
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
JDMF
0
VMF
0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
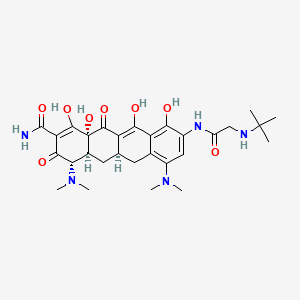

1. 9-(tert-butylglycylamido)minocycline
2. Gar 936
3. Gar-936
4. Gar936
5. Tbg-mino
6. Tygacil
1. 220620-09-7
2. Tygacil
3. Way-gar-936
4. Gar-936
5. Tbg-mino
6. Gar 936
7. (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-9-(2-(tert-butylamino)acetamido)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamide
8. Chebi:149836
9. 70je2n95kr
10. (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-9-(2-(tert-butylamino)acetamido)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide
11. (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-9-[(n-tert-butylglycyl)amino]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide
12. Tigecycline [usan]
13. Tigilcycline
14. Gar-936,tigecycline
15. Tygacil(tm)
16. (4s,4as,5ar,12ar)-9-[[2-(tert-butylamino)acetyl]amino]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-3,12-dioxo-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4h-tetracene-2-carboxamide
17. (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-9-(2-(tert-butylamino)acetamido)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxa
18. (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-9-[[2-(tert-butylamino)acetyl]amino]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4h-tetracene-2-carboxamide
19. 2-naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-((((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)acetyl)amino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-
20. 2-naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-((2-((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)acetyl)amino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-
21. 2-naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-[[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]acetyl]amino]-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-
22. 2-naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-[[2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]acetyl]amino]-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-
23. Tygacil (tn)
24. Gar936
25. Mfcd00935753
26. 9-t-butylglycylamido Minocycline
27. Haizheng Li Xing
28. Tigecycline 95%
29. Ncgc00183095-01
30. T1c
31. Tigecycline (jan/usp)
32. Tigecycline [mi]
33. Tigecycline [inn]
34. Tigecycline [jan]
35. Tigecycline [vandf]
36. Dsstox_cid_28507
37. Dsstox_rid_82779
38. Tigecycline [mart.]
39. Unii-70je2n95kr
40. Dsstox_gsid_48581
41. Tigecycline [usp-rs]
42. Tigecycline [who-dd]
43. (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-9-(2-(tert-butylamino)acetamido)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1
44. Mls006010079
45. Schembl101795
46. Schembl105082
47. Schembl237962
48. Tigecycline [ema Epar]
49. Tigecycline [usan:inn:ban]
50. Chembl376140
51. 9-t-butylglycylamido-minocycline
52. Dtxsid2048581
53. Gtpl10929
54. Hsdb 8172
55. Tigecycline [orange Book]
56. 9-tert-butylglycylamidominocycline
57. Bcpp000045
58. Hms3714i13
59. Tigecycline [ep Monograph]
60. Tigecycline [usp Monograph]
61. Act08710
62. Bcp01397
63. Hy-b0117
64. Tox21_112910
65. Bdbm50247905
66. Nsc794945
67. S1403
68. Zinc14879972
69. Akos015895663
70. Akos025401452
71. Akos037643695
72. Zinc100022633
73. Zinc102200515
74. Ac-1798
75. Ccg-270150
76. Cs-1876
77. Db00560
78. Nsc-794945
79. (4s,12as)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-{2-[(tert-butyl)amino]acetylamino}-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-4,5,6,12a,4a,5a-hexahydronaphthacene-2-carboxamide
80. 121ge002
81. As-30703
82. Smr002530064
83. A5226
84. Am20090708
85. Cas-220620-09-7
86. T3589
87. D01079
88. Ab01566818_01
89. 620t097
90. A815890
91. Q420595
92. Tigecycline, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
93. Q-101396
94. (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-9-(2-t-butylaminoacetylamino)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydronaphthacene-2-carboxamide
95. 2-naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-((((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)acetyl)amino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4s,4as,5ar,12as)-
| Molecular Weight | 585.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H39N5O8 |
| XLogP3 | 1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 585.27986322 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 585.27986322 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 206 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 42 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1240 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tygacil |
| PubMed Health | Tigecycline (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | TYGACIL (tigecycline) is a tetracycline derivative (a glycylcycline) for intravenous infusion. The chemical name of tigecycline is (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-9-[2-(tert-butylamino)acetamido]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-te... |
| Active Ingredient | Tigecycline |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pf Prism Cv |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tygacil |
| PubMed Health | Tigecycline (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | TYGACIL (tigecycline) is a tetracycline derivative (a glycylcycline) for intravenous infusion. The chemical name of tigecycline is (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-9-[2-(tert-butylamino)acetamido]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-te... |
| Active Ingredient | Tigecycline |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 50mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pf Prism Cv |
Anti-Bacterial Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Tigecycline. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of January 30, 2014: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Tygacil is a tetracycline-class antibacterial drug indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms in the /following condition/ for patients 18 years of age and older: Complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates), Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus grp. (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Bacteroides fragilis. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
Tygacil is a tetracycline-class antibacterial drug indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms in the /following condition/ for patients 18 years of age and older: Complicated intra-abdominal infections caused by Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates), Streptococcus anginosus grp. (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides vulgatus, Clostridium perfringens, and Peptostreptococcus micros. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
Tygacil is a tetracycline-class antibacterial drug indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms in the /following condition/ for patients 18 years of age and older: Community-acquired bacterial pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible isolates), including cases with concurrent bacteremia, Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase negative isolates), and Legionella pneumophila. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: ALL-CAUSE MORTALITY: An increase in all-cause mortality has been observed in a meta-analysis of Phase 3 and 4 clinical trials in Tygacil-treated patients versus comparator. The cause of this mortality risk difference of 0.6% (95% CI 0.1, 1.2) has not been established. Tygacil should be reserved for use in situations when alternative treatments are not suitable.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
Increased risk of all-cause mortality has been reported in a pooled analysis of over 7400 patients from 13 phase 3 and 4, active-controlled clinical trials evaluating tigecycline for the treatment of serious infections. Data indicate a 4% mortality rate in tigecycline-treated patients versus 3% in patients treated with comparator anti-infectives. The adjusted risk difference in all-cause mortality between patients receiving tigecycline and those receiving comparators was 0.6%.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 427
Acute pancreatitis, including fatalities, has been reported in patients receiving tigecycline. Some cases have been reported in patients with no known risk factors for pancreatitis. Improvement usually occurs after the drug is discontinued. A diagnosis of pancreatitis should be considered in any patient receiving tigecycline who develops symptoms, signs, or laboratory abnormalities suggestive of acute pancreatitis. In suspected cases of pancreatitis, consideration should be given to discontinuing tigecycline.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 427
May cause fetal harm; teratogenicity and embryolethality demonstrated in animals. Pregnancy should be avoided during therapy. If the patient becomes pregnant while receiving tigecycline, apprise of potential fetal hazard.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 427
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Tigecycline (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the following conditions: Complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates), Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus grp. (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), Streptococcus pyogenes and Bacteroides fragilis. Complicated intra-abdominal infections caused by Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only), Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates only), Streptococcus anginosus grp. (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides vulgatus, Clostridium perfringens, and Peptostreptococcus micros.
FDA Label
Tygacil is indicated in adults and in children from the age of eight years for the treatment of the following infections:
- Complicated skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI), excluding diabetic foot infections
- Complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI)
Tygacil should be used only in situations where other alternative antibiotics are not suitable.
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents. appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections, Treatment of complicated skin and soft-tissue infections
Tygecycline Accord is indicated in adults and in children from the age of eight years for the treatment of the following infections (see sections 4. 4 and 5. 1):
- Complicated skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI), excluding diabetic foot infections (see section 4. 4)
- Complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI)
Tygecycline Accord should be used only in situations where other alternative antibiotics are not suitable (see sections 4. 4, 4. 8 and 5. 1).
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Tigecycline is the first clinically-available drug in a new class of antibiotics called the glycylcyclines. Glycylcyclines are a new class of antibiotics derived from tetracycline. These tetracycline analogues are specifically designed to overcome two common mechanisms of tetracycline resistance, namely resistance mediated by acquired efflux pumps and/or ribosomal protection. Glycylcycline antibiotics have a similar mechanism of action as tetracycline antibiotics. Both classes of antibiotics bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit to prevent the amino-acyl tRNA from binding to the A site of the ribosome. However, the glycylcyclines appear to bind more effectively than the tetracyclines.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit the synthesis of proteins. They are usually ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS or toxins. Mechanism of the action of inhibition includes the interruption of peptide-chain elongation, the blocking the A site of ribosomes, the misreading of the genetic code or the prevention of the attachment of oligosaccharide side chains to glycoproteins. (See all compounds classified as Protein Synthesis Inhibitors.)
J01AA12
J01AA12
J01AA12
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01A - Tetracyclines
J01AA - Tetracyclines
J01AA12 - Tigecycline
The recovery of total radioactivity in feces and urine following administration of (14)C-tigecycline indicates that 59% of the dose is eliminated by biliary/fecal excretion, and 33% is excreted in urine. Approximately 22% of the total dose is excreted as unchanged tigecycline in urine. Overall, the primary route of elimination for tigecycline is biliary excretion of unchanged tigecycline and its metabolites. Glucuronidation and renal excretion of unchanged tigecycline are secondary routes.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
... The safety and tolerability of tigecycline administered as single or multiple doses or at various infusion rates were explored in three phase 1, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in healthy subjects. Full pharmacokinetic profiles of tigecycline were determined in two of these studies. Subjects in the single-dose study received 12.5 to 300 mg of tigecycline, which differed with respect to the duration of infusion, subjects' feeding status, and ondansetron pretreatment. Subjects in the ascending multiple-dose study received 25 to 100-mg doses of tigecycline as a 1-hr infusion every 12 hr. The variable volume and infusion rate study consisted of administration of 100-mg loading dose of tigecycline, followed by 50 mg every 12 hr for 5 days. Serum samples were analyzed for tigecycline by validated high-pressure liquid chromatography or liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry methods. Systemic clearance ranged from 0.2 to 0.3 liters/hr/kg, and the tigecycline half-life ranged from 37 to 67 hr. Tigecycline had a large volume of distribution (7 to 10 liters/kg), indicating extensive distribution into the tissues. Food increased the maximum tolerated single-dose from 100 to 200 mg, but the duration of infusion did not affect tolerability. ...
PMID:15616299 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC538906 Muralidharan G et al; Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49 (1): 220-9 (2005)
In a single-dose study, tigecycline 100 mg was administered to subjects prior to undergoing elective surgery or medical procedure for tissue extraction. Concentrations at 4 hours after tigecycline administration were higher in gallbladder (38-fold, n=6), lung (3.7-fold, n=5), and colon (2.3-fold, n=6), and lower in synovial fluid (0.58-fold, n=5), and bone (0.35-fold, n=6) relative to serum. The concentration of tigecycline in these tissues after multiple doses has not been studied.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
Results from animal studies using (14)C-labeled tigecycline indicate that tigecycline is excreted readily via the milk of lactating rats. Consistent with the limited oral bioavailability of tigecycline, there is little or no systemic exposure to tigecycline in nursing pups as a result of exposure via maternal milk.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Tigecycline (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Tigecycline is not extensively metabolized. In vitro studies with tigecycline using human liver microsomes, liver slices, and hepatocytes led to the formation of only trace amounts of metabolites. A glucuronide, an N-acetyl metabolite, and a tigecycline epimer (each at no more than 10% of the administered dose) are the primary metabolites.
Tigecycline is not extensively metabolized. In vitro studies with tigecycline using human liver microsomes, liver slices, and hepatocytes led to the formation of only trace amounts of metabolites. In healthy male volunteers receiving (14)C-tigecycline, tigecycline was the primary (14)C-labeled material recovered in urine and feces, but a glucuronide, an N-acetyl metabolite, and a tigecycline epimer (each at no more than 10% of the administered dose) were also present.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for TYGACIL (tigecycline) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution (October 2013). Available from, as of February 7, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2ccdb48e-c14a-4eeb-348c-4920ccfd7465
Tigecycline was minimally metabolised in the animal species tested, consistent with that observed in humans. Consistent with rat and dog data, the 4-epimer of tigecycline (a non-enzymatic epimerization product) was also the most abundant tigecycline-derived component detected in human serum and urine. The major metabolic pathways for tigecycline in humans were glucuronidation (M7: tigecycline glucuronide metabolite, approximately 12%, and its epimer M6) and amide hydrolysis of the tbutylaminoacetylamino side chain (M9: N-acetyl-9- aminominocycline, approximately 3% and its epimer M8, approximately 10% of the administered tigecycline dose). Thehuman metabolites (M7 and M9), have not been observed in rats and dogs, but are present in mice and rabbits. Further studies showed that tigecycline and its epimer as well as M3, M7 and its epimer M6 were detected in both species, mice and rabbits, but M9 and its epimer M8 were only observed in rabbits,although quantitative information on the individual metabolites was not provided.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Tygacil, Scientific Discussion p.5 (2007). Available from, as of February 10, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000644/WC500044511.pdf
27-43 hours
... The terminal elimination half-life is approximately 40 hr. ...
PMID:16080071 Meagher AK et al; Clin Infect Dis 41 (Suppl 5): S333-40 (2005)
Tigecycline, a glycylcycline, inhibits protein translation in bacteria by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit and blocking entry of amino-acyl tRNA molecules into the A site of the ribosome. This prevents incorporation of amino acid residues into elongating peptide chains. Tigecycline carries a glycylamido moiety attached to the 9-position of minocycline. The substitution pattern is not present in any naturally occurring or semisynthetic tetracycline and imparts certain microbiologic properties to tigecycline. Tigecycline is not affected by the two major tetracycline resistance mechanisms, ribosomal protection and efflux. Accordingly, tigecycline has demonstrated in vitro and in vivo activity against a broad spectrum of bacterial pathogens. There has been no cross resistance observed between tigecycline and other antibiotics. Tigecycline is not affected by resistance mechanisms such as beta-lactamases (including extended spectrum beta-lactamases), target site modifications, macrolide efflux pumps or enzyme target changes (e.g. gyrase/topoisomerase). In vitro studies have not demonstrated antagonism between tigecycline and other commonly used antibacterial drugs. In general, tigecycline is considered bacteriostatic.
Pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic mediators have been involved in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Tigecycline (Tig), a glycylcycline antibiotic and an analog of Minocycline, is shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects that are distinct from its anti-microbial activity. Its neuroprotective mechanism is unknown. In this study, we investigated the direct protective mechanisms of tigecycline against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced Rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. The results showed that tigecycline significantly attenuated the expression and the release of nuclear factor-kappa beta (NF-kappaB), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-a) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), as well as nitric oxide (NO) levels in LPS-induced PC12 cells. In addition, tigecycline dose-dependently decreased cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activity. This later finding corroborated the results of decreased pro-apoptotic Bad, and increased anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein expression thus, confirming a neuroprotective effect of the drug in differentiated PC12 cells induced with LPS. The findings of /this/ study suggest new targets for tigecycline and support the potential for tigecycline to be investigated as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative disorders.
PMID:23200736 Yagnik RM, Benzeroual KE; Toxicol In Vitro 27 (2): 686-93 (2013)
Tigecycline is a glycylcycline antibiotic derived from the tetracycline group, that acts by inhibiting protein synthesis at the level of the bacterial ribosome. Tigecycline shows higher binding affinity than tetracyclines, being active against bacterial strains with either mechanism of tetracycline resistance (efflux and ribosomal protection). The fact that tigecycline overcomes most of the known tetracycline resistance mechanisms is interpreted as a result of steric hindrance due to the large substituent at position 9. Tigecycline showed a number of differences between the in vitro/in vivo antibacterial activity with respect to the tetracycline group that could be attributed to the specific interaction with a different region of the ribosomal A-site. Since mutational resistance to tetracyclines at the A-site is considered extremely rare, it is unlikely that mutational resistance to tigecycline will arise at the Asite. Tigecycline is able to inhibit mitochondrial protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells, which may have some toxicological relevance. However, in this respect tigecycline resembles classical tetracyclines and some other antimicrobial drugs inhibiting prokaryotic protein synthesis. In addition, the in vitro data show that tigecycline is active against microorganisms harbouring some tetracycline determinants of resistance.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Tygacil, Scientific Discussion p.4 (2007). Available from, as of February 10, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000644/WC500044511.pdf

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
81
PharmaCompass offers a list of Tigecycline API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Tigecycline manufacturer or Tigecycline supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Tigecycline manufacturer or Tigecycline supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Tigecycline API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Tigecycline API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Tigecycline Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Tigecycline Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Tigecycline manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Tigecycline, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Tigecycline manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Tigecycline API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Tigecycline manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Tigecycline supplier is an individual or a company that provides Tigecycline active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Tigecycline finished formulations upon request. The Tigecycline suppliers may include Tigecycline API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Tigecycline suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Tigecycline DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Tigecycline active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Tigecycline DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Tigecycline USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Tigecycline DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Tigecycline USDMF includes data on Tigecycline's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Tigecycline USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Tigecycline suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Tigecycline Drug Master File in Korea (Tigecycline KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Tigecycline. The MFDS reviews the Tigecycline KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Tigecycline KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Tigecycline KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Tigecycline API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Tigecycline suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Tigecycline CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Tigecycline Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Tigecycline CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Tigecycline EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Tigecycline to their clients by showing that a Tigecycline CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Tigecycline CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Tigecycline CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Tigecycline CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Tigecycline DMF.
A Tigecycline CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Tigecycline CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Tigecycline suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Tigecycline written confirmation (Tigecycline WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Tigecycline manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Tigecycline active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Tigecycline APIs or Tigecycline finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Tigecycline WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Tigecycline suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Tigecycline as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Tigecycline API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Tigecycline as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Tigecycline and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Tigecycline NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Tigecycline suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Tigecycline Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Tigecycline GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Tigecycline GMP manufacturer or Tigecycline GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Tigecycline CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Tigecycline's compliance with Tigecycline specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Tigecycline CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Tigecycline CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Tigecycline may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Tigecycline EP), Tigecycline JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Tigecycline USP).

