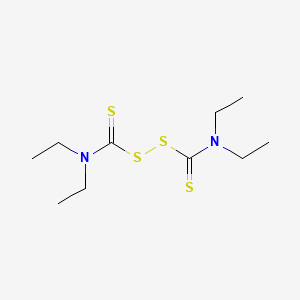

1. Alcophobin
2. Antabus
3. Antabuse
4. Anticol
5. Bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) Disulfide
6. Dicupral
7. Disulfide, Tetraethylthiuram
8. Esperal
9. Tetraethylthioperoxydicarbonic Diamide, ((h2n)c(s))2s2
10. Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide
11. Teturam
1. Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide
2. 97-77-8
3. Antabuse
4. Bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) Disulfide
5. Antabus
6. Tetd
7. Alcophobin
8. Anticol
9. Esperal
10. Teturam
11. Dicupral
12. Exhorran
13. Hoca
14. Ethyldithiurame
15. Abstensil
16. Antaethyl
17. Antietanol
18. Antivitium
19. Contralin
20. Tetradine
21. Tetraetil
22. Teturamin
23. Abstinil
24. Abstinyl
25. Antadix
26. Antalcol
27. Antetan
28. Antetil
29. Antietil
30. Antikol
31. Aversan
32. Averzan
33. Cronetal
34. Krotenal
35. Refusal
36. Etabus
37. Ethyl Tuads
38. Ethyl Thiram
39. Ethyl Thiurad
40. Ethyl Tuex
41. Antaenyl
42. Antaetil
43. Antiaethan
44. Contrapot
45. Disulfan
46. Disulfuram
47. Ephorran
48. Stopetyl
49. Thiuranide
50. Anteyl
51. Bonibal
52. Disetil
53. Nocbin
54. Tenurid
55. Tenutex
56. Tetidis
57. Ekagom Teds
58. Ekagom Tetds
59. Ethyldithiourame
60. Noxal
61. Anti-ethyl
62. Alk-aubs
63. Tetraethylthiuram Disulphide
64. Thiuram E
65. Tatd
66. Soxinol Tet
67. Tetraethylthiram Disulfide
68. Ekagom Dtet
69. Accel Tet
70. Espenal
71. Exhoran
72. Sanceler Tet-g
73. Ro-sulfiram
74. Tetraethylthiuram
75. Tuads, Ethyl
76. Usaf B-33
77. Sanceler Tet
78. Tetraethylthioperoxydicarbonic Diamide
79. Stopaethyl
80. Thireranide
81. Antaethan
82. Antethyl
83. Tetradin
84. Tillram
85. Accel Tet-r
86. Ethyl Thiudad
87. Dupon 4472
88. Tetraethylthiuran Disulfide
89. Anthethyl
90. Disulphuram
91. Dupont Fungicide 4472
92. Hocakrotenalnci-c02959
93. Tetraethylthiram Disulphide
94. Bis(diethylthiocarbamyl) Disulfide
95. Tetraethylthiuram Sulfide
96. Thiuram Disulfide, Tetraethyl-
97. N,n,n',n'-tetraethylthiuram Disulfide
98. Antabuse (tn)
99. Bis(n,n-diethylthiocarbamoyl) Disulfide
100. 1,1'-dithiobis(n,n-diethylthioformamide)
101. Disulfide, Bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl)
102. Diethylcarbamothioylsulfanyl N,n-diethylcarbamodithioate
103. Ent 27,340
104. Nsc 190940
105. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide, Tetraethyl-
106. Bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl)disulphide
107. Nci-c02959
108. Tts
109. Nsc-25953
110. Bis(n,n-diethylthiocarbamoyl)disulphide
111. N,n,n',n'-tetraethylthiuram Disulphide
112. Bis((diethylamino)thioxomethyl)disulphide
113. Bis((diethylamino)thioxomethyl) Disulfide
114. Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide;tetd
115. Disulfiram (antabuse)
116. Tr3mlj1uai
117. N,n-diethyl[(diethylcarbamothioyl)disulfanyl]carbothioamide
118. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ([(h2n)c(s)]2s2), Tetraethyl-
119. Chembl964
120. Mls000069818
121. Chebi:4659
122. Ora102
123. Ora-102
124. Bis(diethylthiocarbamyoyl)disulfide
125. 1,1',1'',1'''-[disulfanediylbis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetraethane
126. Nsc25953
127. Esperal [france]
128. Cas-97-77-8
129. Ncgc00016000-08
130. Ncgc00016000-13
131. Smr000059171
132. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide (((h2n)c(s))2s2), Tetraethyl-
133. Dsstox_cid_1322
134. Ancazide Et
135. Akrochem Tetd
136. Perkacit Tetd
137. Ekaland Tetd
138. Perkait Tetd
139. Dsstox_rid_76082
140. Dsstox_gsid_21322
141. Ethyl Tuads Rodform
142. C10h20n2s4
143. Disulfiramum [inn-latin]
144. Disulfiramo [inn-spanish]
145. Bis[(diethylamino)thioxomethyl] Disulfide
146. Ccris 582
147. 1,1'-dithiobis[n,n-diethylthioformamide]
148. Hsdb 3317
149. Sr-01000076145
150. Unii-tr3mlj1uai
151. Einecs 202-607-8
152. Mfcd00009048
153. Nsc 25953
154. Disulfarim
155. Ai3-27340
156. Formamide, 1,1'-dithiobis(n,n-diethylthio-
157. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide (((h2n)c(s))2s2), N,n,n',n'-tetraethyl-
158. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ([(h2n)c(s)]2s2), N,n,n',n'-tetraethyl-
159. Disulfiram [usp:inn:ban:jan]
160. Prestwick_182
161. Spectrum_001010
162. Cpd000059171
163. Disulfiram [mi]
164. Opera_id_224
165. Disulfiram [inn]
166. Disulfiram [jan]
167. Prestwick0_000097
168. Prestwick1_000097
169. Prestwick2_000097
170. Prestwick3_000097
171. Spectrum2_001176
172. Spectrum3_000405
173. Spectrum4_000228
174. Spectrum5_001590
175. Disulfiram [hsdb]
176. Disulfiram [iarc]
177. Lopac-t-1132
178. 1,n-diethylthioformamide]
179. Disulfiram [vandf]
180. Formamide, 1,1'-dithiobis(n,n-diethylthio)-
181. Upcmld-dp090
182. Ec 202-607-8
183. T 1132
184. Tetraethyl Thiuram Disulfide
185. Disulfiram [mart.]
186. Tetraethyldithiuram Disulfide
187. Disulfiram [who-dd]
188. Lopac0_001164
189. Schembl27213
190. Bspbio_000054
191. Bspbio_001930
192. Kbiogr_000895
193. Kbioss_001490
194. Mls000758264
195. Mls001076475
196. Mls001423963
197. Spectrum1500262
198. Spbio_001191
199. Spbio_001993
200. Bpbio1_000060
201. Disulfiram (jp17/usp/inn)
202. Gtpl7168
203. Disulfiram [ep Impurity]
204. Disulfiram [orange Book]
205. Dtxsid1021322
206. Upcmld-dp090:001
207. Kbio2_001490
208. Kbio2_004058
209. Kbio2_006626
210. Kbio3_001150
211. Disulfiram [ep Monograph]
212. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ((h2n)c(s))2s2, Tetraethyl-
213. Disulfiram [usp Monograph]
214. Hms1568c16
215. Hms1920i16
216. Hms2051m17
217. Hms2090c18
218. Hms2091o22
219. Hms2095c16
220. Hms2230k06
221. Hms3263j09
222. Hms3371b21
223. Hms3393m17
224. Hms3655i19
225. Hms3712c16
226. Hms3867h13
227. Pharmakon1600-01500262
228. Bcp07331
229. Hy-b0240
230. Zinc1529266
231. Bis-(diethyl-thiocarbamyl)-disulfide
232. Tox21_110280
233. Tox21_300403
234. Tox21_400072
235. Tox21_501164
236. Bdbm50058655
237. Ccg-39549
238. Dl-379
239. N,n',n'-tetraethylthiuram Disulfide
240. Nsc756748
241. Nsc800739
242. S1680
243. Stl069539
244. 1,1',1'',1'''-{disulfanediylbis[(thioxomethylene)-nitrilo]}tetraethane
245. Akos000120201
246. Tox21_110280_1
247. At13284
248. Db00822
249. Hs-0057
250. Lp01164
251. Nc00063
252. Nsc-756748
253. Nsc-800739
254. Sdccgsbi-0051131.p005
255. Wln: 2n2 & Yus & S 2
256. Ncgc00016000-01
257. Ncgc00016000-02
258. Ncgc00016000-03
259. Ncgc00016000-04
260. Ncgc00016000-05
261. Ncgc00016000-06
262. Ncgc00016000-07
263. Ncgc00016000-09
264. Ncgc00016000-10
265. Ncgc00016000-11
266. Ncgc00016000-12
267. Ncgc00016000-14
268. Ncgc00016000-15
269. Ncgc00016000-18
270. Ncgc00016000-29
271. Ncgc00094423-01
272. Ncgc00094423-02
273. Ncgc00094423-03
274. Ncgc00094423-05
275. Ncgc00094423-06
276. Ncgc00094423-07
277. Ncgc00254447-01
278. Ncgc00261849-01
279. N,n,n'',n''-tetraethylthiuram Disulfide
280. Bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) Disulphide
281. Formamide,1'-dithiobis(n,n-diethylthio)-
282. Sbi-0051131.p004
283. 1,1''-dithiobis(n,n-diethylthioformamide)
284. Db-057683
285. Ab00051976
286. B0479
287. Eu-0101164
288. Ft-0631502
289. Ft-0667720
290. Sw196492-4
291. Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide, >=97.0% (s)
292. C01692
293. D00131
294. S00294
295. Ab00051976-20
296. Ab00051976-21
297. Ab00051976-23
298. Ab00051976_22
299. Ab00051976_25
300. A845750
301. Q409665
302. Q-201812
303. Sr-01000076145-1
304. Sr-01000076145-5
305. Sr-01000076145-8
306. Brd-k32744045-001-05-6
307. Brd-k32744045-001-17-1
308. Z1522553469
309. Disulfiram, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
310. Disulfiram, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
311. 1,1',1'',1'''-[disulfanediylbis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetra
312. Disulfiram, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
313. 1,1'',1'''',1''''''-[disulfanediylbis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetraethane
314. Disulfiram, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
315. N,n-diethylcarbamodithioic Acid [[diethylamino(sulfanylidene)methyl]thio] Ester
316. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ((h2n)c(s))(sub 2) S(sub 2), Tetraethyl-
317. Tetraethylthioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ((((c(sub 2)h(sub 5))(sub 2)n)c(s))(sub 2)s(sub 2))
| Molecular Weight | 296.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H20N2S4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 296.05093334 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 296.05093334 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 121 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 201 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Antabuse |
| PubMed Health | Disulfiram (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Ethanol Dependency |
| Drug Label | Disulfiram is an alcohol antagonist drug. CHEMICAL NAME:bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide.STRUCTURAL FORMULA:C10H20N2S4 M.W. 296.54Disulfiram occurs as a white to off-white, odorless, and almost tasteless powder, soluble in water to the extent of a... |
| Active Ingredient | Disulfiram |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Odyssey Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Disulfiram |
| PubMed Health | Disulfiram (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Ethanol Dependency |
| Drug Label | Disulfiram is an alcohol antagonist drug. CHEMICAL NAME: bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide. STRUCTURAL FORMULA:Disulfiram occurs as a white to off-white, odorless, and almost tasteless powder, soluble in water to the extent of about 20 mg in 100 mL... |
| Active Ingredient | Disulfiram |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Sigmapharm Labs; Roxane; Alvogen Pine Brook |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Antabuse |
| PubMed Health | Disulfiram (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Ethanol Dependency |
| Drug Label | Disulfiram is an alcohol antagonist drug. CHEMICAL NAME:bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide.STRUCTURAL FORMULA:C10H20N2S4 M.W. 296.54Disulfiram occurs as a white to off-white, odorless, and almost tasteless powder, soluble in water to the extent of a... |
| Active Ingredient | Disulfiram |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Odyssey Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Disulfiram |
| PubMed Health | Disulfiram (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Ethanol Dependency |
| Drug Label | Disulfiram is an alcohol antagonist drug. CHEMICAL NAME: bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide. STRUCTURAL FORMULA:Disulfiram occurs as a white to off-white, odorless, and almost tasteless powder, soluble in water to the extent of about 20 mg in 100 mL... |
| Active Ingredient | Disulfiram |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Sigmapharm Labs; Roxane; Alvogen Pine Brook |
Alcohol Deterrents; Enzyme Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Disulfiram is used to help maintain sobriety in the treatment of chronic alcoholism in conjunction with supportive and psychotherapeutic measures.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1133
Case reports suggest that disulfiram may be useful for the treatment of nickel dermatitis. However, small double-blind placebo-controlled study of patients with hand eczema and nickel allergy did not find a clinically significant difference between those treated with disulfiram and those treated with placebo. Because some patients worsen with this therapy and because patients treated for nickel dermatitis have developed disulfiram induced hepatitis, this therapy is not generally indicated.
Goldfrank, L.R. (ed). Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies. 7th Edition McGraw-Hill New York, New York 2002., p. 977
The oral efficacy of several chelating drugs, incl disulfiram, was studied in relation to their ability to prevent lethality due to acute inhalation exposure to nickel carbonyl. Disulfiram resulted in very high, but transient, plasma levels. Small, repeated oral doses of disulfiram would be just as effective in nickel carbonyl poisoning as a single large dithiocarb dose. However, disulfiram increase the nickel retained in brain tissue, possibly accounting for its limited efficacy. Caution in the use of oral disulfiram in human nickel carbonyl intoxication is recommended.
PMID:6293022 Baselt RC, Hanson VW; Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 38 (1): 113-24 (1982)
... Alarming reactions may result from the ingestion of even small amt of alc in persons being treated with disulfiram. Marked resp depression, cardiovascular collapse, cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, acute congestive heart failure, unconsciousness, convulsions, and sudden and unexplained fatalities have occurred.
Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 388
The ingestion of alcohol by individuals previously treated with disulfiram gives rise to marked signs and symptoms. Within about 5-10 min face feels hot, and soon afterwards it is flushed and scarlet in appearance. As vasodilatation spreads over whole body, intense throbbing is felt in head and neck, and a pulsating headache may develop. Respiratory difficulties, nausea, copious vomiting, sweating, thirst, chest pain, considerable hypotension, orthostatic syncope, marked uneasiness, weakness, vertigo, blurred vision, and confusion are observed. Facial flush is replaced by pallor, and blood pressure may fall to shock level.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 441
May decrease urinary vanilmandelic acid excretion, although ... not sufficient to interfere with diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. /Disulfiram's/ inhibition of dopamine hydroxylase ... may increase urinary concn of homovanillic acid /adverse effect, oral/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1977
Patients receiving disulfiram should be warned to avoid cough syrups, sauces, vinegars, elixirs, and other preparations that contain alcohol. External application of alcoholic liniments or lotions, including aftershave or back rub, may be sufficient to produce a disulfiram-alcohol reaction. Patients should be cautioned that disulfiram-alcohol reactions may occur for several weeks after discontinuance of disulfiram.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3558
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DISULFIRAM (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment and management of chronic alcoholism
Disulfiram produces a sensitivity to alcohol which results in a highly unpleasant reaction when the patient under treatment ingests even small amounts of alcohol. Disulfiram blocks the oxidation of alcohol at the acetaldehyde stage during alcohol metabolism following disulfiram intake, the concentration of acetaldehyde occurring in the blood may be 5 to 10 times higher than that found during metabolism of the same amount of alcohol alone. Accumulation of acetaldehyde in the blood produces a complex of highly unpleasant symptoms referred to hereinafter as the disulfiram-alcohol reaction. This reaction, which is proportional to the dosage of both disulfiram and alcohol, will persist as long as alcohol is being metabolized. Disulfiram does not appear to influence the rate of alcohol elimination from the body. Prolonged administration of disulfiram does not produce tolerance; the longer a patient remains on therapy, the more exquisitely sensitive he becomes to alcohol.
Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase Inhibitors
Compounds that bind to and inhibit the enzymatic activity of acetaldehyde dehydrogenases. (See all compounds classified as Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase Inhibitors.)
Alcohol Deterrents
Substances interfering with the metabolism of ethyl alcohol, causing unpleasant side effects thought to discourage the drinking of alcoholic beverages. Alcohol deterrents are used in the treatment of alcoholism. (See all compounds classified as Alcohol Deterrents.)
N07BB01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N07 - Other nervous system drugs
N07B - Drugs used in addictive disorders
N07BB - Drugs used in alcohol dependence
N07BB01 - Disulfiram
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P03 - Ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides, insecticides and repellents
P03A - Ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides
P03AA - Sulfur containing products
P03AA04 - Disulfiram
Absorption
Disulfiram is absorbed slowly from the gastrointestinal tract (80 to 90% of oral dose).
Absorption /of disulfiram is/ slow. Eighty to ninety percent of an oral dose is absorbed. /Its/ biotransformation /is predominately/ hepatic /and/ a single dose will begin to affect ethanol metabolism within 1 to 2 hours.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1133
Disulfiram is ... completely absorbed from the human GI tract. However, a period of 12 hr is required for its full action, perhaps because, being highly sol in lipid, it is initially localized in fat. Elimination is relatively slow, and about 1/5 still remains in body at end of a week. The greater part of the absorbed drug is ... excreted in the urine as the sulfate, partly free and partly esterified.
Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 388
After a single oral dose of 50, 100, 200, or 400 mg/kg, disulfiram was found in dose-dependent quantities in blood, liver, kidney, spleen, brain, muscle, and peri-epididymal adipose tissue of rats. After a 2-mo treatment, accumulation was not dose-dependent, suggesting a saturation point for various organs.
De Saint-Blanquat G et al; Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 3 (4): 205-9 (1978)
The human plasma protein binding characteristics of disulfiram and its therapeutically active metabolite, diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester were investigated. Both compounds were bound principally to albumin over the ranges 200-800 and 345-2756 nM, respectively. The average number of binding sites was approximately one for both substances, whereas the average association constants were 7.1X10+4 and 6.1X10+3/M, respectively.
PMID:1982309 Johansson B; J Pharm Pharmacol 42 (Nov): 806-7 (1990)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DISULFIRAM (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic.
Disulfiram is slowly metabolized in the liver to diethyldithiocarbamate, diethylamine, and carbon disulfide. Six hr after oral administration of the drug, one third of plasma disulfiram is in the form of diethyldithiocarbamate.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3559
In rats the following metabolites of disulfiram were found: diethyldithiocarbamate; diethyldithiocarbamate s-glucuronide; inorganic sulfate; diethylamine and carbon disulfide. A small amount of S was bound to proteins as mixed disulfides. ... Metabolism of disulfiram in man is similar to that in animals.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V12 89 (1976)
Recently, n,n-diethylthiocarbamoyl-1-thio-beta-glucopyranosiduronic acid was isolated from combined urine of 4 men given oral doses of tetraethylthiuram disulfide.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides. U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife, Publication 127. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1969., p. 331
Diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester, in contrast to other disulfiram metabolites, is a potent inhibitor of liver aldehyde dehydrogenase in vitro. Like disulfiram, diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester had a pronounced hypothermic effect in rats. This hypothermic effect and the augmented blood pressure response to ethanol challenge in rats developed rapidly with diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester but were somewhat delayed with disulfiram. The blood pressure response outlasted the presence of diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester in plasma (less than 24 hr); a significant effect was found 48 hr after pretreatment but not 72 hr after a single dose. No effect was observed when ethanol was given 15 min before diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester or disulfiram. These latter two observations are consistent with a function of diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester as a suicide inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Since diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester has been reported to inhibit aldehyde dehydrogenase in vitro, even under anaerobic conditions, diethylthiocarbamic acid methyl ester may be the active metabolite of disulfiram.
PMID:2806369 Petersen EN; Eur J Pharmacol 166 (3): 419-25 (1989)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for DISULFIRAM (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The elimination half-life of disulfiram in plasma is 7.3 hr. /From table/
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 424
Following a 250 mg dose, the half-lives of disulfiram, diethyldithiocarbamate and carbon disulfide are 7.3 +/-1.5 hours, 15.5 +/-4.5 hours, and 8.9 +/-1.4 hours, respectively.
Goldfrank, L.R. (ed). Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies. 7th Edition McGraw-Hill New York, New York 2002., p. 972
Disulfiram blocks the oxidation of alcohol at the acetaldehyde stage during alcohol metabolism following disulfiram intake causing an accumulation of acetaldehyde in the blood producing highly unpleasant symptoms. Disulfiram blocks the oxidation of alcohol through its irreversible inactivation of aldehyde dehydrogenase, which acts in the second step of ethanol utilization. In addition, disulfiram competitively binds and inhibits the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor, which may indicate some value in the treatment of the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, however this activity has not been extensively studied.
Acetaldehyde, produced as a result of oxidation of ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase, ordinarily does not accumulate in the body, because it is further oxidized almost as soon as it is formed, primarily by aldehyde dehydrogenase. Following the administration of disulfiram, both cytosolic and mitochondrial forms of this enzyme are irreversibly inactivated to varying degrees, and the concentration of acetaldehyde rises. It is unlikely that disulfiram itself is responsible for the enzyme inactivation in vivo; several active metabolites of the drug, especially diethylthiomethylcarbamate, behave as suicide-substrate inhibitors of aldehyde dehydrogenase in vitro. These metabolites reach significant concentrations in plasma following the administration of disulfiram.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 441
Disulfiram (700 mg/kg, orally) increase brain levels of serotonin (i) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-hiaa) in rats. Ethanol (1 g/kg and 2x1.5 g/kg, ip) did not affect the serotonin level, but at the higher dose it increase the 5-hiaa level. When disulfiram was given in combination with ethanol, the brain level of serotonin was higher and the 5-hiaa level was lower, compared to the results with disulfiram alone. Thus, the biogenic aldehyde derived from serotonin may influence serotonin metab and the elimination of 5-hiaa from the brain.
PMID:6153360 Fukumori R et al; Eur J Pharmacol 61 (2): 199-202 (1980)
When disulfiram was given orally to rats at 40-400 mg/kg, the serum and, to a lesser extent, the liver cholesterol concentrations were increased and the liver microsome cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase activity decreased. The 7alpha-hydroxylase inhibition was completely reversed by dithiothreitol, indicating that disulfiram acted through its disulfide on 7alpha-hydroxylase. Increased serum cholesterol of alcoholics treated with disulfiram may be related to the inhibition of 7alpha-hydroxylase.
PMID:6477650 Anderson S, Bostroem H; Biochem Pharmacol 33 (18): 2930-2 (1984)
Human aldehyde dehydrogenase consists of two main isozymes with low and high Km for acetaldehyde. Studies regarding the inhibitory reaction of disulfiram and its metabolites were performed. Among the metabolites, diethylamine inhibited the low Km enzyme strongly. Vasomotor symptoms and high acetaldehyde concn in blood after ethanol intake in patients who are treated with disulfiram might be mainly due to a decrease in activity of the low Km enzyme caused by diethylamine which is produced in vivo as one of the metabolites from disulfiram, rather than to an inhibitory reaction of disulfiram only. Thus, alcohol sensitivity in Mongoloids and the disulfiram-ethanol reaction may have a common mechanism.
Harada S et al; Subst Alcohol Actions/Misuse 3 (1-2): 107-15 (1982)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for DISULFIRAM (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.