
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
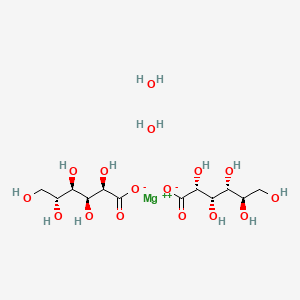

1. Boron Gluconate
2. D-gluconate
3. D-gluconic Acid
4. Dextronic Acid
5. Gluconate
6. Gluconic Acid
7. Gluconic Acid, (113)indium-labeled
8. Gluconic Acid, (14)c-labeled
9. Gluconic Acid, (159)dysprosium-labeled Salt
10. Gluconic Acid, (99)technecium (5+) Salt
11. Gluconic Acid, 1-(14)c-labeled
12. Gluconic Acid, 6-(14)c-labeled
13. Gluconic Acid, Aluminum (3:1) Salt
14. Gluconic Acid, Ammonium Salt
15. Gluconic Acid, Calcium Salt
16. Gluconic Acid, Cesium(+3) Salt
17. Gluconic Acid, Cobalt (2:1) Salt
18. Gluconic Acid, Copper Salt
19. Gluconic Acid, Fe(+2) Salt, Dihydrate
20. Gluconic Acid, Lanthanum(+3) Salt
21. Gluconic Acid, Magnesium (2:1) Salt
22. Gluconic Acid, Manganese (2:1) Salt
23. Gluconic Acid, Monolithium Salt
24. Gluconic Acid, Monopotassium Salt
25. Gluconic Acid, Monosodium Salt
26. Gluconic Acid, Potassium Salt
27. Gluconic Acid, Sodium Salt
28. Gluconic Acid, Strontium (2:1) Salt
29. Gluconic Acid, Tin(+2) Salt
30. Gluconic Acid, Zinc Salt
31. Lithium Gluconate
32. Magnerot
33. Maltonic Acid
34. Manganese Gluconate
35. Pentahydroxycaproic Acid
36. Sodium Gluconate
37. Zinc Gluconate
1. 59625-89-7
2. Magnesium Gluconate,dihydrate
3. Magnesium Gluconate Dihydrate
4. Magnesium D-gluconate (1:2) Hydrate
5. Magnesium Gluconicum
6. Magnesium Gluconate, Dihydrate
7. Magnesium D-gluconate (1:2) Dihydrate
8. Magnesium (as Gluconate)
9. T42nad2khc
10. E-580(magnesium Gluconate)
11. Ins-580(magnesium Gluconate)
12. Ins No.580(magnesium Gluconate)
13. Magnesium Gluconate [usp]
14. D-gluconic Acid, Magnesium Salt (2:1), Hydrate
15. Unii-t42nad2khc
16. Magnesium Gluconate [ep]
17. Chembl3989640
18. Magnesium Gluconate [fcc]
19. Magnesium Gluconate [inci]
20. Magnesium Gluconate [vandf]
21. Magnesium Gluconate [mart.]
22. Db13749
23. Magnesium (as Gluconate) [vandf]
24. Magnesium Gluconate [ep Monograph]
25. Magnesium Gluconate [usp Monograph]
26. Magnesium Gluconate,dihydrate [vandf]
27. W-105312
28. Q27888486
29. Magnesium (2r,3s,4r,5r)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate Dihydrate
30. Magnesium;(2r,3s,4r,5r)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate;dihydrate
| Molecular Weight | 450.63 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H26MgO16 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 12 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 450.1071264 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 450.1071264 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 285 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 165 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 5 |
Magnesium gluconate is a mineral supplement which is used to prevent and treat low levels of magnesium. Magnesium is very important for the normal physiologic functioning of cells, nerves, muscles, bones, and the heart. Generally, a well-balanced diet provides the necessary amounts of magnesium for homeostasis. However, certain conditions causing chronic magnesium deficiency may decrease levels of magnesium. These conditions include treatment with diuretics, a poor diet, alcoholism, or other medical conditions (e.g., severe diarrhea/vomiting, stomach/intestinal absorption problems, poorly controlled diabetes).
Magnesium is a cofactor in over 300 enzyme systems that regulate a variety of biochemical reactions in the body, including protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and blood pressure regulation. Magnesium is necessary for energy production, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis.
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A12 - Mineral supplements
A12C - Other mineral supplements
A12CC - Magnesium
A12CC03 - Magnesium gluconate
Absorption
A high-fat diet may decrease the amount of magnesium absorbed in the diet. Over-cooking food also may decrease the amount of magnesium absorbed from dietary sources. About 1/3 of magnesium is absorbed from the small intestine. The fraction of magnesium absorbed is inversely proportional to amount ingested. Oral absorption is estimated to be 15% to 30%.
Route of Elimination
Oral: Via urine (absorbed fraction); feces (unabsorbed fraction). Phosphate depletion is associated with a significant increase in urinary magnesium excretion and may lead to hypomagnesemia. Hypercalcemia is associated with an increased urinary excretion of magnesium. The increase in magnesium excretion in hypercalcemia is greater than the increase in calcium excretion and is due to decreased reabsorption in the loop of Henle. Hypercalcaemia leads to a reduction in isotonic reabsorption in the proximal renal tubule causing greater delivery of sodium, water, calcium and magnesium to the loop of Henle. As a result of this increased flow to thick ascending loop of henle, calcium and magnesium transport may be inhibited. In addition, the high peritubular concentration of calcium directly inhibits the transport of both ions in this segment. Osmotic diuretics such as mannitol and glucose cause a marked increase in magnesium excretion. Loop diuretics induce hypermagnesuria, and the increase in magnesium excretion is greater than that of sodium or calcium suggesting that loop diuretics may directly inhibit magnesium transport.
Volume of Distribution
About 60% of the magnesium is present in bone, of which 30% is exchangeable and functions as a reservoir to stabilize the serum concentration. About 20% is found in skeletal muscle, 19% in other soft tissues and less than 1% in the extracellular fluid. Skeletal muscle and liver contain between 79 mmol/Kg wet tissue; between 2030% of this is readily exchangeable. In healthy adults, the total serum magnesium is in the range of 0.70 and 1.10 mmol/L. Approximately 20% of this is protein bound, 65% is ionized and the rest is combined with various anions such as phosphate and citrate.
Clearance
The kidney plays a major role in magnesium homeostasis and the maintenance of plasma magnesium concentration. Under normal circumstances, when 80% of the total plasma magnesium is ultrafiltrable, 84 mmol of magnesium is filtered daily and 95% of this amount it reabsorbed leaving about 35 mmol to be excreted in the urine.
Replaces deficient circulating levels of magnesium. By competing with calcium for membrane binding sites and by stimulating calcium sequestration by sarcoplasmic reticulum, magnesium helps in the maintenance of a low resting intracellular free calcium ion concentration, which is essential in various cellular functions. The electrical properties of membranes and their permeability characteristics are also affected by magnesium. Magnesium is essential to many enzymatic reactions in the body, serving as a cofactor in protein synthesis and in carbohydrate metabolism. Magnesium contributes to the structural development of bone and is also essential in the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and the antioxidant glutathione. Magnesium also plays an important role in the active transport of calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes, a process which is important to nerve impulse conduction, muscle contraction, and normal heart rhythm. In addition to the above, magnesium is an essential mineral required for the regulation of body temperature, nucleic acid and protein synthesis, and in preserving nerve and muscle cell electrical potentials. Magnesium supplementation during pregnancy may help to reduce fetal growth restriction and pre-eclampsia, as well to increase birth weight.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
69
PharmaCompass offers a list of U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate manufacturer or U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate manufacturer or U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate supplier is an individual or a company that provides U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate finished formulations upon request. The U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate suppliers may include U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate USDMF includes data on U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate GMP manufacturer or U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate's compliance with U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate EP), U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (U.S.P. Magnesium Gluconate USP).
