
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
VMF
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
Annual Reports
NA
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
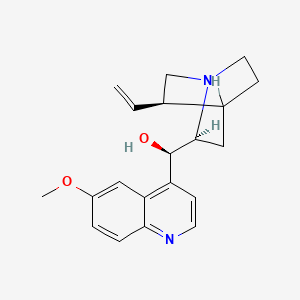

1. Ncgc00166281-01
2. Dsstox_cid_24280
3. Dsstox_rid_80140
4. Dsstox_gsid_44280
5. 130-95-0
6. Cas-130-95-0
7. Sr-01000075160
8. Quinine (ban)
9. Kinder Quinina (tn)
10. Lopac0_001029
11. Mls001304041
12. Chembl387326
13. Schembl12310700
14. Hms2233l08
15. Tox21_112389
16. Bdbm50411276
17. Akos015955637
18. Tox21_112389_1
19. Ncgc00274071-01
20. Smr000718748
21. C06526
22. D08460
23. Sr-01000075160-1
24. Sr-01000075160-12
25. (alphar,2s)-alpha-(6-methoxy-4-quinolyl)-5beta-vinyl-2alpha-quinuclidinemethanol
| Molecular Weight | 324.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H24N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 324.183778013 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 324.183778013 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 45.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 457 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Quinine sulfate |
| Drug Label | Quinine sulfate is a cinchona alkaloid chemically described as cinchonan-9-ol, 6'-methoxy-, (8, 9R)-, sulfate (2:1) (salt), dihydrate with a molecular formula of (C20H24N2O2)2H2SO42H2O and a molecular weight of 782.96.The structural formula o... |
| Active Ingredient | Quinine sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 324mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Teva Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Quinine sulfate |
| Drug Label | Quinine sulfate is a cinchona alkaloid chemically described as cinchonan-9-ol, 6'-methoxy-, (8, 9R)-, sulfate (2:1) (salt), dihydrate with a molecular formula of (C20H24N2O2)2H2SO42H2O and a molecular weight of 782.96.The structural formula o... |
| Active Ingredient | Quinine sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 324mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Teva Pharms |
Analgesics, Non-Narcotic; Antimalarials; Muscle Relaxants, Central
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Quinine. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of August 28, 2014: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Qualaquin (quinine sulfate) is an antimalarial drug indicated only for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Quinine sulfate has been shown to be effective in geographical regions where resistance to chloroquine has been documented. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Qualaquin (Quinine Sulfate) Capsule (Revised: April 2013). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1f66fba7-4026-4504-918d-4c88f2835cc0
Oral quinine sulfate is used in conjunction with IV or oral clindamycin for the treatment of babesiosis caused by Babesia microti. /NOT included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
Although quinine sulfate is not approved by the FDA for the treatment of severe or complicated malaria, the CDC states that oral quinine sulfate can be used in conjunction with doxycycline, tetracycline, or clindamycin for follow-up treatment after an appropriate initial parenteral regimen.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for QUININE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Qualaquin use for the treatment or prevention of nocturnal leg cramps may result in serious and life-threatening hematologic reactions, including thrombocytopenia and hemolytic uremic syndrome/thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (HUS/TTP). Chronic renal impairment associated with the development of TTP has been reported. The risk associated with Qualaquin use in the absence of evidence of its effectiveness in the treatment or prevention of nocturnal leg cramps outweighs any potential benefit.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Qualaquin (Quinine Sulfate) Capsule (Revised: April 2013). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1f66fba7-4026-4504-918d-4c88f2835cc0
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic shock, anaphylactoid reactions, urticaria, serious skin rashes (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis), angioedema, facial edema, bronchospasm, and pruritus, have been reported with quinine. In addition, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic uremic syndrome/thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (HUS/TTP), immune thrombocytopenic purpura, blackwater fever, disseminated intravascular coagulation, leukopenia, neutropenia, granulomatous hepatitis, and acute interstitial nephritis have been reported and may also be due to hypersensitivity reactions to the drug.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
Potentially fatal cardiac arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes and ventricular fibrillation, have been reported rarely during quinine therapy. At least 1 case of fatal ventricular arrhythmia has been reported in a geriatric patient with preexisting prolonged QT interval treated with IV quinine sulfate for Plasmodium falciparum malaria.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
Serious, life-threatening, and sometimes fatal hematologic reactions, including thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopenia, hemolytic uremic syndrome/thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (HUS/TTP), have been reported in patients receiving quinine, especially patients using the drug for unlabeled indications (prevention or treatment of leg cramps or restless leg syndrome). Subsequent development of chronic renal impairment has occurred in patients with quinine-associated TTP.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for QUININE (37 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The average fatal dose for an adult is about 8 g although deaths have been reported from as little as 1.5 g in an adult and 900 mg in a child.
IPCS; UK Poison Information Documents (UKPID) for Quinine (Last updated March 1996). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ukpids.html
A lethal dose of quinine has not been clearly defined, but fatalities have been reported after the ingestion of 2 to 8 grams in adults.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Qualaquin (Quinine Sulfate) Capsule (Revised: April 2013). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1f66fba7-4026-4504-918d-4c88f2835cc0
Following oral administration of a single 600-mg dose of quinine sulfate in healthy adults, the mean plasma clearance was 0.08-0.47 L/hour per kg (median: 0.17 L/hour per kg) and the mean plasma elimination half-life was 9.7-12.5 hours. Following oral administration of 10 mg/kg of quinine sulfate in patients with uncomplicated malaria, mean total clearance of quinine was decreased (approximately 0.09 L/hour per kg) during the acute phase of the infection and increased (approximately 0.16 L/hour per kg) during the recovery or convalescent phase.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
Following oral administration of a single 600-mg dose of quinine sulfate in geriatric and younger adults, the mean clearance of the drug was decreased (0.06 versus 0.08 L/hour per kg) and the mean elimination half-life was significantly increased (18.4 versus 10.5 hours) in geriatric adults compared with younger adults. Although renal clearance of quinine was similar in geriatric and younger adults, geriatric adults excreted a larger proportion of the dose in urine as unchanged drug compared with younger adults (16.6 versus 11.2%). The steady-state pharmacokinetics after a quinine sulfate dosage of 648 mg 3 times daily for 7 days were similar in healthy geriatric adults 65-78 years of age and healthy younger adults 20-39 years of age; however, the mean elimination half-life was 24 hours in the geriatric individuals compared with 20 hours in the younger adults.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
Following oral administration of a single dose of 10 mg/kg of quinine sulfate in healthy children or pediatric patients 1.5-12 years of age with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria, the mean total clearance (0.06 versus 0.3 L/hour per kg) is reduced and the plasma elimination half-life increased (12.1 versus 3.21 hours) in pediatric patients with malaria as compared to that observed in healthy children.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
In 15 patients with uncomplicated malaria who received a 10 mg/kg oral dose of quinine sulfate, the mean total clearance of quinine was slower (approximately 0.09 L/hr/kg) during the acute phase of the infection, and faster (approximately 0.16 L/hr/kg) during the recovery or convalescent phase.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Qualaquin (Quinine Sulfate) Capsule (Revised: April 2013). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1f66fba7-4026-4504-918d-4c88f2835cc0
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for QUININE (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In vitro studies using human liver microsomes and recombinant P450 enzymes have shown that quinine is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4. Depending on the in vitro experimental conditions, other enzymes, including CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP2E1 were shown to have some role in the metabolism of quinine.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Qualaquin (Quinine Sulfate) Capsule (Revised: April 2013). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1f66fba7-4026-4504-918d-4c88f2835cc0
Quinine is metabolized almost exclusively via hepatic oxidative cytochrome P450 (CYP) pathways, resulting in four primary metabolites, 3-hydroxyquinine, 2'-quinone, O-desmethylquinine, and 10,11-dihydroxydihydroquinine. Six secondary metabolites result from further biotransformation of the primary metabolites. The major metabolite, 3-hydroxyquinine, is less active than the parent drug.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Qualaquin (Quinine Sulfate) Capsule (Revised: April 2013). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=1f66fba7-4026-4504-918d-4c88f2835cc0
Compared with administration of quinine alone, administration of a single 600-mg dose of quinine sulfate in healthy individuals who were receiving ritonavir (200 mg every 12 hours) resulted in an increased quinine mean elimination half-life (11.2 hours versus 13.4 hours).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
The plasma elimination half-life of quinine reportedly averages 8-21 hours in adults with malaria and 7-12 hours in healthy or convalescing adults.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
The steady-state pharmacokinetics after a quinine sulfate dosage of 648 mg 3 times daily for 7 days were similar in healthy geriatric adults 65-78 years of age and healthy younger adults 20-39 years of age; however, the mean elimination half-life was 24 hours in the geriatric individuals compared with 20 hours in the younger adults.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
In children 1-12 years of age, the plasma elimination half-life of quinine reportedly averages 11-12 hours in those with malaria and 6 hours in those convalescing from the disease.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014
At toxic levels elimination half life is reported to be 26.5 + or - 5.8 hrs.
IPCS; UK Poison Information Documents (UKPID) for Quinine (Last updated March 1996). Available from, as of November 20, 2014: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ukpids.html
Quinine has a local anesthetic action and analgesic, antipyretic, and oxytocic effects. Quinine also has cardiovascular effects similar to those of quinidine.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
63
PharmaCompass offers a list of Quinine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Quinine manufacturer or Quinine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Quinine manufacturer or Quinine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Quinine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Quinine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Quinine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Quinine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Quinine Sulfate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Quinine Sulfate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Quinine Sulfate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Quinine Sulfate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Quinine Sulfate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Quinine Sulfate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Quinine Sulfate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Quinine Sulfate finished formulations upon request. The Quinine Sulfate suppliers may include Quinine Sulfate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Quinine Sulfate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Quinine Sulfate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Quinine Sulfate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Quinine Sulfate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Quinine Sulfate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Quinine Sulfate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Quinine Sulfate USDMF includes data on Quinine Sulfate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Quinine Sulfate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Quinine Sulfate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Quinine Sulfate CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Quinine Sulfate Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Quinine Sulfate CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Quinine Sulfate EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Quinine Sulfate to their clients by showing that a Quinine Sulfate CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Quinine Sulfate CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Quinine Sulfate CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Quinine Sulfate CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Quinine Sulfate DMF.
A Quinine Sulfate CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Quinine Sulfate CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Quinine Sulfate suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Quinine Sulfate written confirmation (Quinine Sulfate WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Quinine Sulfate manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Quinine Sulfate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Quinine Sulfate APIs or Quinine Sulfate finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Quinine Sulfate WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Quinine Sulfate suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Quinine Sulfate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Quinine Sulfate API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Quinine Sulfate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Quinine Sulfate and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Quinine Sulfate NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Quinine Sulfate suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Quinine Sulfate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Quinine Sulfate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Quinine Sulfate GMP manufacturer or Quinine Sulfate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Quinine Sulfate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Quinine Sulfate's compliance with Quinine Sulfate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Quinine Sulfate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Quinine Sulfate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Quinine Sulfate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Quinine Sulfate EP), Quinine Sulfate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Quinine Sulfate USP).
