
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
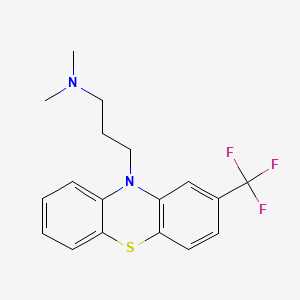

1. Fluopromazine
2. Siquil
3. Trifluopromazine
1. Fluopromazine
2. Trifluopromazine
3. Vesprin
4. 146-54-3
5. Adazine
6. Psyquil
7. 2-(trifluoromethyl)promazine
8. Triflupromazina
9. Triflupromazinum
10. Psyquil; Siquil
11. 10h-phenothiazine-10-propanamine, N,n-dimethyl-2-(trifluoromethyl)-
12. N,n-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazin-10-yl]propan-1-amine
13. 2-trifluoromethyl-10-(gamma-dimethylaminopropyl)phenothiazine
14. 10-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazine
15. Vesprin (tn)
16. Ro16tqf95y
17. Chebi:9711
18. 10-3-(dimethylamino)propyl-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazine
19. Vetame
20. Trifluopromazine Hydrochloride
21. N,n-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10h-phenothiazin-10-yl]propan-1-amine
22. Fluopromazine Monohydrochloride
23. Phenothiazine, 10-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)-
24. Triflupromazine [inn]
25. Triflupromazinum [inn-latin]
26. Triflupromazina [inn-spanish]
27. Dimethyl({3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10h-phenothiazin-10-yl]propyl})amine
28. Nsc14959
29. Nsc17473
30. Hsdb 3407
31. N,n-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazin-10-yl]propan-1-amine Hydrochloride
32. Einecs 205-673-6
33. Cas-1098-60-8
34. Unii-ro16tqf95y
35. Triflupromazine (usp/inn)
36. Triflupromazin
37. 10-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazine
38. Phenothiazine, 10-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)-
39. Sr-01000000224-4
40. Triflupromazine [usp:inn:ban]
41. N,n-dimethyl-2-(trifluoromethyl)-10h-phenothiazine-10-propanamine
42. Spectrum_000095
43. Prestwick0_000053
44. Prestwick1_000053
45. Prestwick2_000053
46. Prestwick3_000053
47. Spectrum4_000741
48. Spectrum5_001282
49. Lopac-t-2896
50. Chembl570
51. Triflupromazine [mi]
52. Lopac0_001146
53. Schembl44085
54. Bspbio_000205
55. Bspbio_003444
56. Kbiogr_001062
57. Kbioss_000515
58. Cid_66069
59. Divk1c_000808
60. Triflupromazine [hsdb]
61. Spbio_002126
62. Triflupromazine [vandf]
63. Bpbio1_000227
64. Gtpl4330
65. Triflupromazine [mart.]
66. Dtxsid9023704
67. Triflupromazine [who-dd]
68. Bdbm67544
69. Kbio1_000808
70. Kbio2_000515
71. Kbio2_003083
72. Kbio2_005651
73. Ninds_000808
74. Zinc538507
75. Pdsp1_001344
76. Pdsp2_001328
77. Triflupromazine [orange Book]
78. N,n-dimethyl-3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-10h-phenothiazin-10-yl)-1-propanamine
79. Ccg-205220
80. Db00508
81. Sdccgsbi-0051113.p004
82. Triflupromazine [usp Monograph]
83. Idi1_000808
84. Ncgc00016012-01
85. Ncgc00016012-02
86. Ncgc00016012-03
87. Ncgc00016012-04
88. Ncgc00016012-05
89. Ncgc00016012-06
90. Ncgc00016012-07
91. Ncgc00016012-08
92. Ncgc00016012-09
93. Ncgc00016012-16
94. Ncgc00024300-04
95. Ls-14640
96. Nci60_001029
97. Nci60_001426
98. Sbi-0051113.p003
99. Ab00053647
100. D00390
101. Ab00053647_16
102. Ab00053647_17
103. 146t543
104. L001149
105. Q510494
106. Brd-k63675182-003-14-5
107. Dimethyl-[3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazin-10-yl]propyl]amine;hydrochloride
108. N,n-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10-phenothiazinyl]-1-propanamine;hydrochloride
109. N,n-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10h-phenothiazin-10-yl]-1-propanamine #
| Molecular Weight | 352.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H19F3N2S |
| XLogP3 | 5.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 352.12210427 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 352.12210427 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 31.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 416 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antiemetics; Antipsychotic Agents, Phenothiazine; Dopamine Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
THIS PHENOTHIAZINE IS EFFECTIVE IN MGMNT OF POSTOPERATIVE NAUSEA & VOMITING, RADIATION SICKNESS, & NAUSEA & VOMITING CAUSED BY TOXINS. /HYDROCHLORIDE/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 1104
TREATMENT OF ORG BRAIN SYNDROMES, BOTH CHRONIC & ACUTE, IS ANOTHER USE...USE... IN /TREATMENT OF/ MANIA & DEPRESSION HAS MET WITH SOME SUCCESS... ANXIETY IS CONSIDERED...INDICATION FOR USE... /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 173
PHENOTHIAZINES...FAVORABLY MODIFY PATHOGNOMONIC SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA, THAT IS, THOUGHT DISORDER; BLUNTED AFFECT, WITHDRAWAL, & RETARDATION; & AUTISTIC BEHAVIOR & MANNERISMS. FAVORABLE CHANGES IN BELLIGERENCE, RESISTIVENESS, PERCEPTUAL DISTURBANCES, & PARANOID PROJECTION ALSO OCCUR... /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 172
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for TRIFLUPROMAZINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
TRIFLUPROMAZINE PRODUCES LESS SEDATION THAN SOME OTHER PHENOTHIAZINES (EG, PROMAZINE), BUT IT PROLONGS POSTANESTHESIA SLEEPING TIME. EXTRAPYRAMIDAL REACTIONS HAVE BEEN OBSERVED FOLLOWING EVEN SINGLE DOSES OF THIS ALIPHATIC COMPD. /HYDROCHLORIDE/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 1105
PHENOTHIAZINES ARE BEST UTILIZED IN CONTROL OF NAUSEA & VOMITING OF SHORT DURATION, SINCE WITH PROLONGED USE INCIDENCE OF MOST OF THEIR ADVERSE EFFECTS INCR. /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 1062
...PRECAUTIONS SHOULD BE OBSERVED IN USE OF PHENOTHIAZINES FOR NAUSEA & VOMITING...BECAUSE THEY MAY MASK DIAGNOSTIC SYMPTOMS IN ACUTE SURGICAL CONDITIONS OR NEUROLOGICAL SYNDROMES. /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 166
PHENOTHIAZINES SHOULD BE USED WITH EXTREME CAUTION, IF @ ALL, IN UNTREATED EPILEPTIC PT & IN PT UNDERGOING WITHDRAWAL FROM CENTRAL DEPRESSANT DRUGS SUCH AS ALCOHOL & BARBITURATES. /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 159
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TRIFLUPROMAZINE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
4. 4= VERY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 50-500 MG/KG, BETWEEN 1 TEASPOON & 1 OZ FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /HYDROCHLORIDE/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-223
Used mainly in the management of psychoses. Also used to control nausea and vomiting.
Triflupromazine is a member of a class of drugs called phenthiazines, which are dopamine D1/D2 receptor antagonists. Phenothiazines are used to treat serious mental and emotional disorders, including schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. It reduces anxiety, emotional withdrawal, hallucinations, disorganized thoughts, blunted mood, and suspiciousness. Triflupromazine is used particularly to control violent behavior during acute episodes of psychotic disorders. It can also be used to control severe nausea and vomiting, severe hiccups, and moderate to severe pain in some hospitalized patients. Triflupromazine acts on the central nervous system.
Antiemetics
Drugs used to prevent NAUSEA or VOMITING. (See all compounds classified as Antiemetics.)
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05A - Antipsychotics
N05AA - Phenothiazines with aliphatic side-chain
N05AA05 - Triflupromazine
Absorption
Absorption may be erratic and peak plasma concentrations show large interindividual differences.
FATE OF SEVERAL (14)C QUATERNARY PHENOTHIAZINES, SUCH AS...TRIFLUPROMAZINE METHIODIDE...HAVE BEEN STUDIED IN RAT. ...MORE OF IP DOSE OF PHENOTHIAZINE WAS EXCRETED IN FECES (VIA BILE). WHERE EXAMINED, NO N-DEALKYLATION OF QUATERNARY NITROGEN WAS DETECTED. /METHIODIDE/
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 86
Hepatic.
...METAB...BY OXIDATIVE PROCESSES MEDIATED LARGELY BY HEPATIC MICROSOMAL & OTHER DRUG-METABOLIZING ENZYMES. CONJUGATION WITH GLUCURONIC ACID...PROMINENT ROUTE.../PRC: REACTIONS INCL HYDROXYLATION, DEMETHYLATION, SULFOXIDE FORMATION; METABOLIC ALTERATIONS IN SIDE CHAIN MAY ALSO OCCUR/. /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 405
Triflupromazine binds to the dopamine D1 and dopamine D2 receptors and inhibits their activity. The mechanism of the anti-emetic effect is due predominantly to blockage of the dopamine D2 neurotransmitter receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) and vomiting centre. Triflupromazine blocks the neurotransmitter dopamine and the vagus nerve in the gastrointestinal tract. Triflupromazine also binds the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1 and M2) and the tryptamine D receptors (5HT2B).
...PHENOTHIAZINES, BLOCK DOPAMINE RECEPTORS & INCR TURNOVER RATE OF DOPAMINE IN CORPUS STRIATUM. INCR TURNOVER RATE IS BELIEVED TO BE RESULT OF NEURONAL FEEDBACK MECHANISM. ...FIRING OF.../IDENTIFIED DOPAMINERGIC NEURONS IN SUBSTANTIA NIGRA & VENTRAL TEGMENTAL AREAS/ IS INCR BY ANTIPSYCHOTIC PHENOTHIAZINES. /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 159
THERE IS AN ADENYLATE CYCLASE IN LIMBIC SYSTEM, AS WELL AS IN CAUDATE NUCLEUS, THAT IS SPECIFICALLY ACTIVATED BY DOPAMINE. ...ACTIVATION OF...ENZYME IS... BLOCKED BY...PHENOTHIAZINES. ...THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY & SIDE EFFECTS MAY RELATE TO INHIBITION OF DOPAMINE ACTIVATION OF ADENYLATE CYCLASE. /PHENOTHIAZINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 160
ABOUT THIS PAGE
82
PharmaCompass offers a list of Triflupromazine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Triflupromazine manufacturer or Triflupromazine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Triflupromazine manufacturer or Triflupromazine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Triflupromazine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Triflupromazine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Triflupromazine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Triflupromazine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Triflupromazine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Triflupromazine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Triflupromazine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Triflupromazine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Triflupromazine manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Triflupromazine supplier is an individual or a company that provides Triflupromazine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Triflupromazine finished formulations upon request. The Triflupromazine suppliers may include Triflupromazine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Triflupromazine suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Triflupromazine DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Triflupromazine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Triflupromazine DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Triflupromazine USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Triflupromazine DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Triflupromazine USDMF includes data on Triflupromazine's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Triflupromazine USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Triflupromazine suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
Triflupromazine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Triflupromazine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Triflupromazine GMP manufacturer or Triflupromazine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Triflupromazine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Triflupromazine's compliance with Triflupromazine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Triflupromazine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Triflupromazine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Triflupromazine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Triflupromazine EP), Triflupromazine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Triflupromazine USP).
