
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book
0
Canada
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Biaxsig
2. Claramid
3. Infectoroxit
4. Macrosil
5. Mtw-roxithromycin
6. Rotesan
7. Rotramin
8. Roxi 1a Pharma
9. Roxi Basics
10. Roxi Tad
11. Roxi Von Ct
12. Roxi-paed 1a Pharma
13. Roxi-puren
14. Roxi-q
15. Roxi-saar
16. Roxi-wolff
17. Roxibeta
18. Roxidura
19. Roxigamma
20. Roxigrn
21. Roxihexal
22. Roxithro-lich
23. Roxithromycin
24. Ru 28965
25. Ru 965
26. Ru-28965
27. Ru-965
28. Ru28965
29. Ru965
30. Rulid
1. Roxithromycin
2. 80214-83-1
3. Roxithromycine
4. Roxithromycinum
5. Roxitromicina
6. Ru 965
7. Ru 28965
8. Ru-965
9. Rulid
10. Chebi:48935
11. Nsc-758443
12. Erythromycin 9-(o-((2-methoxyethoxy)methyl)oxime)
13. 21kof230fa
14. Ru-28965
15. 9-(o-((2-methoxyethoxy)methyl)oxime)erythromycin
16. (9e)-erythromycin 9-(o-((2-methoxyethoxy)methyl)oxime)
17. (e)-roxithromycin
18. Roxithromycine [french]
19. Roxithromycinum [latin]
20. Roxitromicina [spanish]
21. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,11s,12r,13s,14r,e)-6-(((2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-(((2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-10-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)imino)-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2-one
22. Rulide (tn)
23. 9-[o-[(2-methoxyethoxy)methyl]oxime]erythromycin
24. Sr-05000001850
25. Chebi:48844
26. Unii-21kof230fa
27. Erythromycin, 9-(o-((2-methoxyethoxy)methyl)oxime), (9e)-
28. Ccris 3461
29. Roxithromycin,(s)
30. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,10e,11s,12r,13s,14r)-6-[(2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-[(2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy-10
31. Roxithromycin [usan:inn:ban:jan]
32. Rc2952
33. Brn 4286925
34. Spectrum5_001058
35. Roxithromycin [mi]
36. Roxithromycin [inn]
37. Roxithromycin [jan]
38. Roxithromycin [usan]
39. Schembl65985
40. Bspbio_002717
41. Roxithromycin [mart.]
42. Spectrum1503276
43. 9-[o-(2-methoxyethoxymethyl)-oxime] Of Erythromycin
44. Erythromycin, 9-(o-((2-methoxyethoxy)methyl)oxime)
45. Roxithromycin [who-dd]
46. Chembl1214185
47. Hms501d04
48. Hms1922o19
49. Hms2093c11
50. Hms3714l09
51. Pharmakon1600-01503276
52. Roxithromycin (jp17/usan/inn)
53. Roxithromycin [ep Impurity]
54. Hy-b0435
55. Roxithromycin [ep Monograph]
56. Bdbm50248154
57. Ccg-39329
58. Mfcd00214389
59. Nsc758443
60. Zinc96061888
61. Akos015969730
62. Db00778
63. Nsc 758443
64. Idi1_000382
65. Ncgc00178510-01
66. Roxithromycin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
67. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,10e,11s,12r,13s,14r)-6-[(2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-[(2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy-10-(2-methoxyethoxymethoxyimino)-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-oxacyclotetradecan-2-one
68. Roxithromycin 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
69. Sbi-0051809.p002
70. Roxithromycin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
71. D01710
72. Ab00052342_02
73. Sr-05000001850-1
74. Sr-05000001850-2
75. Brd-k38684403-001-03-9
76. Brd-k38684403-001-05-4
77. Q27895851
78. 9-[o-[(2-methoxyethoxy)methyl]oxime]erythromycin, (9e)-
79. (e)-erythromycin-9-(o-((2-methoxyethoxy)methyl)oxime)
80. Erythromycin 9-(e)-(o-((2-methoxyethoxy)methyl)oxime)
81. Erythromycin A, 9-(o-(2-methoxyethoxymethyl)-oxime)
82. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,10e,11s,12r,13s,14r)-4-(2,6-dideoxy-3-c-methyl-3-o-methyl-alpha-l-ribo-hexopyranosyloxy)-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-10-{[(2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy]imino}-6-[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-beta-d-xylo-hexopyranosyloxy]-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2-one
83. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,10e,11s,12r,13s,14r)-6-[(2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxy-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-[(2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyl-tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxy-10-(2-methoxyethoxymethoxyimino)-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-oxacyclotetradecan-2-one
84. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,10e,11s,12r,13s,14r)-6-{[(2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-10-{[(2-methoxyethoxy)m
85. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,10e,11s,12r,13s,14r)-6-{[(2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-10-{[(2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy]imino}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2-one
86. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,10e,11s,12r,13s,14r)-6-{[(2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione 10-{o-[(2-methoxyethoxy)methyl]oxime} (non-preferred Name)
87. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,11s,12r,13s,14r)-4-((2,6dideoxy-3-c-methyl-3-o-methyl-.alpha.-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-10-((e)((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)imino)-3,5,7,9,11,13hexamethyl-6-((3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-.beta.-d-xylohexopyranosyl)oxy)oxacyclotetradecan-2-one
88. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,11s,12r,13s,14r)-4-(2,6-dideoxy-3-c-methyl-3-o-methyl-alpha-l-ribo-hexopyranosyloxy)-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-10-{[(2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy]imino}-6-[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-beta-d-xylo-hexopyranosyloxy]-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2-one
89. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,11s,12r,13s,14r)-6-{[(2s,3r,4s,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-10-(2,4,7-trioxa-1-azaoctan-1-ylidene)-1-oxacyclotetradecan-2-one
90. (3r,4s,5s,6r,7r,9r,11s,12r,13s,14r,e)-6-(((2s,3r,6r)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-(((2r,4r,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-10-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)imino)-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2-one
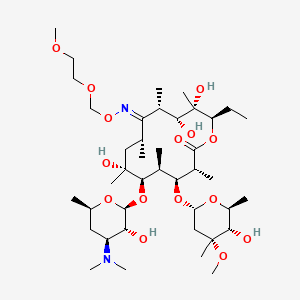
| Molecular Weight | 837.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C41H76N2O15 |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 17 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Exact Mass | 836.52456972 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 836.52456972 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 217 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 58 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1310 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 18 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used to treat respiratory tract, urinary and soft tissue infections.
Roxithromycin has the following antibacterial spectrum in vitro: Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (Pneumococcus), Neisseria meningitides (Meningococcus), Listeria monocytogenes, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Legionella pneumophila, Helicobacter (Campylobacter), Gardnerella vaginalis, Bordetella pertussis, Moraxella catarrhalis (Branhamella Catarrhalis), and Haemophilus ducreyi. Roxithromycin is highly concentrated in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages, achieving intracellular concentrations greater than those outside the cell. Roxithromycin enhances the adhesive and chemotactic functions of these cells which in the presence of infection produce phagocytosis and bacterial lysis. Roxithromycin also possesses intracellular bactericidal activity.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01F - Macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins
J01FA - Macrolides
J01FA06 - Roxithromycin
Absorption
Very rapidly absorbed and diffused into most tissues and phagocytes.
Hepatic. Roxithromycin is only partially metabolised, more than half the parent compound being excreted unchanged. Three metabolites have been identified in urine and faeces: the major metabolite is descladinose roxithromycin, with N-mono and N-di-demethyl roxithromycin as minor metabolites. The respective percentage of roxithromycin and these three metabolites is similar in urine and faeces.
12 hours
Roxithromycin prevents bacterial growth by interfering with their protein synthesis. It binds to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes and inhibits the translocation of peptides.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
16
PharmaCompass offers a list of Roxithromycin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Roxithromycin manufacturer or Roxithromycin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Roxithromycin manufacturer or Roxithromycin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Roxithromycin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Roxithromycin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Roxithromycin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Roxithromycin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Roxithromycin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Roxithromycin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Roxithromycin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Roxithromycin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Roxithromycin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Roxithromycin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Roxithromycin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Roxithromycin finished formulations upon request. The Roxithromycin suppliers may include Roxithromycin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Roxithromycin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Roxithromycin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Roxithromycin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Roxithromycin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Roxithromycin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Roxithromycin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Roxithromycin USDMF includes data on Roxithromycin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Roxithromycin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Roxithromycin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Roxithromycin Drug Master File in Japan (Roxithromycin JDMF) empowers Roxithromycin API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Roxithromycin JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Roxithromycin JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Roxithromycin suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Roxithromycin Drug Master File in Korea (Roxithromycin KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Roxithromycin. The MFDS reviews the Roxithromycin KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Roxithromycin KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Roxithromycin KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Roxithromycin API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Roxithromycin suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Roxithromycin CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Roxithromycin Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Roxithromycin CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Roxithromycin EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Roxithromycin to their clients by showing that a Roxithromycin CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Roxithromycin CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Roxithromycin CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Roxithromycin CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Roxithromycin DMF.
A Roxithromycin CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Roxithromycin CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Roxithromycin suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Roxithromycin written confirmation (Roxithromycin WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Roxithromycin manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Roxithromycin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Roxithromycin APIs or Roxithromycin finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Roxithromycin WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Roxithromycin suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
Roxithromycin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Roxithromycin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Roxithromycin GMP manufacturer or Roxithromycin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Roxithromycin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Roxithromycin's compliance with Roxithromycin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Roxithromycin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Roxithromycin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Roxithromycin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Roxithromycin EP), Roxithromycin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Roxithromycin USP).

