
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
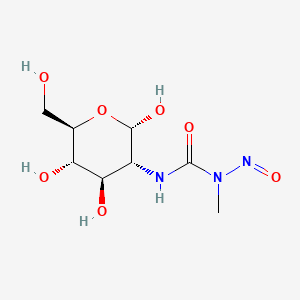

1. 2-deoxy-2-((methylnitrosoamino)carbonyl)amino-d-glucose
2. Streptozotocin
3. Streptozotocine
4. Zanosar
1. Streptozotocin
2. 18883-66-4
3. Streptozosin
4. Estreptozocina
5. Streptozocine
6. Streptozocinium
7. Streptozocinum
8. 66395-18-4
9. 2-desoxy-2-(3-methyl-3-nitrosoureido)-d-glucopyranose
10. N-d-glucosyl-(2)-n'-nitrosomethylurea
11. Alpha-streptozocin
12. Streptozotocin (stz)
13. N-d-glucosyl-(2)-n'-nitrosomethylharnstoff
14. 2-deoxy-2-(((methylnitrosoamino)carbonyl)amino)-d-glucopyranose
15. Chebi:9288
16. Stz
17. 8h27gur065
18. Alkylating Agent
19. Dsstox_cid_1282
20. Dsstox_rid_76055
21. Dsstox_gsid_21282
22. C8h15n3o7
23. Mfcd00006607
24. Binds To Dna
25. 3-methyl-3-nitroso-1-[(2s,3r,4r,5s,6r)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]urea
26. Zanosar (tn)
27. Sr-05000001720
28. 2-deoxy-2-[[(methylnitrosoamino)carbonyl]amino]-d-glucose
29. 2-deoxy-2-({[methyl(nitroso)amino]carbonyl}amino)-alpha-d-glucopyranose
30. Ncgc00016738-01
31. Cas-18883-66-4
32. Spectrum_000960
33. Streptozotocin - Zanosar
34. 2-deoxy-2-{[methyl(nitroso)carbamoyl]amino}-alpha-d-glucopyranose
35. Prestwick3_000732
36. Spectrum2_000062
37. Spectrum3_001087
38. Spectrum4_001244
39. Spectrum5_001047
40. Epitope Id:134282
41. Schembl4748
42. Streptozocin; Streptozotocin
43. .alpha.-streptozocin
44. Bspbio_000684
45. Bspbio_002734
46. Kbiogr_001768
47. Kbioss_001440
48. Mls004774123
49. Divk1c_000531
50. Spectrum1500543
51. Unii-8h27gur065
52. Spbio_000243
53. Bpbio1_000754
54. Streptozocin (jan/usan/inn)
55. Bcbcmap01_000142
56. Hms501k13
57. Kbio1_000531
58. Kbio2_001440
59. Kbio2_004008
60. Kbio2_006576
61. Kbio3_001954
62. Ninds_000531
63. Hms1921a07
64. Hms2092i09
65. Hms2097c06
66. Hms3714c06
67. Pharmakon1600-01500543
68. 2-deoxy-2[[(methylnitrosoamino)-carbonyl]amino]-d-glucopyranose
69. Act03364
70. Zinc3977737
71. Streptozocin, >=98.0% (hplc)
72. Tox21_110585
73. Tox21_201859
74. Tox21_302974
75. Ccg-39870
76. Nsc757321
77. S1312
78. Akos025310730
79. Tox21_110585_1
80. Db00428
81. Nsc-757321
82. Idi1_000531
83. Smp1_000282
84. Ncgc00178500-01
85. Ncgc00178500-02
86. Ncgc00178500-03
87. Ncgc00178500-04
88. Ncgc00178500-07
89. Ncgc00256594-01
90. Ncgc00259408-01
91. 1-methyl-1-nitroso-3-((2s,3r,4r,5s,6r)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2h-pyran-3-yl)urea
92. Smr001233317
93. Sbi-0051517.p003
94. Ab00513906
95. Sw199198-2
96. C07313
97. D05932
98. Ab00052092-03
99. Ab00052092_04
100. Ab00052092_05
101. 883s664
102. A937380
103. N-(methylnitrosocarbamoyl)-a-d-glucosamine
104. Q257331
105. Sr-01000939745
106. Sr-01000939745-3
107. Sr-05000001720-1
108. Sr-05000001720-2
109. W-201687
110. Streptozocin, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%, Powder
111. Streptozocin, >=75% Alpha-anomer Basis, >=98% (hplc), Powder
112. Alpha-d-glucopyranose, 2-deoxy-2-(((methylnitrosoamino)carbonyl)amino)-
113. Wurcs=2.0/1,1,0/[a2122h-1a_1-5_2*ncnn=o/4c/3=o]/1/
114. .alpha.-d-glucopyranose, 2-deoxy-2-(((methylnitrosoamino)carbonyl)amino)-
115. 1-methyl-1-nitroso-3-((2s,3r,4r,5s,6r)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-tetrahydro-2h-pyran-3-yl)urea
116. 1-methyl-1-nitroso-3-[(2s,3r,4r,5s,6r)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydropyran-3-yl]urea
| Molecular Weight | 265.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H15N3O7 |
| XLogP3 | -1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 265.09099983 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 265.09099983 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 152 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 315 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zanosar |
| PubMed Health | Streptozocin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Each vial of ZANOSAR contains 1 g of the active ingredient streptozocin 2-deoxy-2 [[(methylnitrosoamino)carbonyl]amino]- (and )-D-glucopyranose and 220 mg citric acid anhydrous. ZANOSAR is available as a sterile, pale yellow, freeze-dried prepara... |
| Active Ingredient | Streptozocin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zanosar |
| PubMed Health | Streptozocin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Each vial of ZANOSAR contains 1 g of the active ingredient streptozocin 2-deoxy-2 [[(methylnitrosoamino)carbonyl]amino]- (and )-D-glucopyranose and 220 mg citric acid anhydrous. ZANOSAR is available as a sterile, pale yellow, freeze-dried prepara... |
| Active Ingredient | Streptozocin |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
Antibiotics, Aminoglycoside; Antibiotics, Antineoplastic
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
... A SPECIFIC BETA CELL TOXIN & THEREFORE USEFUL IN TREATMENT OF METASTATIC ISLET CELL TUMORS.
American Medical Association, Department of Drugs. Drug Evaluations. 6th ed. Chicago, Ill: American Medical Association, 1986., p. 1191
IT HAS ... BEEN FOUND TO BE ACTIVE IN HODGKIN'S DISEASE, OTHER LYMPHOMAS, & OCCASIONALLY IN MELANOMA & MALIGNANT CARCINOID TUMORS ... .
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1222
THE PROFUSE WATERY DIARRHEA OBSERVED IN PATIENTS WITH PANCREATIC CHOLERA (VERNER MORRISON SYNDROME, SECRETORY DIARRHEA) PRODUCED BY METASTATIC NONBETA CELL TUMORS HAS BEEN RELIEVED BY INFUSION OF STREPTOZOCIN INTO THE HEPATIC ARTERY.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 964
MEDICATION (VET): ... EMPLOYED AS DIABETOGENIC AGENT IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1269
PATIENTS WITH PRE-EXISTING IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION SHOULD NOT RECEIVE STREPTOZOTOCIN.
American Medical Association, Department of Drugs. Drug Evaluations. 6th ed. Chicago, Ill: American Medical Association, 1986., p. 1191
STREPTOZOTOCIN FREQUENTLY ASSOCIATED WITH CHANGES IN LIVER SCAN. SUGGESTED THAT MINOR SCAN CHANGES MIGHT BE ATTRIBUTED ERRONEOUSLY TO INTRINSIC HEPATIC DISEASE.
PMID:7356745 KAPLAN ET AL; J NUCL MED 21 (JAN): 84 (1980)
For the treatment of malignant neoplasms of pancreas (metastatic islet cell carcinoma).
Streptozocin is an antitumour antibiotic consisting of a nitrosourea moiety interposed between a methyl group and a glucosamine. Streptozocin is indicated in the treatment of metastatic islet cell carcinoma of the pancreas. Streptozocin inhibits DNA synthesis in bacterial and mammalian cells. In bacterial cells, a specific interaction with cytosine moieties leads to degradation of DNA. The biochemical mechanism leading to mammalian cell death has not been definitely established; streptozocin inhibits cell proliferation at a considerably lower level than that needed to inhibit precursor incorporation into DNA or to inhibit several of the enzymes involved in DNA synthesis. Although streptozocin inhibits the progression of cells into mitosis, no specific phase of the cell cycle is particularly sensitive to its lethal effects.
Antibiotics, Antineoplastic
Chemical substances, produced by microorganisms, inhibiting or preventing the proliferation of neoplasms. (See all compounds classified as Antibiotics, Antineoplastic.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01A - Alkylating agents
L01AD - Nitrosoureas
L01AD04 - Streptozocin
Absorption
Poor oral absorption (17-25%)
Route of Elimination
As much as 20% of the drug (or metabolites containing an N-nitrosourea group) is metabolized and/or excreted by the kidney.
IN ALL THESE SPECIES /MICE, RATS, CATS, MONKEYS & DOGS/ STR /STREPTOZOTOCIN/ GIVEN PARENTERALLY ... MARKEDLY CONCENTRATED IN LIVER & KIDNEY; FOR EXAMPLE, IN DOGS ... RETAINED IN LIVER FOR MANY HR AFTER ... NO LONGER ... DETECTED IN BLOOD .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V4 224
STREPTOZOTOCIN ... WELL ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT IN MICE, BUT ABSORPTION WAS POOR IN MONKEYS & NEGLIGIBLE IN DOGS.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V17 343
(14)C-LABELLED STREPTOZOTOCIN GIVEN BY IV INJECTION WAS RAPIDLY CLEARED FROM BLOOD OF RATS, SO THAT LESS THAN 1% REMAINED AFTER 10 MINUTES.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V17 343
STREPTOZOTOCIN (NSC-85998) WAS RAPIDLY EXCRETED IN URINE OF TREATED MICE; 72% OF AN INJECTED DOSE IN THE 4-HR URINE. FIVE URINARY METABOLITES WERE DETECTED ... .
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 4: A Review of the Literature Published during 1974 and 1975. London: The Chemical Society, 1977., p. 151
Following intraperitoneal or IV administration of streptozocin in animals, the drug and its metabolites are rapidly distributed mainly into the liver, kidneys, intestine, and pancreas, with lower concentrations being distributed into skeletal muscle, spleen, lungs, heart, and thymus. Concentrations of the drug or its metabolites in the liver, kidneys, intestine, and pancreas are consistently higher than those in plasma. Streptozocin does not appear to cross the blood-brain barrier in animals or humans; however, in humans, metabolites of streptozocin readily distribute into CSF. ... The drug readily crosses the placenta in monkeys.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). AHFS Drug Information 90. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1990 (Plus Supplements 1990)., p. 547
Primarily hepatic
STUDIES WITH STREPTOZOTOCIN LABELLED WITH (14)C IN DIFFERENT POSITIONS INDICATE THAT ITS RAPID METABOLISM IN RAT ... RESULTS IN METABOLITE DERIVED FROM METHYL BEARING NITROSOUREIDO SIDECHAIN. /SRP: DIAZOMETHANE/
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 5: A Review of the Literature Published during 1976 and 1977. London: The Chemical Society, 1979., p. 380
/IN MICE URINE/ FIVE URINARY METABOLITES WERE DETECTED; 2 OF THEM WERE THE ALPHA AND BETA-ANOMERS OF THE ANTIBIOTIC.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 4: A Review of the Literature Published during 1974 and 1975. London: The Chemical Society, 1977., p. 151
Streptozocin and metabolites have a short distribution phase (t1/2 6 min) followed by possibly two elimination phases representing active metabolites (t1/2 beta 3.5 hr, t1/2 gamma 40 hr).
Knoben, J.E. and P.O. Anderson (eds.) Handbook of Clinical Drug Data. 6th ed. Bethesda, MD: Drug Intelligence Publications, Inc. 1988., p. 425
Streptozocin is not orally active. After intravenous administration, it is rapidly cleared from plasma and is undetectable after three hours. Metabolites are detected in plasma for up to 24 hours. The drug concentrates in certain tissues; the liver and kidneys contain the highest levels, and pancreas also concentrates streptozocin. Parent drug and metabolites are eliminated rapidly by the kidney; 60% to 70% of a dose is recovered in urine within four hours. Only 10% to 20% of an excreted dose is parent drug.
American Medical Association, Department of Drugs. Drug Evaluations. 6th ed. Chicago, Ill: American Medical Association, 1986., p. 1191
5-15 minutes
AFTER IV INFUSIONS OF 200-1600 MG/SQ M, PEAK CONCN IN PLASMA ARE 30-40 UG/ML; HALF-LIFE OF DRUG IS APPROX 15 MIN. ONLY 10-20% OF DOSE IS RECOVERED IN URINE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1222
... STREPTOZOTOCIN ... FOLLOW APPARENT TWO-COMPARTMENT MODEL KINETICS IN MAN AFTER BOLUS IV INJECTION, WITH MEAN FAST & SLOW DISPOSITION HALF-TIME VALUES OF 4.6 & 40 MIN RESPECTIVELY. THE LATTER VALUE IS 2.5-FOLD GREATER THAN REPORTED PREVIOUSLY FOR PT RECEIVING STREPTOZOTOCIN BY SLOW IV INFUSION.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 5: A Review of the Literature Published during 1976 and 1977. London: The Chemical Society, 1979., p. 80
SEVEN PATIENTS GIVEN SINGLE 1.5 G/SQ M IV DOSE SHOWED MEAN HALF-LIFE OF APPROX 40 MINUTES & HALF-LIFE OF ELIMINATION OF ABOUT 15 MINUTES.
PMID:142097 ADOLPHE ET AL; J CLIN PHARMACOL 17 (JUL): 379 (1977)
Although its mechanism of action is not completely clear, streptozocin is known to inhibit DNA synthesis, interfere with biochemical reactions of NAD and NADH, and inhibit some enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis. Its activity appears to occur as a result of formation of methylcarbonium ions, which alkylate or bind with many intracellular molecular structures including nucleic acids. Its cytotoxic action is probably due to cross-linking of strands of DNA, resulting in inhibition of DNA synthesis.
DRUG IS CAPABLE OF INHIBITING SYNTH OF DNA IN MICROORGANISMS & MAMMALIAN CELLS; IT AFFECTS ALL STAGES OF MAMMALIAN CELL CYCLE. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES HAVE ALSO REVEALED POTENT INHIBITORY EFFECTS ON PYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDES & ON KEY ENZYMES INVOLVED IN GLYCONEOGENESIS.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1271
Mechanisms underlying cytotoxicity by the monofunctional nitrosourea streptozotocin were evaluated in DNA repair-deficient E coli mutants. Strains not proficient in recombinational repair which lack either RecA protein or RecBC gene products were highly sensitive to streptozotocin (1X10-4 to 1X10-6 M concn for 30 min at 37 C). In contrast, cells that constituitively synthesize RecA protein and cannot initiate SOS repair mechanisms because of uncleavable LexA repressor (recAo98 lexA3) were resistant to this drug compared to a lexA3 strain. E coli cells lacking both 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylases I (tag) and II (alkA) also were highly sensitive to streptozotocin. DNA synthesis was most inhibited by streptozotocin in recA and alkA tag E coli mutants, but was suppressed less markedly in wild-type and recBC cells. DNA degradation was most extensive in recA E coli after streptozotocin treatment (400 ul 10-3 M for 30 min at 37 C), while comparable in recBC, alkA tag, and wild-type cells. Although incr single-stranded DNA breaks were present after streptozotocin treatment in recA and recBC mutants compared to the wild type, no significant incr in DNA single-stranded breaks was noted in alkA tag E coli. Further, DNA breaks in recBC cells were repaired, while those present in recA cells were not.
PMID:2475773 Fram RJ et al; Mutat Res 218 (2): 125-33 (1989)

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Market Place

ABOUT THIS PAGE
89
PharmaCompass offers a list of Streptozocin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Streptozocin manufacturer or Streptozocin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Streptozocin manufacturer or Streptozocin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Streptozocin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Streptozocin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Streptozocin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Streptozocin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Streptozocin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Streptozocin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Streptozocin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Streptozocin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Streptozocin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Streptozocin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Streptozocin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Streptozocin finished formulations upon request. The Streptozocin suppliers may include Streptozocin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Streptozocin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Streptozocin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Streptozocin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Streptozocin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Streptozocin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Streptozocin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Streptozocin USDMF includes data on Streptozocin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Streptozocin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Streptozocin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Streptozocin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Streptozocin API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Streptozocin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Streptozocin and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Streptozocin NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Streptozocin suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Streptozocin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Streptozocin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Streptozocin GMP manufacturer or Streptozocin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Streptozocin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Streptozocin's compliance with Streptozocin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Streptozocin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Streptozocin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Streptozocin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Streptozocin EP), Streptozocin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Streptozocin USP).
