
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
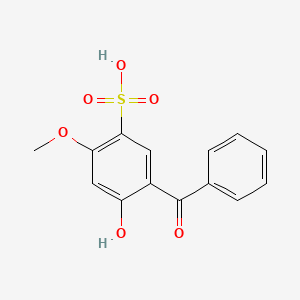

1. 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone-5-sulfonic Acid
2. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzene Sulfonic Acid
3. Benzophenone-4
4. Bp-4 Benzophenone
5. Sulisobenzone, Monosodium Salt
6. Uval
1. 4065-45-6
2. Benzophenone-4
3. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzenesulfonic Acid
4. 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone-5-sulfonic Acid
5. Sungard
6. Benzophenone 4
7. Uval
8. Seesorb 101s
9. Syntase 230
10. Uvinul Ms 40
11. Spectra-sorb Uv 284
12. Benzenesulfonic Acid, 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-
13. Sulisobenzona
14. Sulisobenzonum
15. 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-5-sulfobenzophenone
16. Ms 40
17. Uvinuc Ms 40
18. Sulfisobenzone
19. Uvinul Ms-40
20. Uvasorb S 5
21. Escalol 577
22. Viosorb 111
23. Uvinul D 5030
24. Nsc-60584
25. 1-phenol-4-sulfonic Acid, 2-benzoyl-5-methoxy-
26. 3-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzenesulfonic Acid
27. 2-benzoyl-5-methoxy-1-phenol-4-sulfonic Acid
28. 1w6l629b4k
29. Mfcd00024962
30. Nsc-760350
31. Uval Sodium Salt
32. Ncgc00159404-02
33. Ncgc00159404-04
34. Nsc 60584
35. Dsstox_cid_22436
36. Dsstox_rid_80023
37. Dsstox_gsid_42436
38. Uvinul Ms 40 Sodium Salt
39. Cyasorb Uv 284 Sodium Salt
40. Sulisobenzonum [inn-latin]
41. Sulisobenzona [inn-spanish]
42. Cas-4065-45-6
43. Nsc60584
44. Nsc654266
45. Hsdb 7422
46. Uvinul Ms-40 Substanz
47. 6628-37-1
48. Einecs 223-772-2
49. Brn 2889165
50. Unii-1w6l629b4k
51. Sulisobenzone [usan:usp:inn]
52. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzene Sulfonic Acid
53. Sungard (tn)
54. Hmbs
55. Benzenesulfonic Acid, 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-, Sodium Salt
56. Uval (*sodium Salt*)
57. Uvinul Ms40
58. Cbmicro_016354
59. Sulisobenzone (usp/inn)
60. Sulisobenzone [mi]
61. Ec 223-772-2
62. Sulisobenzone [inn]
63. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzolsulfonsaeure
64. Spectra-sorb U.v. 284
65. Sulisobenzone [hsdb]
66. Sulisobenzone [usan]
67. Schembl16330
68. 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-5-sulfonylbenzophenone(bp-4)
69. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-benzenesulfonic Acid
70. Mls004734662
71. Sulfisobenzone [vandf]
72. Sulisobenzone [mart.]
73. Benzophenone-4 [inci]
74. Sulisobenzone [usp-rs]
75. Sulisobenzone [who-dd]
76. Cyasorb Uv 284 (salt/mix)
77. Chembl2059073
78. Dtxsid2042436
79. 4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-5-(phenylcarbonyl)benzenesulfonic Acid
80. Chebi:135312
81. Sulisobenzone, Analytical Standard
82. Uvinul Ms 40 (*sodium Salt*)
83. Albb-025816
84. Cyasorb Uv 284 (*sodium Salt*)
85. Hy-b1162
86. Zinc1690324
87. Tox21_111639
88. Tox21_202332
89. Tox21_303469
90. S4652
91. Sulisobenzone [usp Monograph]
92. Akos015895600
93. Tox21_111639_1
94. Ccg-267557
95. Cs-4610
96. Db11185
97. Sulisobenzone (usan) (*sodium Salt*)
98. Ncgc00159404-03
99. Ncgc00159404-05
100. Ncgc00257488-01
101. Ncgc00259881-01
102. Ac-19869
103. As-12605
104. Smr001262265
105. Sy036839
106. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-besylic Acid
107. Db-049626
108. Ft-0612547
109. H0466
110. 2-benzoyl-5-methoxy-1-phenol-4-sulphonic Acid
111. D05964
112. F11240
113. A825218
114. J-509633
115. Q7636301
116. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzenesulfonic Acid Ammoniate
117. 1-phenol-4-sulfonic Acid, 2-benzoyl-5-methoxy-, Sodium Salt
118. 4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-5-(oxo-phenylmethyl)benzenesulfonic Acid
119. Sulisobenzone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
120. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzenesulfonic Acid, >=97.0% (hplc)
121. 5-benzoyl-4-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzenesulfonic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
| Molecular Weight | 308.31 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H12O6S |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 308.03545927 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 308.03545927 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 109 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 462 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Daily use of a sunscreen with a high SPF (greater than 15) on usually exposed skin is recommended for residents of areas of high ... /solar radiation/ who work outdoors or ... /enjoy/ regular outdoor recreation. Daily use of a sunscreen can reduce the cumulative ... /solar/ exposure that causes actinic keratoses and squamous-cell carcinoma.
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Cancer-Preventive Agents (2001) Sunscreens (IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention, Vol. 5), Lyon, IARC; Unit of Chemoprevention: Cancer-Preventive Effects of Sunscreens.
Sunscreen agents are indicated for the prevention of sunburn. In addition to limiting the skin's exposure to the sun, using sunscreen agents regularly when in the sun may help reduce long-term sun damage such as premature aging of the skin and skin cancer. /Sunscreen agents, topical; Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
The manufacturers of sunscreen preparations with propellants warn that concentrating and subsequently inhaling the fumes from these preparations may be harmful or fatal. /Propellants/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Because the absorptive characteristics of skin of children younger than 6 months of age may differ from those of adults and because the immaturity of metabolic and excretory pathways of these children may limit their ability to eliminate any percutaneously absorbed sunscreen agent, sunscreen products should be used in children younger than 6 months of age only as directed by a clinician. It is possible that the characteristics of geriatric skin also differ from those of skin in younger adults, but these characteristics and the need for special considerations regarding use of sunscreen preparations in this age group are poorly understood. /Sunscreens/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Little information is available regarding the safety of chronic sunscreen usage, but commercially available physical and chemical sunscreens appear to have a low incidence of adverse effects. Derivatives of PABA, benzophenone, cinnamic acid, and salicylate and 2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid have caused skin irritation including burning, stinging, pruritus, and erythema on rare occasions. /Sunscreens/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Sunscreens should not be used as a means of extending the duration of solar exposure, such as prolonging sunbathing, and should not be used as a substitute for clothing on usually unexposed sites, such as the trunk and buttocks. /Sunscreens/
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Cancer-Preventive Agents (2001) Sunscreens (IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention, Vol. 5), Lyon, IARC; Unit of Chemoprevention: Cancer-Preventive Effects of Sunscreens.
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for SULISOBENZONE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Sunscreening agents are used to prevent sunburn, actinic keratosis, and premature skin aging and to reduce the incidence of skin cancer.
Benzophenone sunscreens, applied topically, protect the skin from these harmful effects of ultraviolet light by chemically absorbing light energy (photons). Correct use of sunscreens serves to reduce the risk of sunburn. Sunscreen agents prevent the occurrence of squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin when used mainly during unintentional sun exposure. No conclusion can be drawn about the cancer-preventive activity of topical use of sunscreens against both basal-cell carcinoma and cutaneous melanoma. Use of sunscreens can extend the duration of intentional sun exposure, such as bathing in the sun.
Absorption
Does not penetrate the skin to a large degree, but enhances the ability of other chemicals to penetrate.
Route of Elimination
This drug's main metabolite is excreted in urine conjugated with glucuronic acid. No p-hydroxybenzohydrol was detected in urine or feces, in a study of pharmacokinetics in rats.
Solvents used in sunscreen products affect the stability and binding of the drug to the skin; in general, alcoholic solvents allow for the most rapid and deepest epidermal penetration of sunscreens. It appears that sunscreen agents are absorbed by the intact epidermis to varying degrees. /Sunscreens/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
Benzophenone's main metabolic pathway in the rabbit is by reduction to benzhydrol. A small amount (1%) is converted to p-hydroxybenzophenone following oral administration to rats.
A surface coating of benzophenones decreases the amount of UV radiation absorbed by the skin by limiting the total amount of energy that reaches the skin. Benzophenone sunscreens, applied topically, protect the skin from these harmful effects of ultraviolet light by chemically absorbing light energy (photons). As this occurs, the benzophenone molecule becomes activated to higher energy levels. As the excited molecule returns to its ground state, the energy is released in the form of thermal energy. The hydroxyl group in the ortho position to the carbonyl group is believed to be a structural requirement for the benzophenones' absorption of UV light. This structural arrangement also contributes to the electronic stability of the molecule. Benzophenones absorb energy throughout the UV range, although the maximum UV absorbance is between 284 and 287 nm for the 2-hydroxybenzophenones.
Benzophenone sunscreens, applied topically, protect the skin from these harmful effects of ultraviolet light by chemically absorbing light energy (photons). As this occurs, the Benzophenone molecule becomes excited to higher energy levels. As the excited molecule returns to its ground state, the energy is released in the form of thermal energy. The hydroxyl group in the ortho position to the carbonyl group is believed to be a structural requirement for the Benzophenones' absorption of UV light. This structural arrangement also contributes to the electronic stability of the molecule. Thus, a surface coating of Benzophenones decreases the amount of UV radiation absorbed by the skin by limiting the total amount of energy that reaches the skin. Benzophenones absorb energy throughout the UV range, though maximum absorbance is between 284 and 287 nm for the 2-hydroxybenzophenones ...
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of Benzophenones-1, -3, -4, -5, -9, and -11; Journal of the American College of Toxicology 2 (5): 35-78 (1983). Available form, as of September 12, 2013: https://online.personalcarecouncil.org/ctfa-static/online/lists/cir-pdfs/pr219.pdf
Diminish the penetration of ultraviolet (UV) light through the epidermis by absorbing UV radiation within a specific wavelength range. The amount and wavelength of UV radiation absorbed are affected by the molecular structure of the sunscreen agent. /Sunscreen agents, topical/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
34
PharmaCompass offers a list of Sulisobenzone API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Sulisobenzone manufacturer or Sulisobenzone supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Sulisobenzone manufacturer or Sulisobenzone supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Sulisobenzone API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Sulisobenzone API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Sulisobenzone Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Sulisobenzone Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Sulisobenzone manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Sulisobenzone, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Sulisobenzone manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Sulisobenzone API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Sulisobenzone supplier is an individual or a company that provides Sulisobenzone active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Sulisobenzone finished formulations upon request. The Sulisobenzone suppliers may include Sulisobenzone API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Sulisobenzone suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Sulisobenzone DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Sulisobenzone active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Sulisobenzone DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Sulisobenzone USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Sulisobenzone DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Sulisobenzone USDMF includes data on Sulisobenzone's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Sulisobenzone USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Sulisobenzone suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Sulisobenzone as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Sulisobenzone API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Sulisobenzone as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Sulisobenzone and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Sulisobenzone NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Sulisobenzone suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Sulisobenzone Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Sulisobenzone GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Sulisobenzone GMP manufacturer or Sulisobenzone GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Sulisobenzone CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Sulisobenzone's compliance with Sulisobenzone specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Sulisobenzone CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Sulisobenzone CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Sulisobenzone may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Sulisobenzone EP), Sulisobenzone JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Sulisobenzone USP).
