
Synopsis
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
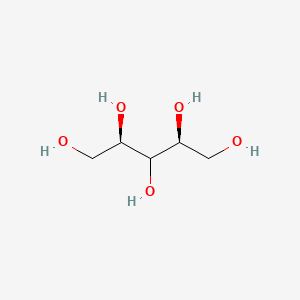

1. Ribitol
2. Adonitol
3. Xylite
4. 488-81-3
5. 87-99-0
6. D-xylitol
7. Adonite
8. Adonit
9. D-ribitol
10. Xyliton
11. Eutrit
12. Klinit
13. Xylite (sugar)
14. Kannit
15. Xylit
16. Newtol
17. 1,2,3,4,5-pentanepentol
18. Pentitol
19. Fluorette
20. Xylisorb
21. Kylit
22. Meso-ribitol
23. Xylo-pentitol
24. L-ribitol
25. (2r,3r,4s)-pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaol
26. (2r,3s,4s)-pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
27. Xylitab 300
28. Meso-xylitol
29. L-xylitol
30. D-adonitol
31. (2s,4r)-pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
32. Nsc 25283
33. Xylitol, D-
34. Xylitol Cm 90
35. Brn 1720523
36. 16277-71-7
37. Chebi:15963
38. Chebi:17151
39. Xylo-pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
40. 2,3-dihydro Acrivastine
41. C-xylidex Cr 16055
42. 353zq9tvda
43. Vcq006kq1e
44. Ins No.967
45. (2r,3s,4s)-pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaol
46. Xylooligosaccharide
47. Ins-967
48. Nsc-25283
49. 87849-01-2
50. 1,2,3,4,5-pentahydroxypentane
51. E-967
52. (2r,3r,4s)-pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
53. 4-01-00-02832 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
54. Mfcd00064291
55. Einecs 201-788-0
56. Unii-353zq9tvda
57. Unii-vcq006kq1e
58. Adonito
59. Xylitol [inn:ban:jan:nf]
60. Nsc-16868
61. Dl-arabinit
62. Xylitol C
63. Hsdb 7967
64. Xylitab Dc
65. Wood Sugar Alcohol
66. Rb0
67. Xylitol,(s)
68. Einecs 207-685-7
69. Ribitol (adonitol)
70. Adonitol (7ci)
71. Xylisorb 300
72. Xylisorb 700
73. Mfcd00064292
74. Nsc 16868
75. Xylitab 100
76. Ribo-pentitol
77. Brn 1720524
78. D-ribitol (incorrect)
79. L-ribitol (incorrect)
80. Adonitol, >=99%
81. Xylitol [vandf]
82. Xylitol [inci]
83. Xylitol, >=99%
84. Adonitol [mi]
85. Xylitol [fcc]
86. Xylitol [jan]
87. Xylitol [ii]
88. Xylitol [mi]
89. Xylitol [mart.]
90. Xylitol [usp-rs]
91. Xylitol [who-dd]
92. Bmse000062
93. Bmse000129
94. Bmse000886
95. Epitope Id:114702
96. Epitope Id:114703
97. Ec 201-788-0
98. Schembl4250
99. Xylitol, Analytical Standard
100. Dsstox_cid_22514
101. Dsstox_rid_80046
102. Dsstox_gsid_42514
103. Schembl15318
104. Mls002695898
105. Chembl96783
106. Ribitol (6ci,8ci,9ci)
107. Xylitol [ep Impurity]
108. Xylitol [ep Monograph]
109. Qspl 191
110. Schembl1924966
111. Chembl1865120
112. Chembl3137744
113. Dtxsid601032335
114. Hy-n0538
115. Tox21_201056
116. S2612
117. S4546
118. Zinc18068098
119. Akos015903403
120. Akos015915193
121. Zinc100014205
122. Zinc100018612
123. Ccg-214167
124. Ccg-266218
125. Cs-6043
126. Db01904
127. Db11195
128. Db14704
129. Cas-87-99-0
130. Ncgc00165982-01
131. Ncgc00165982-02
132. Ncgc00258609-01
133. Ncgc00390798-01
134. Adonitol, Bioxtra, >=99.0% (hplc)
135. As-55964
136. Ds-11416
137. E967
138. Smr001562099
139. Hy-100582
140. Xylitol, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, >=99%
141. A0171
142. N1725
143. Sw220290-1
144. X0018
145. Xylite 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile:water
146. A-3000
147. Adonitol, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
148. C00379
149. C00474
150. X-7000
151. Wurcs=2.0/1,1,0/[h212h]/1/
152. Wurcs=2.0/1,1,0/[h222h]/1/
153. A842433
154. Q212093
155. Q416534
156. Xylitol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
157. 5dcf4f57-e023-469a-b4f3-91e8349a6705
158. Xylitol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
159. 6684f574-c267-40cb-8828-12f2550e58d0
160. Xylitol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 152.15 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H12O5 |
| XLogP3 | -2.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 152.06847348 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 152.06847348 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 101 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 76.1 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Sweetening Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Indicated for use as a sugar substitute, and oral hygiene active ingredient.
There has been evidence of xylitol in dental hygiene in reducing dental caries disease and also reversing the process of early caries. Xylitol increases salivary flow and pH, reduces the levels of _Streptococcus mutans_ in plaque and saliva and reduces the adhesion on the microorganism to the teeth surface. _Streptococcus mutans_ is the main target plaque microorganism, but xylitol may potentially have inhibitory actions against several other bacterial species. It prevents a shift of the bacterial community towards a more cariogenic microflora in oral environment. Oral ingestion of xylitol causes a smaller rise in plasma glucose and insulin concentrations than does the ingestion of glucose in healthy men and diabetics.
Sweetening Agents
Substances that sweeten food, beverages, medications, etc., such as sugar, saccharine or other low-calorie synthetic products. (From Random House Unabridged Dictionary, 2d ed) (See all compounds classified as Sweetening Agents.)
Absorption
Xylitol is absorbed in the small intestine via passive diffusion with a slow absorption rate.
Route of Elimination
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Volume of Distribution
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Clearance
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Five healthy human volunteers (two males and three females) received an orange flavored drink containing 30 g xylitol with breakfast. Before dosing, urine was collected for 24 hr and collections were continued 24 hr after the dose of xylitol. During the collection period no foods rich in oxalate were permitted. No significant changes in urinary oxalate excretion could be detected.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 18: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1983). Available from, as of July 11, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Diets containing 20% of xylitol or one of the following carbohydrates: glucose, fructose, sucrose, xylose, sorbitol or mannitol were fed to groups of five Wistar rats for seven days. The rats were fasted for 12 hr and given a 5 uCi dose of U(14)C-oxalic acid mixed with 0.625 g/kg of xylitol or respective carbohydrate. Urine and feces were collected for 72 hr and counted for recovery of activity. Ten rats were gradually adapted to 20% xylitol diets. After a 12-hr fast these rats and 20 controls received 5 uCi of U(14)C-oxalic acid mixed with water only or together with 0.625 g/kg xylitol/body weight. Urine and feces were collected from five rats/group; tail vein blood from the other rats at intervals up to 24 hours. Urinary excretion of the label was virtually identical in all groups. The mean excretion of label in feces of control rats receiving oxalic acid was significantly lower (P <0.001) than in control rats receiving oxalate alone, or xylitol adapted rats receiving oxalate with xylitol (fecal recoveries were 77.8 and 83% respectively). The urinary excretion of label was also significantly higher among control rats receiving oxalate with xylitol when compared to control rats receiving oxalate alone. However, xylitol adapted rats excreted a significantly smaller proportion of oxalate in urine compared to controls receiving oxalate alone. The mean plasma levels of radioactivity in control rats receiving oxalic acid with xylitol were significantly higher (P <0.05) immediately after the start of the study when compared to controls receiving oxalic acid with water only or xylitol adapted rats. When samples of plasma, urine and feces were analyzed by use of thin layer chromatography, the major part of the radioactivity was recovered as oxalic acid.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 18: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1983). Available from, as of July 11, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Male (30) and female (20) CD-1 mice were either gradually adapted to 20% xylitol diets or fed a control diet. After a 12-hour fast the mice received a single oral dose of 2 uCi of U(14)C-oxalic acid in water or in an xylitol solution (a total dose of 0.625 g/kg bw). For five xylitol adapted male mice the oxalic acid dose was given with sorbitol (0.625 g/kg bw) and for another group of five with mannitol (0.625 g/kg bw). Urine and feces were collected at intervals for 72 hours to monitor the excretion of the label. ... Adaptation of male mice to 20% dietary xylitol increased the urinary excretion of the label fourfold (4.5 versus 20%). No major changes were seen in fecal excretion. Both sorbitol and mannitol increased the urinary excretion of the label while only sorbitol also affected fecal excretion of the label. Urinary excretion of oxalic acid was significantly higher in xylitol adapted mice when compared to controls receiving oxalic acid only. Even greater urinary recovery of label was observed in control mice receiving oxalic acid with xylitol. In female mice xylitol appeared to induce an even more pronounced increase in oxalic acid excretion.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 18: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1983). Available from, as of July 11, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Six groups of three Sprague-Dawley male weanling rats received semi-synthetic diets for 28 days; four of the groups were pyridoxine deficient. Diets contained either 50% glucose by weight or 30% glucose and 20% fructose. On day 28 the rats were injected three times at spaced intervals with either 15% glucose; 10% xylitol + 5% glucose; 15% fructose; or 10% xylitol + 5% fructose. Urine was collected on days 28 and 29 and rats were sacrificed and livers collected 30 minutes after a final injection on day 30. The final body weights for the rats show that the group with the best growth received fructose + xylitol injections and was pyridoxine adequate (mean weight 216.6 g) versus the group receiving fructose + fructose injection (15%) and were pyridoxine deficient (119.7 g). The poorest growing groups received glucose diets only and either xylitol or glucose and glucose injections, and were pyridoxine deficient (107.1 g, 103.1 g). The rats on the pyridoxine deficient diets tended to excrete more oxalate and have higher liver oxalate levels. Within the pyridoxine deficient group only, rats injected with xylitol tended to excrete more oxalate and have higher liver oxalate levels, but these differences were not significant. Fructose had no effect on oxalate excretion or liver oxalate levels in the rats injected with xylitol.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 18: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1983). Available from, as of July 11, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Xylitol (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In mammals, xylitol is mainly metabolized in the liver where it is oxidized to D-xylulose by xylitol dehydrogenase and cofactor NAD. D-xyluose is further phosphorylated and metabolized by xylulose kinase to xylulose 5-phosphate (Xu5P), an intermediate of the nonoxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway. Xu5P is reported to activate nuclear transport and the DNA-binding activities of carbohydrate response element binding protein (ChREBP) via activation of activation of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) _in vitro_. Activation of ChREBP thereby upregulates the gene transcription of lipogenic enzymes in vitro, which may stimulate lipogenesis in the liver.
The biochemical pathways for formation of oxalate after intravenous injection of xylitol in humans were studied using enzymes derived from human liver. It was concluded that metabolic pathways based on a combination of the transketolase, fructokinase, and aldolase reactions can account for the production of glucose, lactate, tertronates (D-threonic and D-erythronic acids) and oxalate (precursors) during the metabolism of xylitol administered parenterally.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 18: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1983). Available from, as of July 11, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
After xylitol ingestion increase of serum lactate concentration and lactate-pyruvate ratio was observed, but to a degree less than after glucose. /Investigators/ also found a marked increase of alpha-dihydroxybutyrate. Complete metabolism of xylitol produces 35 equivalents of ATP compared to 32 from glucose.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 12: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1977). Available from, as of July 6, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
/In humans/ exogenous xylitol enters the pathway by conversion to D-xylulose by a nonspecific cytoplasmic polyol dehydrogenase. Phosphorylation then yields D-xylulose phosphate, the link between the glucuronic acid and the pentose phosphate pathways; the latter leads to the formation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate, intermediate metabolites of the Embden-Meyerhof (glycolytic) pathway. Thus xylitol can be metabolized via glucose-6-phosphate to glycogen and pyruvate or lactate via the citric acid cycle to CO2. Xylitol is mainly metabolized in the liver (80% to glucose only 20%) but a small amount also in kidney, myocardium, erythrocytes, adrenal, brain, lungs and adipose tissue. Exogenous xylitol can be metabolized in large quantities, intravenously 0.4 gm/kg/hour or 40 g/day orally raises the plasma level to a maximum of 1.5-16 mg/100 mL. The metabolic rate for xylitol is identical in both healthy and diabetic or uraemic patients and patients who suffered from liver diseases.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 12: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1977). Available from, as of July 6, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
In /human/ studies with (14)C-xylitol 90% of C-atoms taken up could be recovered in products and intermediates of the glycolytic and pentose phosphate pathway.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 12: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1977). Available from, as of July 6, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Xylitol (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
No pharmacokinetic data available.
/In humans/ the initial fast distribution phase /for xylitol/ had a half life of about four minutes, while the apparent half life of elimination was approximately 20 minutes.
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 12: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1977). Available from, as of July 6, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
(14)C-xylitol disappeared extremely rapidly and the calculated half life is 165 seconds. ...
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 12: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1977). Available from, as of July 6, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
The half-life of exhalation of (14)CO2 after feeding with xylitol in unadapted /rats/ is 295 minutes, whereas rats which were adapted for 14 days to xylitol had a half-life of 237 minutes...
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives Series 12: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1977). Available from, as of July 6, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
...Rats were administered (14)C-xylitol (250 mg) by intubation, the half-live of the resorption of xylitol was about 7 to 8 hr. The resorption rate is about 15-20% of that of glucose. After the animals had been fed xylitol for 14 days the half-life fell to 4.5 hr. ...
WHO/FAO: Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary of Toxicological Data of Certain Food Additives: Xylitol (87-99-0) (1977). Available from, as of July 6, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Xylitol is initially taken up by the microorganism and accumulates intracellularly. Accumulated xylitol is transported into an energy-consuming cycle, or the inducible fructose transport system. It is converted to non-metabolizable, toxic xylitol-5-phosphate via phosphoenolpyruvate: a constitutive fructose phosphotransferase system by _S. mutans_. This metabolic process of xylitol, without the gain of any energy molecules, results in the development of intracellular vacuoles and cell membrane degradation. _S. mutans_ dephosphorylates xylitol-5-phosphate and expels it from the cell, in which requires energy consumption. This ultimately leading to starving of microorganism and growth inhibition. Long-term exposure to xylitol can cause microorganisms to develop resistance to xylitol. This clinically beneficial selection process creates xylitol-resistant mutans strains that are less virulent and less cariogenic than their parent strains. Xylitol also increases the concentrations of ammonia and amino acids in plaque, thereby neutralizing plaque acids. A study suggests that xylitol may also promote remineralization of deeper layers of demineralized enamel by facilitating Ca2+ and phosphate movement and accessibility.
 Rochem, your partner in developing, sourcing, and supplying pharmaceutical & animal health ingredients of Chinese origin.
Rochem, your partner in developing, sourcing, and supplying pharmaceutical & animal health ingredients of Chinese origin.

Certificate Number : CEP 2024-101 - Rev 00
Issue Date : 2025-02-07
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 1381
Status : Valid
USDMF, CEP/COS, JDMF, EU-WC, NDC, KDMF, VMF, Others
USDMF, CEP/COS, JDMF, EU-WC, NDC, KDMF, VMF, Others
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 2711
Submission : 1976-07-09
Status : Inactive
Type : IV

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
USDMF, CEP/COS, JDMF, EU-WC, NDC, KDMF, VMF, Others
USDMF, CEP/COS, JDMF, EU-WC, NDC, KDMF, VMF, Others
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 8316
Submission : 1989-12-07
Status : Inactive
Type : II

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF

Registration Number : 217MF10326
Registrant's Address : 1-1-3 Yurakucho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo
Initial Date of Registration : 2005-07-14
Latest Date of Registration :


Registration Number : 218MF10313
Registrant's Address : 24-12 Kitahamacho, Chita City, Aichi Prefecture
Initial Date of Registration : 2006-02-28
Latest Date of Registration :



NDC Package Code : 51552-0754
Start Marketing Date : 2004-09-01
End Marketing Date : 2026-03-21
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1g/g)
Marketing Category : BULK INGREDIENT FOR HUMAN PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
88
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ribitol API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ribitol manufacturer or Ribitol supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ribitol manufacturer or Ribitol supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ribitol API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ribitol API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ribitol Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ribitol Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Ribitol manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Ribitol, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Ribitol manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Ribitol API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Ribitol manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Ribitol supplier is an individual or a company that provides Ribitol active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Ribitol finished formulations upon request. The Ribitol suppliers may include Ribitol API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Ribitol suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Ribitol DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Ribitol active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Ribitol DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Ribitol USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Ribitol DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Ribitol USDMF includes data on Ribitol's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Ribitol USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Ribitol suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Ribitol Drug Master File in Japan (Ribitol JDMF) empowers Ribitol API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Ribitol JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Ribitol JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Ribitol suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Ribitol CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Ribitol Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Ribitol CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Ribitol EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Ribitol to their clients by showing that a Ribitol CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Ribitol CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Ribitol CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Ribitol CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Ribitol DMF.
A Ribitol CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Ribitol CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Ribitol suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Ribitol as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Ribitol API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Ribitol as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Ribitol and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Ribitol NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Ribitol suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Ribitol Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ribitol GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ribitol GMP manufacturer or Ribitol GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Ribitol CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Ribitol's compliance with Ribitol specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Ribitol CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Ribitol CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Ribitol may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Ribitol EP), Ribitol JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Ribitol USP).
