
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
API
0
FDF
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
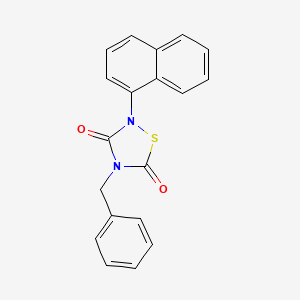

1. 4-benzyl-2-(naphthalene-1-yl)-1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione
2. Np 031112
3. Np-031112
4. Np-12 Compound
5. Np031112
6. Np12 Compound
1. 865854-05-3
2. Np031112
3. Np-12
4. 4-benzyl-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)-1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione
5. Tideglusib [inn]
6. Np-031112
7. Np 031112
8. 4-benzyl-2-naphthalen-1-yl-1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione
9. Q747y6tt42
10. 1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione, 2-(1-naphthalenyl)-4-(phenylmethyl)-
11. 2-(1-naphthalenyl)-4-(phenylmethyl)-1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione
12. Tideglusibum
13. Zentylor
14. Nypta
15. Unii-q747y6tt42
16. Tideglusib [who-dd]
17. Tideglusib(np-031112)
18. Schembl676929
19. Gtpl6929
20. Chembl3545157
21. Tideglusib, >=98% (hplc)
22. Dtxsid90235682
23. Ex-a600
24. Chebi:147398
25. Hms3673g17
26. Hms3744e05
27. Hms3884j18
28. 4-benzyl-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)-(1,2,4)thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione
29. Bcp06016
30. Tideglusib,cas:865854-05-3
31. Bdbm50166940
32. Mfcd18633296
33. Nsc800950
34. S2823
35. Zinc13985228
36. Akos025149085
37. Ccg-267855
38. Cs-0613
39. Db12129
40. Nsc-800950
41. Sb19268
42. Tideglusib (np031112, Np-12)
43. Ncgc00386380-06
44. Ac-31056
45. As-56156
46. Da-41071
47. Hy-14872
48. Ft-0700382
49. A857027
50. J-514478
51. Q10382411
52. 4-benzyl-2-(a-naphtyl)-1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione
53. 4-benzyl-2-(a-naphthyl)-1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione
| Molecular Weight | 334.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H14N2O2S |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 334.07759887 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 334.07759887 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 65.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 492 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Tideglusib was initially formulated for the treatment of Alzheimer and progressive supranuclear palsy. The raising interest for the use of tideglusib comes from the significant upregulation of GSK-3 in the brain in patients with Alzheimer disease. Its function as a degradant of -catenin, was also important, as it prevents the transcription of cell survival genes. All these factors have directed current research towards this kinase as a potential target. Alzheimer disease is the most prevalent form of dementia. The most accepted hypothesis to explain this disease is related to the presence of amyloid , which triggers a cascade that will alter the Tau protein and provoke synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death. GSK-3 importance in the tissue repair pathway has also pointed out a novel application for tideglusib. Thus, it is also under the research for the natural repair treatment of deep caries lesions.
It is reported that tideglusib administration inhibits the activation of astrocytes and microglial cells, thus it presented a neuroprotective effect. It is known as well that the inactivation of GSK-3 protects against excitotoxicity. In pre-clinical trials, there have been reports of decrease Tau hyperphosphorylation, lower brain amyloid plaque load, learning and memory enhancement, prevention of neuronal loss and significant increases of the insulin growth factor 1 which is a potent neurotrophic peptide with therapeutic value.The reports in clinical trials have shown a trend in cognition increase of Alzheimer patients treated for 24 weeks.
GSK-3 is a proline/serine protein kinase that is ubiquitously expressed and involved in many cellular signaling pathways. From all its diverse functions, it plays a key role in Alzheimer's disease. This role is related to its link with -amyloid and tau pathology. It has been suggested that aberrant Wnt or insulin signaling results in increased GSK-3 function. This kinase acts on -secretase producing the hyperphosphorylation of tau, the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques. Tideglusib inhibits GSK-3 irreversibly by presenting a non-competitive inhibition pattern with respect to ATP. The binding of tideglusib seems to directly relate to the motif containing Cys199.
ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?