
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Canada

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Annual Reports
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
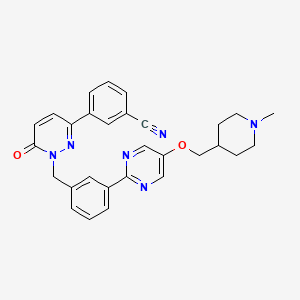

1. 3-(1-(3-(5-((1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy)-2-pyrimidinyl)benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-3-pyridazinyl)benzonitrile
2. Benzonitrile, 3-(1,6-dihydro-1-((3-(5-((1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy)-2-pyrimidinyl)phenyl)methyl)-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)-
3. Tepmetko
1. 1100598-32-0
2. Emd-1214063
3. Emd 1214063
4. Tepotinib [inn]
5. Emd1214063
6. Msc2156119
7. Msc-2156119j
8. Tepmetko
9. Tepotinib [usan]
10. Msc-2156119
11. Msc2156119j
12. 3-[1-[[3-[5-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]pyrimidin-2-yl]phenyl]methyl]-6-oxopyridazin-3-yl]benzonitrile
13. 1ijv77ei07
14. Tepotinib (emd 1214063)
15. 3-(1-(3-(5-((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy)pyrimidin-2-yl)benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazin-3-yl)benzonitrile
16. Benzonitrile, 3-(1,6-dihydro-1-((3-(5-((1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy)-2-pyrimidinyl)phenyl)methyl)-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)-
17. Benzonitrile, 3-[1,6-dihydro-1-[[3-[5-[(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy]-2-pyrimidinyl]phenyl]methyl]-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl]-
18. 3-[1-(3-{5-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]pyrimidin-2-yl}benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazin-3-yl]benzonitrile
19. Unii-1ijv77ei07
20. Tepotinib (usan/inn)
21. Tepotinib [who-dd]
22. Mls006010785
23. Gtpl8293
24. Schembl1296895
25. Tepotinib(emd-1214063)
26. Chembl3402762
27. Dtxsid70149132
28. Ex-a394
29. Who 9934
30. Bdbm50065457
31. Mfcd18452823
32. Nsc758244
33. Nsc781256
34. Nsc800945
35. S7067
36. Zinc43202335
37. Ccg-269632
38. Cs-0647
39. Db15133
40. Nsc-758244
41. Nsc-781256
42. Nsc-800945
43. Sb16609
44. Compound 22 [pmid: 25736998]
45. Ncgc00345793-01
46. Ncgc00345793-08
47. Ac-35185
48. As-16915
49. Hy-14721
50. Smr004701471
51. D11717
52. J-002366
53. Q27088961
54. 1100598-30-8
55. 3-(1-(3-(5-((1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy)-2-pyrimidinyl)benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-3-pyridazinyl)benzonitrile
56. 3-(1-{3-[5-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl-methoxy)pyrimidin-2-yl]benzyl}-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazin-3-yl)benzonitrile
57. 3-(1-{3-[5-(1-methylpiperidin-4-ylmethoxy)pyrimidin-2-yl]benzyl}-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazin-3-yl)benzonitrile
58. 3-[1,6-dihydro-1-[[3-[5-[(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy]-2-pyrimidinyl]phenyl]methyl]-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl]benzonitrile
59. 3e8
| Molecular Weight | 492.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H28N6O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 492.22737416 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 492.22737416 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 880 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Tepotinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have mesenchymal-epithelial transition (_MET_) exon 14 skipping alterations.
Tepmetko as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harbouring alterations leading to mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor gene exon 14 (METex14) skipping, who require systemic therapy following prior treatment with immunotherapy and/or platinum-based chemotherapy.
Tepotinib is a highly-selective inhibitor of MET kinase activity, with an average IC50 of approximately 1.7 nmol/L. It has a moderate duration of action necessitating once-daily administration. Tepotinib has been associated with the development of interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis, which can sometimes be fatal. Patients should be monitored closely for signs of new or worsening respiratory symptoms (e.g. dyspnea, cough), and treatment with tepotinib should be immediately withheld if ILD/pneumonitis is suspected. If no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis are identified, therapy with tepotinib should be suspended indefinitely.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
L01EX21
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX21 - Tepotinib
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of tepotinib following oral administration is approximately 72%. At the recommended dosage of 450mg once daily, the median Tmax is 8 hours and the mean steady-state Cmax and AUC0-24h were 1,291 ng/mL and 27,438 ngh/mL, respectively. Co-administration with a high-fat, high-calorie meal increases the AUC and Cmax of tepotinib by approximately 1.6-fold and 2-fold, respectively.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration, approximately 85% of the given dose is excreted in the feces with the remainder excreted in the urine. Unchanged parent drug accounts for roughly half of the dose excreted in the feces, with the remainder comprising the demethylated M478 metabolite, a glucuronide metabolite, the racemic M506 metabolite, and some minor oxidative metabolites. Unchanged parent drug also accounts for roughly half of the dose excreted in the urine, with the remainder comprising a glucuronide metabolite and a pair of N-oxide diastereomer metabolites.
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution is 1,038L.
Clearance
The apparent clearance of tepotinib is 23.8 L/h.
Tepotinib is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8, with some apparent contribution by unspecified UGT enzymes. The metabolite M506 is the major circulating metabolite, comprising approximately 40.4% of observed drug material in plasma, while the M668 glucuronide metabolite has been observed in plasma at much lower quantities (~4% of an orally administered dose). A total of 10 phase I and phase II metabolites have been detected following tepotinib administration, most of which are excreted in the feces.
Following oral administration, the half-life of tepotinib is approximately 32 hours.
Mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET) is a receptor tyrosine kinase found overexpressed and/or mutated in a variety of tumor types, thus making it a desirable target in their treatment. MET plays a critical role in the proliferation, survival, invasion, and mobilization of tumor cells, and aberrant MET activation is thought to contribute to the development of more aggressive cancers with poorer prognoses. Tepotinib is a kinase inhibitor directed against MET, including variants with exon 14 skipping - it inhibits MET phosphorylation and subsequent downstream signaling pathways in order to inhibit tumor cell proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, and migration of MET-dependent tumor cells. Tepotinib has also been observed to down-regulate the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) promoting genes (e.g. MMP7, COX-2, WNT1, MUC5B, and c-MYC) and upregulate the expression of EMT-suppressing genes (e.g. MUC5AC, MUC6, GSK3, and E-cadherin) in c-MET-amplified gastric cancer cells, suggesting that the tumor-suppressing activity of tepotinib is driven, at least in part, by the negative regulation of c-MET-induced EMT. It has also been shown to inhibit melatonin 1B and nischarin at clinically relevant concentrations, though the relevance of this activity in regards to tepotinib's mechanism of action is unclear.
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
16
PharmaCompass offers a list of Tepotinib API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Tepotinib manufacturer or Tepotinib supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Tepotinib manufacturer or Tepotinib supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Tepotinib API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Tepotinib API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Tepotinib Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Tepotinib Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Tepotinib manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Tepotinib, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Tepotinib manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Tepotinib API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Tepotinib manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Tepotinib supplier is an individual or a company that provides Tepotinib active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Tepotinib finished formulations upon request. The Tepotinib suppliers may include Tepotinib API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Tepotinib suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Tepotinib Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Tepotinib GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Tepotinib GMP manufacturer or Tepotinib GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Tepotinib CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Tepotinib's compliance with Tepotinib specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Tepotinib CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Tepotinib CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Tepotinib may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Tepotinib EP), Tepotinib JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Tepotinib USP).
