
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Canada

0
Australia

0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
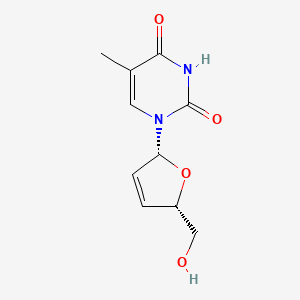

1. 2',3' Didehydro 3' Deoxythymidine
2. 2',3'-didehydro-2',3'-dideoxythmidine
3. 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxythymidine
4. Bmy 27857
5. Bmy-27857
6. Bmy27857
7. D4t
8. Stavudine, Monosodium Salt
9. Zerit
1. 3056-17-5
2. Sanilvudine
3. Zerit
4. 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxythymidine
5. Stavudinum
6. Zerit Xr
7. D4t
8. Bmy-27857
9. Estavudina
10. Stavudinum [inn-latin]
11. Estavudina [inn-spanish]
12. Thymidine, 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxy-
13. 3'-deoxy-2'-thymidinene
14. Ddethd
15. 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxythimidine
16. 3'-deoxy-2',3'-didehydrothymidine
17. Bmy 27857
18. 1-((2r,5s)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4(1h,3h)-dione
19. Dideoxydidehydrothymidine
20. 1-(2,3-dideoxy-beta-d-glycero-pent-2-enofuranosyl)thymine
21. Nsc 163661
22. Sanilvudine (jan)
23. Bo9le4qfzf
24. Stavudine (d4t)
25. 1-[(2r,5s)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4(1h,3h)-dione
26. Stv
27. Chembl991
28. Nsc-759897
29. Zerut Xr
30. Mls000028546
31. D-4t
32. Chebi:63581
33. 1-[(2r,5s)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dione
34. Nsc-163661
35. Ncgc00023212-07
36. Smr000058350
37. D 4t (nucleoside)
38. Sanilvudine [jan]
39. Dsstox_cid_3819
40. Dsstox_rid_77198
41. Dsstox_gsid_23819
42. 1-[(2r,5s)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]-5-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-2,4-dione
43. Stavudine [usan:ban:inn]
44. 1-(2,3-dideoxy-.beta.-d-glycero-pent-2-enofuranosyl)thymine
45. D 4t
46. Ddetyd
47. 1-(cis-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl)-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4(1h,3h)-dione
48. 1-[(2r,5s)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]-5-methyl-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
49. 220020-60-0
50. Cas-3056-17-5
51. Zerit(tm)
52. Zerit (tn)
53. Hsdb 7338
54. Sr-01000075802
55. Unii-bo9le4qfzf
56. Stavudine (usan/inn)
57. Brn 0618327
58. D4t & Gm-csf
59. 2'-thymidinene, 3'-deoxy-
60. Nsc163661
61. Stavudine [usan:usp:inn:ban]
62. Stavudine (dt4)
63. Stavudine- Bio-x
64. D4tmby-27857-3
65. Stavudine [inn]
66. Stavudine [mi]
67. Stavudine [hsdb]
68. Stavudine [usan]
69. Opera_id_1281
70. 3'-deoxythymidin-2'-ene
71. Stavudine [mart.]
72. D 1413
73. Cid_5155
74. Stavudine [usp-rs]
75. Stavudine [who-dd]
76. Stavudine [who-ip]
77. 1-((2r,5s)-5-hydroxymethyl-2,5-dihydro-furan-2-yl)-5-methyl-1h-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
78. 3''-deoxy-2''-thymidine
79. Lopac0_000336
80. Schembl38661
81. Stavudine [ema Epar]
82. Cid_18283
83. Mls000759504
84. Mls001055348
85. Mls001077292
86. Mls001424091
87. Mls006011922
88. Bidd:gt0082
89. 2',3'-anhydrothymidine; D4t
90. Stavudine [ep Impurity]
91. Stavudine [orange Book]
92. Dtxsid1023819
93. Stavudine [ep Monograph]
94. 1-(2,3-dideoxy-beta-d-glycero-2-pentenofuranosyl)thymine
95. Stavudine [usp Monograph]
96. Stavudinum [who-ip Latin]
97. Hms2051o20
98. Hms2234c10
99. Hms3039o05
100. Hms3259l21
101. Hms3261c13
102. Hms3428c07
103. Hms3714n22
104. Pharmakon1600-01502339
105. Stavudine (d4t) [vandf]
106. Stavudine (dt4) [vandf]
107. Zinc137884
108. Bcp02952
109. Hy-b0116
110. Tox21_110886
111. Tox21_201393
112. Tox21_300583
113. Tox21_500336
114. Bbl033763
115. Bdbm50013111
116. Nsc759897
117. Stk801888
118. Akos005622554
119. Tox21_110886_1
120. Ac-5263
121. Ccg-100902
122. Cs-1872
123. Db00649
124. Ks-1115
125. Lp00336
126. Nc00152
127. Nc00684
128. Sdccgsbi-0050324.p002
129. Zidovudine Impurity A [who-ip]
130. 2'',3''-didehydro-3''-deoxythymidine
131. 3''-deoxy-2'',3''-didehydrothymidine
132. Ncgc00023212-03
133. Ncgc00023212-04
134. Ncgc00023212-05
135. Ncgc00023212-08
136. Ncgc00023212-09
137. Ncgc00023212-10
138. Ncgc00023212-11
139. Ncgc00023212-12
140. Ncgc00023212-13
141. Ncgc00023212-14
142. Ncgc00023212-25
143. Ncgc00023212-30
144. Ncgc00254372-01
145. Ncgc00258944-01
146. Ncgc00261021-01
147. Stavudine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
148. 1-[5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydro-2-furanyl]-5-methyl-2,4(1h,3h)-pyrimidinedione & Colony-stimulating Factor 2
149. Bd164571
150. Smr000673569
151. Thymidine, 2',3'-didehydro-, 3'-deoxy-
152. Zidovudine Impurity A [ep Impurity]
153. D3580
154. Eu-0100336
155. 2'',3''-dideoxy-2'',3''-didehydrothymidine
156. C07312
157. D00445
158. Ab00383018_18
159. 056s175
160. Q423984
161. J-700246
162. Q-201742
163. Sr-01000075802-1
164. Sr-01000075802-4
165. 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxythymidine, >=98% (tlc)
166. Z1695906749
167. Stavudine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
168. Stavudine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
169. Thymine, 1-(2,3-dideoxy-beta-d-glycero-pent-2-enofuranosyl)-
170. 1-(5-hydroxymethyl-2,5-dihydro-furan-2-yl)-5-methyl-1h-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
171. 1-(5-hydroxymethyl-2,5-dihydro-furan-2-yl)-5-methyl-1h-pyrimidine-2,4-dione (ddethd)
172. 1-[(2r,5s)-2,5-dihydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furanyl]-5-methyl-2,4(1h,3h)-pyrimidinedione
173. 3'- Azido-3'-deoxythymidine & Granulocyte-macrophage Colony-stimulating Factor
174. Stavudine For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 224.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | -0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 224.07970687 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 224.07970687 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 78.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 388 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Stavudine |
| PubMed Health | Stavudine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | Stavudine (d4T), a synthetic thymidine nucleoside analogue, active against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Stavudine Capsules are supplied for oral administration in strengths of 15, 20, 30, and 40 mg of stavudine. Each capsule also contains... |
| Active Ingredient | Stavudine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; For solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml; 30mg; 15mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Hetero Labs Ltd Iii; Aurobindo Pharma; Cipla; Matrix Labs; Emcure Pharma; Strides Acrolab; Mylan |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zerit |
| PubMed Health | Stavudine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | ZERIT is the brand name for stavudine (d4T), a synthetic thymidine nucleoside analogue, active against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).ZERIT (stavudine) Capsules are supplied for oral administration in strengths of 15, 20, 30, and 40 mg of s... |
| Active Ingredient | Stavudine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; For solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml; 30mg; 15mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bristol Myers Squibb |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Stavudine |
| PubMed Health | Stavudine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | Stavudine (d4T), a synthetic thymidine nucleoside analogue, active against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Stavudine Capsules are supplied for oral administration in strengths of 15, 20, 30, and 40 mg of stavudine. Each capsule also contains... |
| Active Ingredient | Stavudine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; For solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml; 30mg; 15mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Hetero Labs Ltd Iii; Aurobindo Pharma; Cipla; Matrix Labs; Emcure Pharma; Strides Acrolab; Mylan |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zerit |
| PubMed Health | Stavudine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | ZERIT is the brand name for stavudine (d4T), a synthetic thymidine nucleoside analogue, active against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).ZERIT (stavudine) Capsules are supplied for oral administration in strengths of 15, 20, 30, and 40 mg of s... |
| Active Ingredient | Stavudine |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; For solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml; 30mg; 15mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bristol Myers Squibb |
Stavudine in combination with other antiretroviral agents is indicated for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Additionally, stavudine is indicated for the treatment of patients with HIV infection who have received prolonged previous treatment with zidovudine. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 2676
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including some fatalities, have been reported rarely in patients receiving stavudine and also have been reported in patients receiving other NRTIs. Female gender, obesity, and long-term therapy with NRTIs may be risk factors. Fatal lactic acidosis has been reported in pregnant women who received antiretroviral regimens that included both didanosine and stavudine. Stavudine should be used with caution in patients with known risk factors for liver disease; however, lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis have been reported in patients with no known risk factors. Generalized fatigue, digestive symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, sudden unexplained weight loss), respiratory symptoms (tachypnea, dyspnea), or neurologic symptoms (including motor weakness) might be indicative of lactic acidosis development, and patients should be advised to contact their clinician immediately if these symptoms occur. Stavudine therapy should be discontinued in any patient with clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked increases in serum aminotransferase concentrations). Permanent discontinuance of stavudine therapy should be considered in patients with confirmed lactic acidosis. Because an increased risk of potentially fatal hepatotoxicity may occur in patients receiving stavudine in conjunction with didanosine and hydroxyurea, patients receiving such regimens should be closely monitored for signs of hepatotoxicity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 721
Lactic acidosis is a serious complication of antiretroviral therapy. Symptomatic hyperlactatemia is a milder form of this syndrome, but its incidence is unclear. In this prospective ongoing observational study of a large cohort of HIV-infected adults, hyperlactataemia was diagnosed in 64 patients. Incidences were 18.3/1000 person-years with antiretroviral therapy, and 35.8/1000 person-years for stavudine (d4T) regimens. Ten of the 64 patients developed lactic acidosis during the first 13 months of treatment (incidence 2.9/1000 treated person-years). In four of ten patients, symptoms were absent or mild. More patients on d4T first-line therapy developed lactic acidosis than patients previously treated with other drugs (p = 0.008). Despite the occurrence of one death, the subsequent outcome for the remaining patients was favourable after antiretroviral therapy was stopped and supportive treatment with vitamins and antioxidants initiated. The early diagnosis of cases was the result of great vigilance and, combined with routine measurements of the anion gap, might be the most crucial factor explaining the low mortality rate observed here.
PMID:12942856 Gerard Y et al; Therapie 58 (2): 153-8 (2003)
Potentially severe peripheral neuropathy, manifested by numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands or feet, has been reported in about 52% of patients receiving stavudine alone and in 8-21% of patients receiving stavudine in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents (indinavir and either lamivudine or didanosine). Stavudine-associated peripheral neuropathy appears to be dose-related, and has been reported most frequently in patients with advanced HIV, patients with a history of peripheral neuropathy, or patients receiving other neurotoxic drugs, including didanosine. Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy generally resolve if stavudine therapy is promptly discontinued; however, symptoms may worsen temporarily in some patients following discontinuance of the drug. If such symptoms resolve completely, patients may tolerate resumption of stavudine therapy using a reduced dosage. If neuropathy recurs after stavudine therapy is reinitiated, consideration should be given to permanently discontinuing the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 720
Pancreatitis, which has been fatal in some cases, has occurred in patients receiving stavudine in conjunction with didanosine (with or without hydroxyurea) and has been reported in both treatment-naive and previously treated patients, regardless of degree of immunosuppression. In an early clinical study evaluating stavudine, pancreatitis was observed in less than 1% of adult patients receiving stavudine monotherapy. Patients receiving didanosine in conjunction with stavudine (with or without hydroxyurea) may be at increased risk of pancreatitis; there have been at least 2 fatalities related to pancreatitis in patients receiving didanosine concomitantly with stavudine, indinavir, and hydroxyurea. There also has been at least one death related to pancreatitis in a patient receiving didanosine in conjunction with stavudine and nelfinavir. Stavudine, didanosine, hydroxyurea, and any other agent toxic to the pancreas should be discontinued in any patient who develops suspected pancreatitis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 720
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for STAVUDINE (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of human immunovirus (HIV) infections.
FDA Label
* Hard capsules:
Zerit is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV-infected adult patients and paediatric patients (over the age of three months) only when other antiretrovirals can not be used. The duration of therapy with Zerit should be limited to the shortest time possible.
* Powder for oral solution:
Zerit is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of HIV-infected adult patients and paediatric patients (from birth) only when other antiretrovirals can not be used. The duration of therapy with Zerit should be limited to the shortest time possible.
Stavudine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) with activity against Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1). Stavudine is phosphorylated to active metabolites that compete for incorporation into viral DNA. They inhibit the HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme competitively and act as a chain terminator of DNA synthesis. The lack of a 3'-OH group in the incorporated nucleoside analogue prevents the formation of the 5' to 3' phosphodiester linkage essential for DNA chain elongation, and therefore, the viral DNA growth is terminated.
Anti-HIV Agents
Agents used to treat AIDS and/or stop the spread of the HIV infection. These do not include drugs used to treat symptoms or opportunistic infections associated with AIDS. (See all compounds classified as Anti-HIV Agents.)
Antimetabolites
Drugs that are chemically similar to naturally occurring metabolites, but differ enough to interfere with normal metabolic pathways. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2033) (See all compounds classified as Antimetabolites.)
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Inhibitors of reverse transcriptase (RNA-DIRECTED DNA POLYMERASE), an enzyme that synthesizes DNA on an RNA template. (See all compounds classified as Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors.)
J05AF04
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AF - Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
J05AF04 - Stavudine
Absorption
Following oral administration, stavudine is rapidly absorbed (bioavailability is 68-104%).
Volume of Distribution
46 21 L
Clearance
Renal cl=272 mL/min [Healthy subjects receiving 80 mg PO]
594 +/- 164 mL/min [HIV-infected adult and pediatric patients following 1-hour IV infusion]
9.75 +/- 3.76 mL/min/kg [HIV- Exposed or -Infected Pediatric Patients(Age 5 weeks 15 years) following 1-hour IV infusion]
Stavudine is rapidly absorbed following oral administration, and peak plasma concentrations of the drug are attained within 1 hour after the dose. Oral bioavailability of stavudine is reported to be about 86% in adults and 77% in pediatric patients 5 weeks to 15 years of age.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 723
Data from single- and multiple-dose studies indicate that peak plasma concentrations and AUC of stavudine increase in proportion to dose over the dosage range 0.03 -4 mg/kg; there is no evidence that accumulation occurs following multiple doses.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 723
Binding of stavudine to serum proteins is negligible over the concentration range of 0.01-11.4 ug/mL.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 723
Distribution of stavudine into body tissues and fluids has not been fully characterized. The apparent volume of distribution of stavudine following a single oral dose averages 66 L in HIV-infected adults. Following a single IV dose in HIV-infected individuals, the volume of distribution is 58 L in adults and 0.73 L/kg in pediatric patients 5 weeks to 15 years of age.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 723
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for STAVUDINE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Phosphorylated intracellularly to stavudine triphosphate, the active substrate for HIV-reverse transcriptase.
The metabolic fate of stavudine has not been elucidated in humans. Intracellularly, in both virus-infected and uninfected cells, stavudine is converted to stavudine monophosphate by cellular thymidine kinase. The monophosphate is subsequently converted to stavudine diphosphate and then to stavudine triphosphate, presumably by the same cellular kinases involved in the metabolism of zidovudine. Intracellular (host cell) conversion of stavudine to the triphosphate derivative is necessary for the antiviral activity of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 723
0.8-1.5 hours (in adults)
Intracellular half life of stavudine triphosphate: Approximately 3.5 hours. /Stavudine triphosphate/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 2676
Normal renal function: Adults: 0.8 to 1.5 hours (intravenous); 1.14 to 1.74 hours (oral). Children (5 weeks to 15 years): 0.83 to 1/39 hours (intravenous); 0.7 to 1.22 hours (oral). Neonates (14 to 28 days) 1.3 to 1.88 (oral). Neonates (day of birth): 3.26 to 7.28 (oral). Renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 26 to 50 mL/min): Approximately 1 to 6 hours. Renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 9 to 25 mL/min): Approximately 3.7 to 5.5 hours. Renal function impairment (creatinine clearance > 50 mL/min): Approximately 1.3 to 2.1 hours. Renal function impairment (hemodialysis patients): Approximately 4.0 to 6.8 hours.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 2676
Twenty-two patients were studied after the first oral dose of 0.67, 1.33, 2.67, or 4 mg/kg of body weight; 17 of them underwent an additional steady-state pharmacokinetic evaluation after thrice-daily dosing of the above doses. ... The mean values for plasma elimination half-life ranged from 1 to 1.6 hr.
PMID:1323615 Dudley MN et al; J Infect Dis 166 (3):480-5 (1992)
Stavudine inhibits the activity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) both by competing with the natural substrate dGTP and by its incorporation into viral DNA.
Enzymatic conversion of stavudine to d4T-triphosphate appears to be complex, involving several steps and enzymes. Stavudine is first converted to dideoxydidehydrothymidine-5'-monophosphate (d4T-monophosphate) by thymidine kinase. Subsequently, d4T-monophosphate is converted to dideoxydidehydrothymidine-5'-diphosphate (d4T-diphosphate), and then to d4T-triphosphate, presumably by the same cellular kinases involved in the metabolism of zidovudine. ... d4T-Triphosphate is a structural analog of thymidine triphosphate, the natural substrate for viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase. ... d4T-triphosphate appears to compete with thymidine triphosphate for viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase and incorporation into viral DNA. Following incorporation of d4T-triphosphate into the viral DNA chain instead of thymidine triphosphate, synthesis is terminated prematurely because the absence of the 3'-hydroxy group on the drug prevents further 5' to 3' phosphodiester linkages.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 723
Stavudine is phosphorylated by cellular kinases to the active metabolite stavudine triphosphate. Stavudine triphosphate inhibits the activity of HIV reverse transcriptase both by competing with the natural substrate deoxythymidine triphosphate (Ki =0.0083 to 0.032 uM), and by its incorporation into viral DNA causing a termination of DNA chain elongation because stavudine lacks the essential 3'-OH group. Stavudine triphosphate inhibits cellular DNA polymerase beta and gamma, and markedly reduces the synthesis of mitochondrial DNA.
Physicians Desk Reference. 59th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2005., p. 1087
d4T-Triphosphate can bind to and inhibit some mammalian cellular DNA polymerases, particularly beta- and gamma-polymerases, in vitro, and markedly reduce the synthesis of mitochondrial DNA. ...gamma-polymerase, an enzyme involved in mitochondrial DNA synthesis, is the polymerase most susceptible to inhibition. However, d4T-triphosphate and other dideoxynucleoside triphosphates appear to have much greater affinity for viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase than for mammalian DNA polymerases. ... Inhibition of beta- and gamma-polymerases by these drugs may account, to some extent, for the toxic effects associated with stavudine and other nucleosides in humans.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 723
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
67
PharmaCompass offers a list of Stavudine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Stavudine manufacturer or Stavudine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Stavudine manufacturer or Stavudine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Stavudine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Stavudine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Stavudine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Stavudine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Stavudine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Stavudine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Stavudine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Stavudine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Stavudine manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Stavudine supplier is an individual or a company that provides Stavudine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Stavudine finished formulations upon request. The Stavudine suppliers may include Stavudine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Stavudine suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Stavudine DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Stavudine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Stavudine DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Stavudine USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Stavudine DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Stavudine USDMF includes data on Stavudine's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Stavudine USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Stavudine suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Stavudine CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Stavudine Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Stavudine CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Stavudine EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Stavudine to their clients by showing that a Stavudine CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Stavudine CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Stavudine CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Stavudine CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Stavudine DMF.
A Stavudine CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Stavudine CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Stavudine suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Stavudine written confirmation (Stavudine WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Stavudine manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Stavudine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Stavudine APIs or Stavudine finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Stavudine WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Stavudine suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Stavudine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Stavudine API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Stavudine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Stavudine and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Stavudine NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Stavudine suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Stavudine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Stavudine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Stavudine GMP manufacturer or Stavudine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Stavudine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Stavudine's compliance with Stavudine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Stavudine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Stavudine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Stavudine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Stavudine EP), Stavudine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Stavudine USP).
