
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Australia

0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
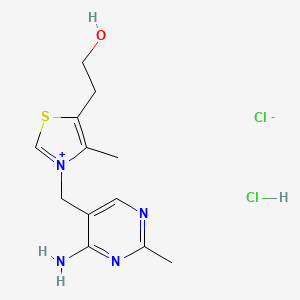

1. Thiamine Chloride Hydrochloride
1. 67-03-8
2. Thiamine Hcl
3. Aneurine Hydrochloride
4. Vitamin B1 Hydrochloride
5. Clotiamina
6. Thiamine Chloride Hydrochloride
7. Eskaphen
8. Betalin S
9. Vitamin B1
10. Thiamine Dichloride
11. Beatine
12. Begiolan
13. Benerva
14. Bethiazine
15. Bevitex
16. Bevitine
17. Bithiamin
18. Bivatin
19. Eskapen
20. Metabolin
21. Slowten
22. Thiaminal
23. Thiamol
24. Thiavit
25. Tiamidon
26. Tiaminal
27. Trophite
28. Vinothiam
29. Vitaneuron
30. Bedome
31. Beuion
32. Bivita
33. Berin
34. Bewon
35. Biuno
36. Hybee
37. Apate Drops
38. Lixa-beta
39. Thiamin Chloride
40. Thiaminum Hydrochloricum
41. Vetalin S
42. Thiaminium Chloride
43. Betaxin
44. Thiadoxine
45. Bequin
46. Thiamin Hydrochloride
47. Betabion Hydrochloride
48. Usaf Cb-20
49. Fema No. 3322
50. Vitamin B Hydrochloride
51. Thiaminium Chloride Hydrochloride
52. Thiamine(2+) Dichloride
53. Thiamine Monohydrochloride
54. Mfcd00012780
55. Betabion
56. Betamin
57. Biamine
58. Vitamin B(sub 1) Hydrochloride
59. Thiamine, Hydrochloride
60. Thiamine (hydrochloride)
61. Nsc-36226
62. 3-((4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazol-3-ium Chloride Hydrochloride
63. Thiamine, Monohydrochloride
64. Thiamine Hcl (vitamin B1)
65. Vitamin B1 (thiamine Hcl)
66. 67-03-8 (hcl Salt)
67. Chebi:49105
68. Thiamine Hydrochloride (vitamin B1)
69. M572600e5p
70. Cas-67-03-8
71. Ncgc00017013-01
72. 2-[3-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium-5-yl]ethanol Chloride Hydrochloride
73. 2-[3-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium-5-yl]ethanol;chloride;hydrochloride
74. 3-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium Chloride Hydrochloride
75. Thiamine Hydrochloride 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
76. Thiamine Chloride Hydrochloride;vitamin B1 Hydrochloride
77. Thd
78. Thiamin Dichloride
79. Smr000875246
80. Nsc36226
81. Ccris 1906
82. Vitamin Bl
83. Unii-m572600e5p
84. Vitamin B1 Hydrochloride (van)
85. Thiamine Hydrochloride [usp:jan]
86. Vitamin B(sup1)
87. Aneurinehydrochloride
88. Prestwick_441
89. Einecs 200-641-8
90. Nsc 36226
91. Thiamini Hydrochloridum
92. Thiamine Hcl (tn)
93. Vitamin B1hydrochloride
94. Ai3-18993
95. Thiazolium, Hydrochloride
96. Vitamin B1 [fhfi]
97. Dsstox_cid_20622
98. Dsstox_rid_79516
99. Thiamine Hcl [inci]
100. Thiazolium, Monohydrochloride
101. Dsstox_gsid_40622
102. Schembl41101
103. Mls001332447
104. Mls001332448
105. Thiamine Hydrochloride (usp)
106. Aneurine Hydrochloride Hydrate
107. Thiamine For System Suitability
108. Thiamine Chloride, Hydrochloride
109. Chembl1200941
110. Dtxsid0040622
111. Vitamin B1 Hydrochloride Hydrate
112. Thiamine, Chloride, Hydrochloride
113. Hms1569p04
114. Thiamine Hydrochloride [mi]
115. Bcp27971
116. Hy-n0680
117. Thiamine Hydrochloride [fcc]
118. Tox21_110736
119. S3211
120. Thiamine Hcl (vitamin B1) Solution
121. Thiamine Hydrochloride, P.a., 98%
122. Thiamine Hydrochloride [vandf]
123. Akos015905506
124. Thiamine Hydrochloride [mart.]
125. Thymine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
126. Ccg-220677
127. Chloride-hydrochloride Salt Of Thiamine
128. Cs-8164
129. Sb57886
130. Thiamine Hydrochloride [usp-rs]
131. Thiamine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
132. Thiamine Hydrochloride [who-ip]
133. Thiaminum Hydrochloricum [hpus]
134. Thiamine Chloride Hydrochloride (jp17)
135. Ncgc00017013-02
136. 2-{3-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl}ethan- 1-ol, Chloride, Chloride
137. 3-((4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazolium Chloride Monohydrochloride
138. As-14151
139. Sy010871
140. Thiazolium, 3-((4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl- Chloride, Monohydrochloride
141. Db-054984
142. Thiamine Hydrochloride [ep Impurity]
143. Thiamine Hydrochloride [orange Book]
144. Thiamine Hydrochloride, >=98%, Fcc, Fg
145. Ft-0631293
146. Ft-0777960
147. T0181
148. Thiamine Chloride Hydrochloride [jan]
149. Thiamine Hydrochloride [ep Monograph]
150. Thiamine Hydrochloride [usp Monograph]
151. Thiamini Hydrochloridum [who-ip Latin]
152. D02094
153. Thiamine Hydrochloride 100 Microg/ml In Water
154. Thiamine Hydrochloride (b1), Analytical Standard
155. Thiamine Chloride, Hydrochloride [who-ip]
156. Q-201928
157. Thiamine Hydrochloride, Tested According To Ph.eur.
158. Q27121486
159. Thiamine Hydrochloride, Reagent Grade, >=99% (hplc)
160. Thiamine Hydrochloride, Saj Special Grade, >=98.5%
161. F0001-2415
162. F2173-0852
163. Thiamine Hydrochloride, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
164. Wln: T6n Cnj B1 Dz E1- At5k Csj D2q E1 &q &g &gh
165. Thiamine Hydrochloride, 99% (dry Wt.), May Cont. Up To 5% Water
166. Thiamine Hydrochloride (vitamin B1) 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol (as Free Base)
167. Thiamine Hydrochloride, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
168. Thiamine Hydrochloride, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
169. Thiamine For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
170. Thiamine Hydrochloride, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
171. Thiazolium,3-[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-
172. 3-((4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-m- Ethylthiazolium Chloride, Monohydrochloride
173. 3-[(4-azaniumyl-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium Dichloride
174. Thiamine Hcl (vitamin B1) Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol (as Free Base), Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
175. Thiamine Hydrochloride, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture, Suitable For Insect Cell Culture, Suitable For Plant Cell Culture
176. Thiamine Hydrochloride, Pharmagrade, Ep, Manufactured Under Appropriate Gmp Controls For Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production
177. Thiazolium, 3-((4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-m- Ethyl, Chloride, Monohydrochloride
178. Thiazolium, 3-((4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-, Chloride, Hydrochloride (1:1:1)
179. Thiazolium, 3-((4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-, Chloride, Monohydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 337.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H18Cl2N4OS |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 336.0578378 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 336.0578378 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 269 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Thiamine hydrochloride |
| Drug Label | Thiamine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a sterile solution of thiamine hydrochloride in Water for Injection for intramuscular (IM) or slow intravenous (IV) administration.Each mL contains: Thiamine hydrochloride 100 mg; chlorobutanol anhydrous (chlo... |
| Active Ingredient | Thiamine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 100mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa; Mylan Institutional |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Thiamine hydrochloride |
| Drug Label | Thiamine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a sterile solution of thiamine hydrochloride in Water for Injection for intramuscular (IM) or slow intravenous (IV) administration.Each mL contains: Thiamine hydrochloride 100 mg; chlorobutanol anhydrous (chlo... |
| Active Ingredient | Thiamine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 100mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa; Mylan Institutional |
Thiamine is used to prevent and to treat thiamine deficiency syndromes including beriberi, Wernicke's encephalopathy syndrome, delirium, and peripheral neuritis associated with pellagra or neuritis of pregnancy (if associated with severe vomiting).
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Although thiamine has not been shown by well-controlled trials to have any therapeutic value, the drug has been used for the management of poor appetite, ulcerative colitis, chronic diarrhea, other GI disorders, and the cerebellar syndrome. Thiamine has also been used orally as an insect repellent, but there is a lack of adequate evidence to establish the efficacy of thiamine for this use.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Low plasma thiamine concentrations have been found in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. In a small placebo-controlled study, benfotiamine /a related vitamin B1 substance/ 100 mg given four times daily by mouth significantly improved neuropathic pain in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. /Benfotiamine/
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1976-7.
/This study assessed/ the effect of thiamine repletion on thiamine status, functional capacity, and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in patients with moderate to severe congestive heart failure (CHF) who had received furosemide in doses of 80 mg/d or more for at least 3 months. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Thirty patients were randomized to 1 week of double-blind inpatient therapy with either iv thiamine 200 mg/d or placebo (n = 15 each). All previous drugs were continued. Following discharge, all 30 patients received oral thiamine 200 mg/d as outpatients for 6 weeks. Thiamine status was determined by the erythrocyte thiamine-pyrophosphate effect (TPPE). LVEF was determined by echocardiography. RESULTS: TPPE, diuresis, and LVEF were unchanged with iv placebo. After iv thiamine, TPPE decreased (11.7% +/- 6.5% to 5.4% +/- 3.2%; P < 0.01). LVEF increased (0.28 +/- 0.11 to 0.32 +/- 0.09; P < 0.05), as did diuresis (1,731 +/- 800 mL/d to 2,389 +/- 752 mL/d; P < 0.02), and sodium excretion (84 +/- 52 mEq/d to 116 +/- 83 mEq/d, P < 0.05). In the 27 patients completing the full 7-week intervention, LVEF rose by 22% (0.27 +/- 0.10 to 0.33 +/- 0.11, P < 0.01). CONCLUSIONS: Thiamine repletion can improve left ventricular function and biochemical evidence of thiamine deficiency in some patients with moderate-to-severe CHF who are receiving longterm furosemide therapy.
PMID:7733128 Shimon I et al; Am J Med 98 (5): 485-90 (1995).
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Vitamin B1 (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Serious hypersensitivity/anaphylactic reactions can occur, especially after repeated administration. Deaths have resulted from IV or IM administration of thiamine.
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons2008 Edition. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2008., p. 18
Anaphylaxis as an adverse systemic reaction to thiamine (vitamin B1) has been described in the literature since 1938. Although its precise mechanism is still uncertain, the reaction appears to involve immediate type hypersensitivity and to be exclusively related to parenteral administration...
PMID:9846348 Morinville V et al; Schweiz Med Wochenschr 128 (44): 1743-4 (1998).
Anaphylaxis. There have been occasional reports of serious and even fatal responses to the parenteral administration of thiamin. The clinical characteristics have strongly suggested an anaphylactic reaction. Symptoms associated with thiamin-induced anaphylaxis include anxiety, pruritus, respiratory distress, nausea, abdominal pain, and shock, sometimes progressing to death.
NAS, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine; Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pg. 81, 1998. Available from, as of March 2, 2010: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/6015.html
Adverse reactions with thiamine are rare, but hypersensitivity reactions have occurred, mainly after parenteral doses. These reactions have ranged in severity from very mild to, very rarely, fatal anaphylactic shock ... The UK Committee on Safety of Medicines had received, between 1970 and July, 1988, 90 reports of adverse reactions associated with the use of an injection containing high doses of vitamins B and C. The most frequent reactions were anaphylaxis (41 cases, including 2 fatalities), dyspnea or bronchospasm (13 cases), and rash or flushing (22 cases); 78 of the reactions occurred during, or shortly after, intravenous injection and the other 12 after intramuscular injectdion. They recommended that parenteral treatment be used only when essential, and that, when given, facilities for treating anaphylaxis should be available. They also recommended that, when the intravenous route was used, the injection be given slowly (over 10 minutes). Various authors have noted that parenteral treatment is essential for the prophylaxis and treatment of Wernicke's encephalopathy. However, further reports of anaphylaxis to parenteral thiamine have since been described, including one with a fatal outcome.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1976.
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Vitamin B1 (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Absorption of thiamin occurs mainly in the jejunum. At low concentrations of thiamin, absorption occurs by an active transport system that involves phosphyrylation; at higher concentrations, absorption occurs by passive diffusion. Only a small percentage of a high dose of thiamin is absorbed, and elevated serum values result in active urinary excretion of the vitamin.
Otten JJ, Hellwig JP, Meyers LD, eds; Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements, Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2006, p. 281
Thiamin is transported in blood in both erythrocytes and plasma and is excreted in the urine.
Otten JJ, Hellwig JP, Meyers LD, eds; Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements, Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2006, p.281
Thiamine is absorbed from the small intestine and is phosphorylated in the intestinal mucosa.
Furia, T.E. (ed.). CRC Handbook of Food Additives. 2nd ed. Cleveland: The Chemical Rubber Co., 1972., p. 89
The B vitamins are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, except in malabsorption syndromes. Thiamine is absorbed mainly in the duodenum.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 2647
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Vitamin B1 (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Converted in vivo to thiamine diphosphate, a coenzyme in the decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 1598
Compound 3-(2'-methyl-4'-amino-5'-pyrimidylmethyl)-4-methylthiazole-5-acetic acid, ie thiamine acetic acid, 2-methyl-4-amino-5-formylaminomethylpyrimidine, and 5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazole have been identified as important metabolites of thiamine, vitamin B1.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 248
Biotransformation of thiamine in mammals is generally supposed to /yield/ thiochrome, thiamine disulfide, 5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-thiazole, and some form corresponding to pyrimidine residue of thiamine.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 229
Thiamine is metabolized in the liver of animals. Several urinary metabolites of thiamine have been identified in humans. Little or no unchanged thiamine is excreted in urine following administration of physiologic doses; however, following administration of larger doses, both unchanged thiamine and metabolites are excreted after tissue stores become saturated.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
The biological half-life of the vitamin is in the range of 9-18 days.
Otten JJ, Hellwig JP, Meyers LD, eds; Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements, Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2006, p.281
With higher pharmacological levels, namely repetitive 250-mg amounts taken orally and 500 mg given intramuscularly, nearly 1 week was required for steady state plasma concentrations to be reached; a mean elimination half-life of 1.8 days was estimated.
NAS, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine; Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pg. 59, 1998. Available from, as of March 2, 2010: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/6015.html
Total thiamin content of the adult human has been estimated to be approximately 30 mg, and the biological half-life of the vitamin is probably in the range of 9 to 18 days.
NAS, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine; Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pg. 59, 1998. Available from, as of March 2, 2010: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/6015.html
Metabolic control analysis predicts that stimulators of transketolase enzyme synthesis such as thiamin (vitamin B-1) support a high rate of nucleic acid ribose synthesis necessary for tumor cell survival, chemotherapy resistance, and proliferation. Metabolic control analysis also predicts that transketolase inhibitor drugs will have the opposite effect on tumor cells. This may have important implications in the nutrition and future treatment of patients with cancer.
PMID:10890024 Cascante M et al; Nutr Cancer 36 (2): 150-4 (2000).

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
85
PharmaCompass offers a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Thiamine Hydrochloride manufacturer or Thiamine Hydrochloride supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Thiamine Hydrochloride manufacturer or Thiamine Hydrochloride supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Thiamine Hydrochloride API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Thiamine Hydrochloride API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Thiamine Hydrochloride Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Thiamine Hydrochloride Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Thiamine Hydrochloride, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Thiamine Hydrochloride manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Thiamine Hydrochloride API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride supplier is an individual or a company that provides Thiamine Hydrochloride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Thiamine Hydrochloride finished formulations upon request. The Thiamine Hydrochloride suppliers may include Thiamine Hydrochloride API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Thiamine Hydrochloride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Thiamine Hydrochloride DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Thiamine Hydrochloride USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Thiamine Hydrochloride USDMF includes data on Thiamine Hydrochloride's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Thiamine Hydrochloride USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Thiamine Hydrochloride Drug Master File in Japan (Thiamine Hydrochloride JDMF) empowers Thiamine Hydrochloride API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Thiamine Hydrochloride JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Thiamine Hydrochloride JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Thiamine Hydrochloride Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Thiamine Hydrochloride CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Thiamine Hydrochloride EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Thiamine Hydrochloride to their clients by showing that a Thiamine Hydrochloride CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Thiamine Hydrochloride CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Thiamine Hydrochloride CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Thiamine Hydrochloride CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Thiamine Hydrochloride DMF.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Thiamine Hydrochloride CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride written confirmation (Thiamine Hydrochloride WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Thiamine Hydrochloride manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Thiamine Hydrochloride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Thiamine Hydrochloride APIs or Thiamine Hydrochloride finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Thiamine Hydrochloride WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Thiamine Hydrochloride as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Thiamine Hydrochloride API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Thiamine Hydrochloride as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Thiamine Hydrochloride and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Thiamine Hydrochloride NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Thiamine Hydrochloride Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Thiamine Hydrochloride GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Thiamine Hydrochloride GMP manufacturer or Thiamine Hydrochloride GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Thiamine Hydrochloride CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Thiamine Hydrochloride's compliance with Thiamine Hydrochloride specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Thiamine Hydrochloride CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Thiamine Hydrochloride CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Thiamine Hydrochloride may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Thiamine Hydrochloride EP), Thiamine Hydrochloride JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Thiamine Hydrochloride USP).
