid in a pharmacokinetic simulation study has been estimated at 4.8 0.2 liters/h. According to the FDA label, the clearance of a single 200 mg oral dose of pretomanid is estimated to be 7.6 liters/h in the fasted state, and 3.9 liters/h in the fed state.
Various reductive and oxidative pathways are responsible for pretomanid metabolism, with no single major metabolic pathway identified. According to in vitro studies, CYP3A4 is responsible for a 20% contribution to the metabolism of pretomanid.
The elimination half-life was determined to be 16.9-17.4 hours in a pharmacokinetic study of healthy subjects. An FDA briefing document reports a half-life of 18 hours.
Pretomanid is a prodrug which is metabolically activated by a nitroreductase enzyme, known as Ddn, producing various active metabolites that are responsible for its other therapeutic actions, particularly the induction of nitric oxide. The nitroreductase enzyme which activates pretomanid is deazaflavin dependent and relies on reduced cofactor F420. Reduction of F420 occurs via the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Reduction of pretomanid's imidazole ring at the C-3 position causes the formation of the metabolites, which include a des-nitro derivative. The formation of this derivative leads to increased levels of nitric oxide, leading to bactericidal activities under anaerobic conditions via its action as a bacterial respiratory poison. Bactericidal activity against anaerobes is reported to be associated with a shortened duration of antibiotic treatment. Pretomanid exerts aerobic bactericidal effects through its inhibitory actions on bacterial cell wall mycolic acid biosynthesis. This allows for the killing of actively replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, resulting in the treatment of active tuberculosis infection. The molecular mechanism of the above bactericidal effects is poorly understood at this time, but may involve effects exerted on various genes that affect the cell wall, including the fasI and fasII as well as the efpA and iniBAC operons. Other possible targets include the genes of the cyd operon. The clinical effects of the above target relations are unknown at this time.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
16
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pretomanid API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pretomanid manufacturer or Pretomanid supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Pretomanid manufacturer or Pretomanid supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Pretomanid API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Pretomanid API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Pretomanid Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Pretomanid Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Pretomanid manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Pretomanid, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Pretomanid manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Pretomanid API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Pretomanid manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Pretomanid supplier is an individual or a company that provides Pretomanid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Pretomanid finished formulations upon request. The Pretomanid suppliers may include Pretomanid API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Pretomanid suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Pretomanid DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Pretomanid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Pretomanid DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Pretomanid USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Pretomanid DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Pretomanid USDMF includes data on Pretomanid's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Pretomanid USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Pretomanid suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Pretomanid written confirmation (Pretomanid WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Pretomanid manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Pretomanid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Pretomanid APIs or Pretomanid finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Pretomanid WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Pretomanid suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
Pretomanid Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Pretomanid GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Pretomanid GMP manufacturer or Pretomanid GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Pretomanid CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Pretomanid's compliance with Pretomanid specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Pretomanid CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Pretomanid CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Pretomanid may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Pretomanid EP), Pretomanid JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Pretomanid USP).

