
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Annual Reports
NA
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Cci 779
2. Cci-779
3. Rapamycin, 42-(3-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropanoate)
4. Torisel
1. Cci-779
2. Torisel
3. 162635-04-3
4. 624kn6gm2t
5. Chembl1201182
6. Cci 779
7. Ncgc00167518-01
8. Rapamycin 42-(2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propionate)
9. Rapamycin 42-[3-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropanoate]
10. Rapamycin, 42-(3-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropanoate)
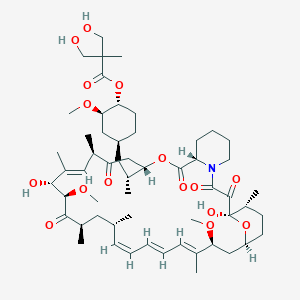
11. (1r,2r,4s)-4-{(2r)-2-[(3s,6r,7e,9r,10r,12r,14s,15e,17e,19e,21s,23s,26r,27r,30s,34as)-9,27-dihydroxy-10,21-dimethoxy-6,8,12,14,20,26-hexamethyl-1,5,11,28,29-pentaoxo-1,4,5,6,9,10,11,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,31,32,33,34,34a-tetracosahydro-3h-23,27-epoxypyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxazacyclohentriacontin-3-yl]propyl}-2-methoxycyclohexyl 3-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropanoate
12. Chebi:79699
13. Temserolimus
14. Nsc-683864
15. Mfcd00934421
16. Temsirolimus (cci-779, Nsc 683864)
17. Temsirolimus [usan]
18. Temsirolimus - Torisel
19. Temsirolimus [mi]
20. Temsirolimus [inn]
21. Temsirolimus [jan]
22. Dsstox_cid_20945
23. Dsstox_rid_79605
24. Temsirolimus [vandf]
25. Unii-624kn6gm2t
26. Dsstox_gsid_40945
27. Schembl18792
28. Temsirolimus [mart.]
29. 42-(3-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropanoate)rapamycin
30. Temsirolimus [who-dd]
31. Way-cci 779
32. Gtpl5892
33. Temsirolimus [ema Epar]
34. Dtxsid2040945
35. Hsdb 7931
36. Temsirolimus, >=98% (hplc)
37. Temsirolimus [orange Book]
38. 42-[3-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropanoate]-rapamycin
39. Temsirolimus [usan:inn:ban:jan]
40. Tox21_112515
41. Bdbm50343413
42. S1044
43. Akos025142069
44. Am84554
45. Ccg-264790
46. Cs-0129
47. Ncgc00167518-02
48. Ncgc00167518-05
49. Ncgc00167518-09
50. Hy-50910
51. Cas-162635-04-3
52. T3574
53. Ab01274736-01
54. Ab01274736_02
55. 635t043
56. Sr-01000898799
57. J-009958
58. Q7699074
59. Sr-01000898799-3
60. Brd-k08177763-001-02-6
61. A4i
| Molecular Weight | 1030.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C56H87NO16 |
| XLogP3 | 5.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 1029.60248569 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1029.60248569 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 242 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 73 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2010 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 15 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Torisel |
| PubMed Health | Temsirolimus (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Temsirolimus |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Intravenous |
| Strength | 25mg/ml (25mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pf Prism Cv |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Torisel |
| PubMed Health | Temsirolimus (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Temsirolimus |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Intravenous |
| Strength | 25mg/ml (25mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pf Prism Cv |
Temsirolimus is indicated for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
Anaphylaxis, dyspnea, flushing, and chest pain have been reported. Temsirolimus should be used with caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or its metabolites (eg, sirolimus), polysorbate 80, or any other ingredient in the formulation.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1242
Pretreatment with an antihistamine prior to each dose of temsirolimus is recommended to prevent hypersensitivity reactions. Temsirolimus should be used with caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to antihistamines or with conditions requiring avoidance of antihistamines.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1242
The safety and pharmacokinetics of temsirolimus were evaluated in a dose escalation phase 1 study in 110 patients with normal or varying degrees of hepatic impairment. Patients with baseline bilirubin >1.5 x ULN experienced greater toxicity than patients with baseline bilirubin /= grade 3 adverse reactions and deaths, including deaths due to progressive disease, were greater in patients with baseline bilirubin >1.5 x ULN. temsirolimus is contraindicated in patients with bilirubin >1.5 x ULN due to increased risk of death. Use caution when treating patients with mild hepatic impairment. Concentrations of temsirolimus and its metabolite sirolimus were increased in patients with elevated AST or bilirubin levels. If temsirolimus must be given in patients with mild hepatic impairment (bilirubin >1 - 1.5 x ULN or AST >ULN but bilirubin
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
No clinical studies were conducted with temsirolimus in patients with decreased renal function. Less than 5% of total radioactivity was excreted in the urine following a 25 mg intravenous dose of (14)C-labeled temsirolimus in healthy subjects. Renal impairment is not expected to markedly influence drug exposure, and no dosage adjustment of temsirolimus is recommended in patients with renal impairment.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Temsirolimus (29 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
* Renal-cell carcinoma:
Torisel is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma (RCC) who have at least three of six prognostic risk factors.
* Mantle-cell lymphoma:
Torisel is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed and / or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL).
MTOR Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit the activity of TOR SERINE-THREONINE KINASES. (See all compounds classified as MTOR Inhibitors.)
L01XE09
L01XE09
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EG - Mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) kinase inhibitors
L01EG01 - Temsirolimus
Following administration of a single 25 mg dose of temsirolimus in patients with cancer, mean temsirolimus Cmax in whole blood was 585 ng/mL (coefficient of variation, CV =14%), and mean AUC in blood was 1627 ng.hr/mL (CV=26%). Typically Cmax occurred at the end of infusion. Over the dose range of 1 mg to 25 mg, temsirolimus exposure increased in a less than dose proportional manner while sirolimus exposure increased proportionally with dose. Following a single 25 mg intravenous dose in patients with cancer, sirolimus AUC was 2.7-fold that of temsirolimus AUC, due principally to the longer half-life of sirolimus.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
Following a single 25 mg intravenous dose, mean steady-state volume of distribution of temsirolimus in whole blood of patients with cancer was 172 liters. Both temsirolimus and sirolimus are extensively partitioned into formed blood elements.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
Following a single 25 mg dose of temsirolimus in patients with cancer, temsirolimus mean (CV) systemic clearance was 16.2 (22%) L/hr.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
It is not known whether temsirolimus is excreted into human milk...
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
Following IV administration of a single radiolabeled dose of temsirolimus, approximately 78% of the total radioactivity is recovered in feces and 4.6% in urine within 14 days.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1243
Sirolimus, an active metabolite of temsirolimus, is the principal metabolite in humans following intravenous treatment. The remainder of the metabolites account for less than 10% of radioactivity in the plasma.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
Temsirolimus is metabolized by hydrolysis to sirolimus, the principal active metabolite. Both temsirolimus and sirolimus also are metabolized by cytochrome P-450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A4. Although temsirolimus is metabolized to sirolimus, temsirolimus itself exhibits antitumor activity and is not considered a prodrug.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1243
The in vitro metabolism of temsirolimus, (rapamycin-42-[2,2-bis-(hydroxymethyl)]-propionate), an antineoplastic agent, was studied using human liver microsomes as well as recombinant human cytochrome P450s, namely CYP3A4, 1A2, 2A6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, and 2E1. Fifteen metabolites were detected by liquid chromatography (LC)-tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS or MS/MS/MS). CYP3A4 was identified as the main enzyme responsible for the metabolism of the compound. Incubation of temsirolimus with recombinant CYP3A4 produced most of the metabolites detected from incubation with human liver microsomes, which was used for large-scale preparation of the metabolites. By silica gel chromatography followed by semipreparative reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, individual metabolites were separated and purified for structural elucidation and bioactivity studies. The minor metabolites (peaks 1-7) were identified as hydroxylated or desmethylated macrolide ring-opened temsirolimus derivatives by both positive and negative mass spectrometry (MS) and MS/MS spectroscopic methods. Because these compounds were unstable and only present in trace amounts, no further investigations were conducted. Six major metabolites were identified as 36-hydroxyl temsirolimus (M8), 35-hydroxyl temsirolimus (M9), 11-hydroxyl temsirolimus with an opened hemiketal ring (M10 and M11), N- oxide temsirolimus (M12), and 32-O-desmethyl temsirolimus (M13) using combined LC-MS, MS/MS, MS/MS/MS, and NMR techniques. Compared with the parent compound, these metabolites showed dramatically decreased activity against LNCaP cellular proliferation.
PMID:17540708 Cai P et al; Drug Metab Dispos 35 (9): 1554-63 (2007)
Temsirolimus exhibits a bi-exponential decline in whole blood concentrations and the mean half-lives of temsirolimus and sirolimus were 17.3 hr and 54.6 hr, respectively.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
Temsirolimus is an inhibitor of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin). Temsirolimus binds to an intracellular protein (FKBP-12), and the protein-drug complex inhibits the activity of mTOR that controls cell division. Inhibition of mTOR activity resulted in a G1 growth arrest in treated tumor cells. When mTOR was inhibited, its ability to phosphorylate p70S6k and S6 ribosomal protein, which are downstream of mTOR in the PI3 kinase/AKT pathway was blocked. In in vitro studies using renal cell carcinoma cell lines, temsirolimus inhibited the activity of mTOR and resulted in reduced levels of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 alpha, and the vascular endothelial growth factor.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TORISEL (temsirolimus) kit (June 2011). Available from, as of July 5, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=95b7dc92-2180-42f1-8699-3c28f609e674
Temsirolimus, an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase, is an antineoplastic agent. Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are involved in the initiation of various cascades of intracellular signaling events that lead to cell proliferation and/or influence processes critical to cell survival and tumor progression (eg, angiogenesis, metastasis), inhibition of apoptosis. Although the exact mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, temsirolimus binds with high affinity to the intracellular protein FK506 binding protein-12 in vitro, forming a drug-protein complex that inhibits the activation of mTOR, which regulates cell division. This disruption of mTOR signaling suppresses proteins that regulate cell-cycle progression, thereby blocking cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Inhibition of mTOR by temsirolimus also has been associated with reduced expression of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha and 2alpha (HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha) in vitro, resulting in reduced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and a potential antiangiogenic effect.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1243
Temsirolimus inhibited T lymphocyte activity in mice, but the effects were reversible and T lymphocyte activity returned to normal within 24 hours of discontinuance. No consistent effect on lymphocyte population or activation was demonstrated in humans. However, infections may result from immunosuppression.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 1243
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signal transduction pathway integrates signals from multiple receptor tyrosine kinases to control cell proliferation and survival. Key components of the pathway are the lipid kinase PI3-K, the small guanosine triphosphate-binding protein Rheb, and the protein kinases Akt and mTOR. Important natural inhibitors of the pathway include the lipid phosphatase PTEN and the tuberous sclerosis complex. Several components of this pathway are targeted by investigational antineoplastic agents. Rapamycin (sirolimus), the prototypic mTOR inhibitor, exhibits activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Three rapamycin analogs, temsirolimus, everolimus, and AP23573, are in clinical trials for various hematologic malignancies. Temsirolimus has produced a 38% overall response rate in relapsed mantle cell lymphoma, and AP23573 has demonstrated activity in acute leukemia. Everolimus is undergoing clinical testing in lymphoma (Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin) and multiple myeloma. In addition, perifosine, an inhibitor of Akt activation that exhibits substantial antimyeloma activity in preclinical models, is being examined in relapsed multiple myeloma. Based on results obtained to date, it appears that inhibitors of the PI3-K/mTOR pathway hold promise as single agents and in combination for hematologic malignancies.
PMID:16916489 Witzig TE, Kaufmann SH; Curr Treat Options Oncol 7 (4): 285-94 (2006)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Temsirolimus (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
62
PharmaCompass offers a list of Temsirolimus API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Temsirolimus manufacturer or Temsirolimus supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Temsirolimus manufacturer or Temsirolimus supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Temsirolimus API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Temsirolimus API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Temsirolimus Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Temsirolimus Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Temsirolimus manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Temsirolimus, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Temsirolimus manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Temsirolimus API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Temsirolimus manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Temsirolimus supplier is an individual or a company that provides Temsirolimus active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Temsirolimus finished formulations upon request. The Temsirolimus suppliers may include Temsirolimus API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Temsirolimus suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Temsirolimus DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Temsirolimus active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Temsirolimus DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Temsirolimus USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Temsirolimus DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Temsirolimus USDMF includes data on Temsirolimus's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Temsirolimus USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Temsirolimus suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Temsirolimus written confirmation (Temsirolimus WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Temsirolimus manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Temsirolimus active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Temsirolimus APIs or Temsirolimus finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Temsirolimus WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Temsirolimus suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Temsirolimus as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Temsirolimus API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Temsirolimus as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Temsirolimus and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Temsirolimus NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Temsirolimus suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Temsirolimus Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Temsirolimus GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Temsirolimus GMP manufacturer or Temsirolimus GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Temsirolimus CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Temsirolimus's compliance with Temsirolimus specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Temsirolimus CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Temsirolimus CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Temsirolimus may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Temsirolimus EP), Temsirolimus JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Temsirolimus USP).
