
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
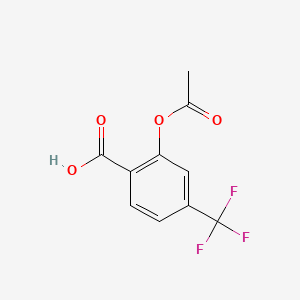

1. 2-acetoxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic Acid
2. Disgren
1. 322-79-2
2. 2-acetoxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic Acid
3. Disgren
4. 2-acetoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic Acid
5. 2-acetyloxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic Acid
6. Triflusal [inn]
7. 2-(acetyloxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic Acid
8. Benzoic Acid, 2-(acetyloxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-
9. 1z0yfi05oo
10. Triflusal (inn)
11. Ncgc00016431-01
12. 2-acetoxy-4-trifluoromethyl-benzoic Acid
13. Cas-322-79-2
14. Triflusalum
15. Grendis
16. Aflen
17. Triflusalum [inn-latin]
18. Ur 1501
19. Drisgen
20. Triflusal [inn:ban]
21. Einecs 206-297-5
22. Unii-1z0yfi05oo
23. 4-trifluoromethylsalicylic Acid Acetate
24. Brn 2945374
25. Tecnosal
26. Triflux
27. Alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-2,4-cresotic Acid Acetate
28. Prestwick_851
29. Alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-2,4-creosotic Acid Acetate
30. Triflusal [mi]
31. Prestwick0_000528
32. Prestwick1_000528
33. Prestwick2_000528
34. Prestwick3_000528
35. Triflusal [mart.]
36. Triflusal [who-dd]
37. Dsstox_cid_25305
38. Dsstox_rid_80791
39. Dsstox_gsid_45305
40. Bspbio_000515
41. 4-10-00-00619 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
42. Schembl136423
43. 3-acetoxy-alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-p-toluic Acid
44. Spbio_002436
45. Bpbio1_000567
46. Zinc2220
47. Chembl1332032
48. Dtxsid8045305
49. Triflusal [ep Monograph]
50. Chebi:94721
51. 2,4-cresotic Acid, Alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-, Acetate
52. Hms1569j17
53. Hms2096j17
54. Hms3652m11
55. Hms3713j17
56. Hms3885i13
57. Bcp10024
58. Hy-b0531
59. Tox21_110436
60. Mfcd00866793
61. S3200
62. Ur1501
63. Akos015890393
64. Ac-1829
65. Ccg-220528
66. Ccg-222319
67. Db08814
68. Mb01536
69. Ur-1501
70. 2-acetoxy-4-trifluoromethyl Benzoic Acid
71. Acetyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)salicylic Acid
72. Ncgc00016431-02
73. Ncgc00016431-04
74. Ncgc00016431-11
75. As-63983
76. A5797
77. B1461
78. Ft-0601555
79. Sw196982-3
80. T3601
81. D07142
82. T72290
83. 322t792
84. Sr-01000872666
85. Q1758668
86. Sr-01000872666-1
87. W-106849
88. Brd-k71696703-001-01-2
| Molecular Weight | 248.15 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H7F3O4 |
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 248.02964319 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 248.02964319 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 313 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Triflusal is indicated as prophylaxis of thromboembolic disorders. It has been registered in Spain and in other countries of Europe, South America and South Korea for the prevention of Stroke and myocardial infarction.
Triflusal is an antithrombotic anticoagulant. It irreversibly inhibits the production of thromboxane-B2 in platelets by acetylating cycloxygenase-1. Triflusal affects many other targets such as NF kappa B, which is a gene expression regulatory factor for cycloxygenase-a and cytokines. Numerous studies comparing the efficacy and safety profile (i.e. systemic hemorrhage) between triflusal and acetylsalsylic acid has shown either no significant difference or a better effacy and safety profile for triflusal. Triflusal has been shown to protect cerebral tissue due to its inhibition of lipid peroxidation resulting from anoxia-reoxygenation.
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B01 - Antithrombotic agents
B01A - Antithrombotic agents
B01AC - Platelet aggregation inhibitors excl. heparin
B01AC18 - Triflusal
Absorption
Absorbed in the small intestine with a bioavailability range from 83% to 100%. There is no significant difference between the absorption of the oral solution and capsule formulation. Triflusal displays a Cmax of 11.6 mcg/ml and a tmax of 0.88 h. The major metabolite of triflusal presents different pharmacokinetic properties by showing a Cmax and tmax of 92.7 mcg/ml and 4.96 h, respectively.
Route of Elimination
The elimination pathway of triflusal is primarily renal. Urine analysis has shown the presence of unchanged triflusal, HTB and the glycine conjugate of HTB.
Volume of Distribution
The reported volume of distribution for triflusal is of 34L.
Clearance
Renal clearance is 0.8 +/- 0.2L/h and 0.18 +/1 0.04L/h for triflusal and HTB, respectively.
In the liver, triflusal undergoes deacetylation, forming its main metabolite 2-OH-4-trifluoromethyl benzoic acid (HTB). This major metabolite seems to have marked antiplatelet properties in vitro.
In the healthy human, the half-life is 0.5 +/- 0.1h, while that of HTB is 34.3 +/- 5.3h.
Triflusal is chemically related to acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and irreversibly inhibits cycloxygenase-1 (COX-1) in platelets. Acetylation of the active group of COX-1 prevents the formation of thromboxane-B2 in platelets. However, it is unique because it spares the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway in endothelial cells. In addition, it favors the production of nitric oxide, a vasodilator.
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
56
PharmaCompass offers a list of Triflusal API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Triflusal manufacturer or Triflusal supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Triflusal manufacturer or Triflusal supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Triflusal API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Triflusal API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Triflusal Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Triflusal Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Triflusal manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Triflusal, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Triflusal manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Triflusal API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Triflusal manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Triflusal supplier is an individual or a company that provides Triflusal active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Triflusal finished formulations upon request. The Triflusal suppliers may include Triflusal API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Triflusal suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Triflusal Drug Master File in Korea (Triflusal KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Triflusal. The MFDS reviews the Triflusal KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Triflusal KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Triflusal KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Triflusal API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Triflusal suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Triflusal CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Triflusal Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Triflusal CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Triflusal EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Triflusal to their clients by showing that a Triflusal CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Triflusal CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Triflusal CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Triflusal CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Triflusal DMF.
A Triflusal CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Triflusal CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Triflusal suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
Triflusal Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Triflusal GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Triflusal GMP manufacturer or Triflusal GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Triflusal CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Triflusal's compliance with Triflusal specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Triflusal CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Triflusal CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Triflusal may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Triflusal EP), Triflusal JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Triflusal USP).

